Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Maths Solutions
covers the Problem Set 1 Algebra 10th Class Maths Part 1 Answers Solutions Chapter 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables.
Choose correct alternative for each of the following questions.
Question 1.
To draw graph of 4x + 5y = 19, find y when x = 1.
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) -3
Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
For simultaneous equations in variables x and y, Dx = 49, Dy = – 63, D = 7 then what is x?
(a) 7
(b) -7
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 } \)
(d) \(\frac { -1 }{ 7 } \)
Answer:
(a)
Question 3.
Find the value of
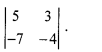
(a) -1
(b) -41
(c) 41
(d) 1
Answer:
(d)
Question 4.
To solvex + y = 3; 3x – 2y – 4 = 0 by determinant method find D.
(a) 5
(b) 1
(c) -5
(d) -1
Answer:
(c)
Question 5.
ax + by = c and mx + n y = d and an ≠ bm then these simultaneous equations have-
(a) Only one common solution
(b) No solution
(c) Infinite number of solutions
(d) Only two solutions.
Answer:
(a)
Question 2.
Complete the following table to draw the graph of 2x – 6y = 3.
Answer:
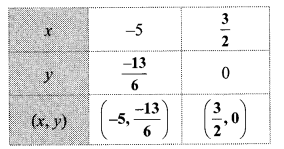
Question 3.
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically.
i. 2x + 3y = 12 ; x – y = 1
ii. x – 3y = 1 ; 3x – 2y + 4 = 0
iii. 5x – 6y + 30 = 0; 5x + 4y – 20 = 0
iv. 3x – y – 2 = 0 ; 2x + y = 8
v. 3x + y= 10 ; x – y = 2
Answer:
i. The given simultaneous equations are
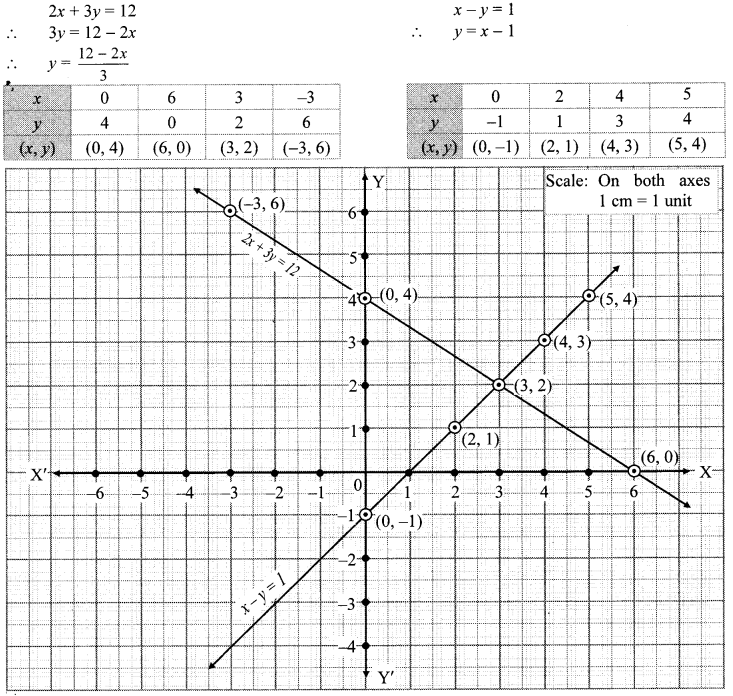
The two lines interest at point (3,2).
∴ x = 3 and y = 2 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 2x + 3y = 12 and x – y = 1.
ii. The given simultaneous equations are
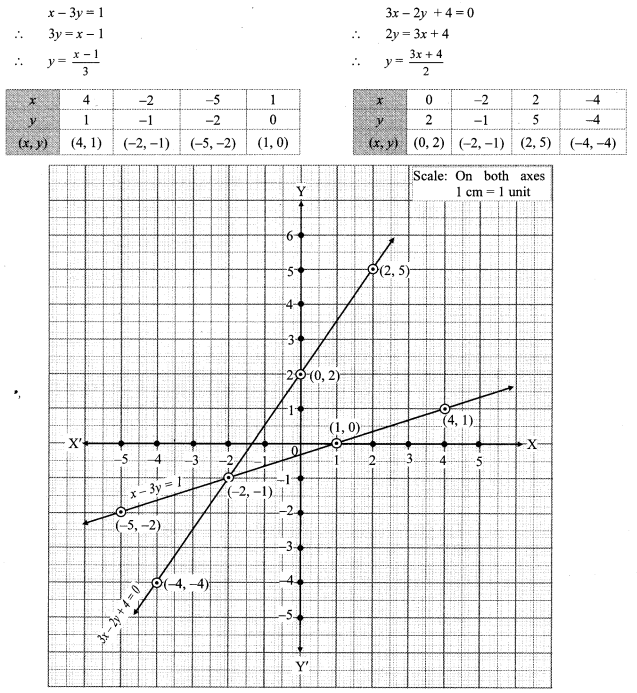
The two lines intersect at point (-2, -1).
∴ x = -2 and y = -1 is the solution of the simultaneous equations x – 3y = 1 and 3x – 2p + 4 = 0.
iii. The given simultaneous equations are
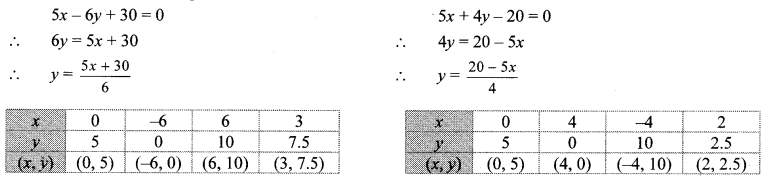
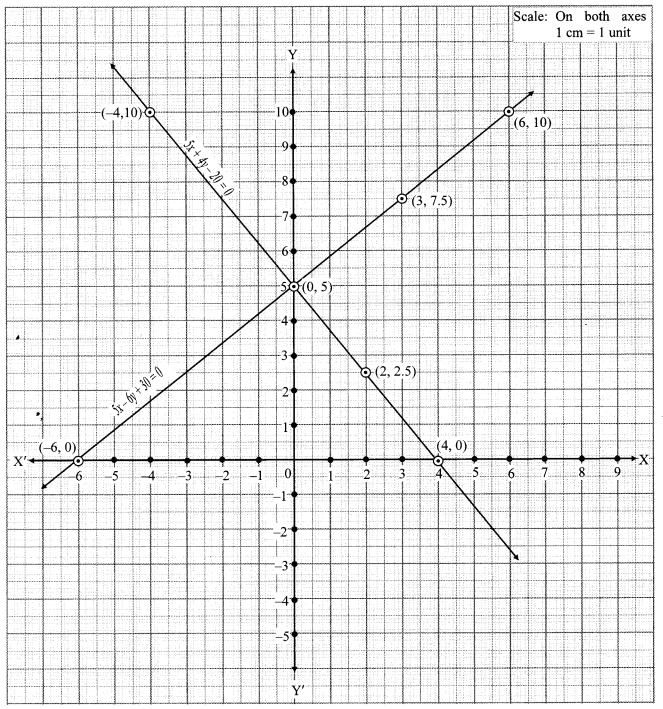
The two lines intersect at point (0, 5).
∴ x = 0 and y = 5 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 5x – 6y + 30 = 0 and 5x + 4y – 20 = 0.
iv. The given simultaneous equations are
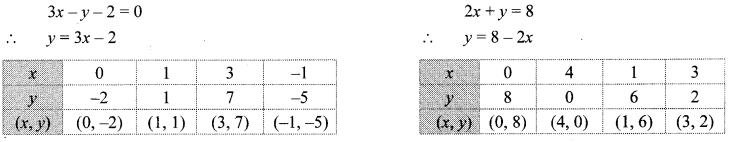
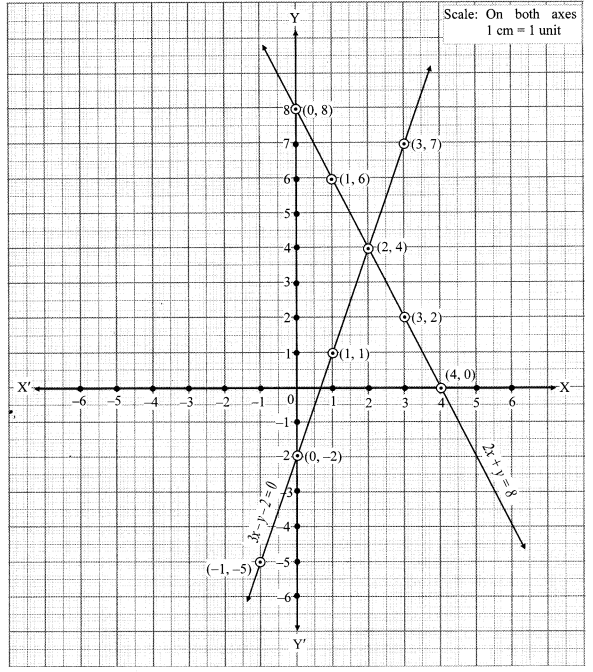
The two lines intersect at point (2, 4).
∴ x = 2 and y = 4 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 3x – y – 2 = 0 and 2x + y = 8.
v. The given simultaneous equations are
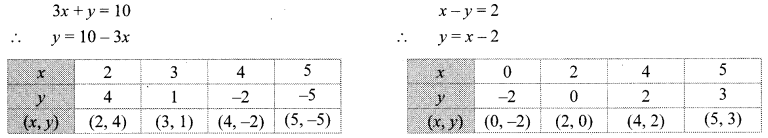
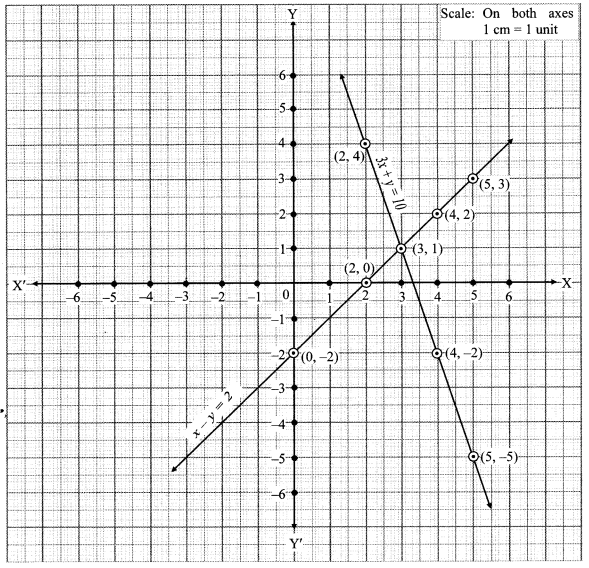
The two lines intersect at point (3, 1).
∴ x = 3 and y = 1 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 3x + y = 10 and x – y = 2.
Question 4.
Find the values of each of the following determinants.

Solution:
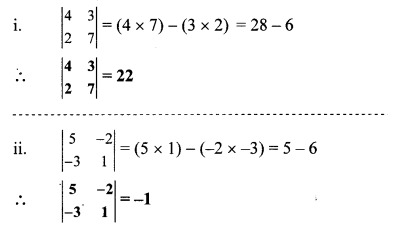
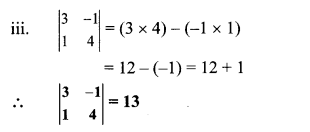
Question 5.
Solve the following equations by Cramer’s method.
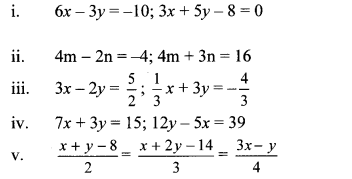
Solution:
i. The given simultaneous equations are
6x – 3y = -10 …(i)
3x + 5y – 8 = 0
∴ 3x + 5y = 8 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form. Comparing the given equations with a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 6, b1 = -3, c1 = 10 and
a2 = 3, b2 = 5, c2 = 8
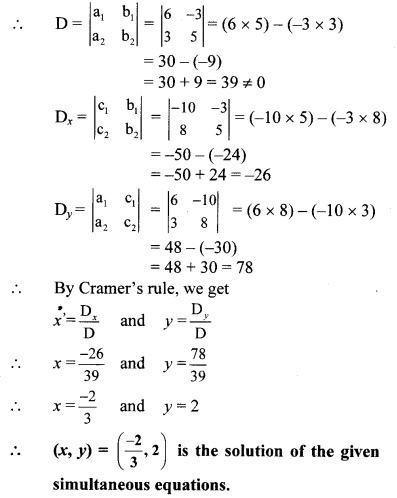
ii. The given simultaneous equations are
4m – 2n = -4 …(i)
4m + 3n = 16 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in am + bn = c form.
Comparing the given equations with a1m + b1n = c1 and a2m + b2n = c2, we get
a1 = 4, b1 = -2, c1 = -4 and
a2 = 4, b2 = 3, c2 = 16
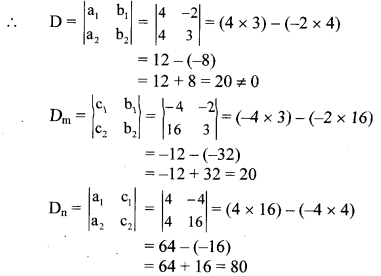

∴ (m, n) = (1, 4) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
iii. The given simultaneous equations are
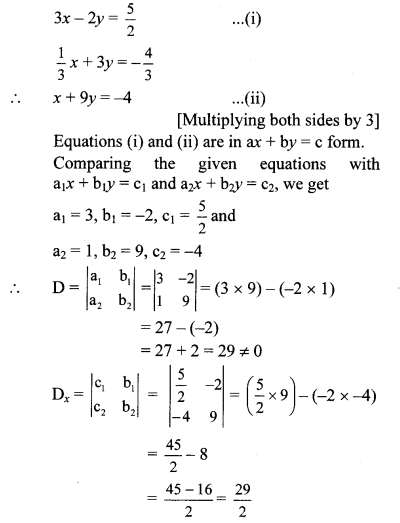

iv. The given simultaneous equations are
7x + 3y = 15 …(i)
12y – 5x = 39
i.e. -5x + 12y = 39 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 7, b1 = 3, c1 = 15 and
a2 = -5, b2 = 12, c2 = 39
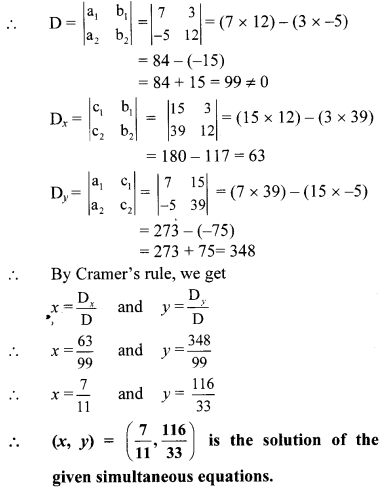
v. The given simultaneous equations are
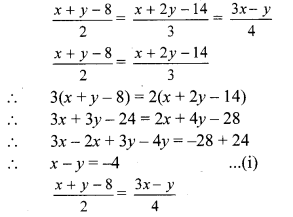
∴ 4(x + y – 8) = 2(3x – y)
∴ 4x + 4y – 32 = 6x – 2y
∴ 6x – 4x – 2y – 4y = -32
∴ 2x – 6y = -32
∴ x – 3y = -16 …(ii)[Dividing both sides by 2]
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form. Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 1, b1 = -1, c1 = -4 and
a2 = 1, b2 = -3, c2 = -16
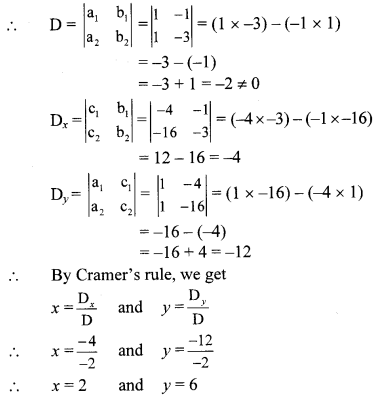
∴ (x, y) = (2, 6) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
Question 6.
Solve the following simultaneous equations:
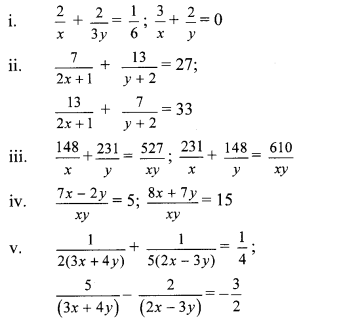
Answer:
i. The given simultaneous equations are

Subtracting equation (iv) from (iii), we get

∴ (x, y) = (6, – 4) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
ii. The given simultaneous equations are

Adding equations (v) and (vi), we get

iii. The given simultaneous equations are

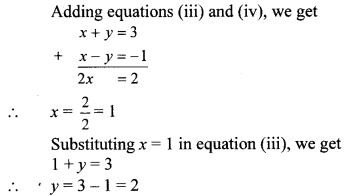
∴ (x, y) = (1, 2) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
iv. The given simultaneous equations are
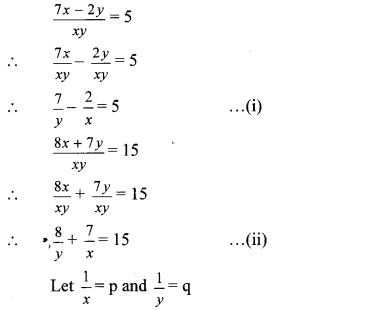
∴ Equations (i) and (ii) become 7q – 2p = 5 …(iii)
8q + 7p = 15 …(iv)
Multiplying equation (iii) by 7, we get
49q – 14p = 35 …(v)
Multiplying equation (iv) by 2, we get
16q + 14p = 30 …(vi)
Adding equations (v) and (vi), we get
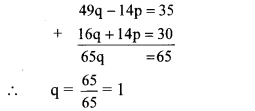
Substituting q = 1 in equation (iv), we get
8(1) + 7p = 15
∴ 8 + 7p = 15
∴ 7p = 15 – 8
∴ 7p = 7
∴ p = \(\frac { 7 }{ 7 } \) = 1
∴ (P, q) = (1,1)
Resubstituting the values of p and q, we get
1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ x } \) and 1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ y } \)
∴ x = 1 and y = 1
∴ (x, y) = (1, 1) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
v. The given simultaneous equations are

Resubstituting the values of p and q, we get
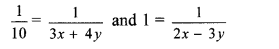
∴ 3x + 4y = 10 …(v)
and 2x – 3y = 1 …(vi)
Multiplying equation (v) by 3, we get
9x + 12y = 30 …(vii)
Multiplying equation (vi) by 4, we get
8x – 12y = 4 …(viii)
Adding equations (vii) and (viii), we get
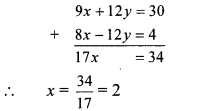
Substituting x = 2 in equation (v), we get
3(2) + 4y = 10
⇒ 6 + 4y = 10
⇒ 4y = 10 – 6
⇒ y = 4/4 = 1
∴ y = 1
∴ (x, y) = (2, 1) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
Question 7.
Solve the following word problems, i. A two digit number and the number with digits interchanged add up to 143. In the given number the digit in unit’s place is 3 more than the digit in the ten’s place. Find the original number.
Solution:
Let the digit in unit’s place be x
and that in the ten’s place be y.

ii. Kantabai bought 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) kg tea and 5 kg sugar from a shop. She paid ₹ 50 as return fare for rickshaw. Total expense was ₹ 700. Then she realised that by ordering online the goods can be bought with free home delivery at the same price. So, next month she placed the order online for 2 kg tea and 7 kg sugar. She paid ₹ 880 for that. Find the rate of sugar and tea per kg.
Solution:
Let the rate of tea be ₹ x per kg and that of sugar be ₹ y per kg.
According to the first condition,
cost of 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) kg tea + cost of 5 kg sugar + fare for rickshaw = total expense
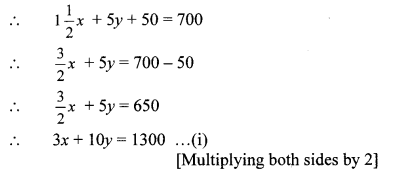
According to the second condition,
cost of 2 kg tea + cost of 7 kg sugar = total expense
2x + 7y = 880 …(ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by 2, we get
6x + 20y = 2600 …(iii)
Multiplying equation (ii) by 3, we get
6x + 21y = 2640 …(iv)
Subtracting equation (iii) from (iv), we get
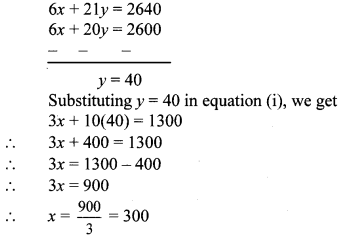
∴ The rate of tea is ₹ 300 per kg and that of sugar is ₹ 40 per kg.
iii. To find number of notes that Anushka had, complete the following activity.
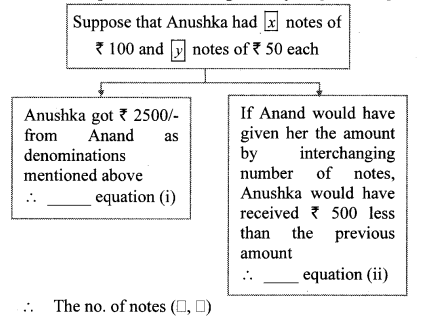
Solution:
Anushka had x notes of ₹ 100 and y notes of ₹ 50.
According to the first condition,
100x + 50y = 2500
∴ 2x + y = 50 …(i) [Dividing both sides by 50]
According to the second condition,
100y + 50x = 2000
∴ 2y + x = 40 … [Dividing both sides by 50]
i.e. x + 2y = 40
∴ 2x + 4y = 80 …(ii) [Multiplying both sides by 2]
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii), we get
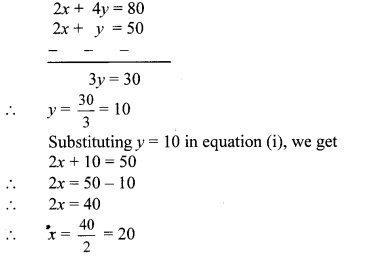
∴ Anushka had 20 notes of ₹ 100 and 10 notes of ₹ 50.
iv. Sum of the present ages of Manish and Savita is 31, Manish’s age 3 years ago was 4 times the age of Savita. Find their present ages.
Solution:
Let the present ages of Manish and Savita be x years and y years respectively.
According to the first condition,
x + y = 31 …(i)
3 years ago,
Manish’s age = (x – 3) years
Savita’s age = (y – 3) years
According to the second condition,
(x – 3) = 4 (y – 3)
∴ x – 3 = 4y – 12
∴ x – 4y = -12 + 3
∴ x – 4y = -9 …(ii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from (i), we get
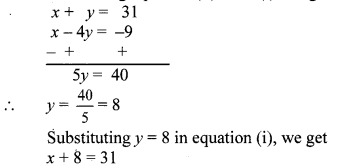
∴ x = 31 – 8
∴ x = 23
The present ages of Manish and Savita are 23 years and 8 years respectively.
v. In a factory the ratio of salary of skilled and unskilled workers is 5 : 3. Total salary of one day of both of them is ₹ 720. Find daily wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
Solution:
Let the daily wages of skilled workers be ₹ x
that of unskilled workers be ₹ y.
According to the first condition,

∴ The daily wages of skilled workers is ₹ 450 and that of unskilled workers is ₹ 270.
vi. Places A and B are 30 km apart and they are on a straight road. Hamid travels from A to B on bike. At the same time Joseph starts from B on bike, travels towards A. They meet each other after 20 minutes. If Joseph would have started from B at the same time but in the opposite direction (instead of towards A), Hamid would have caught him after 3 hours. Find the speed of Hamid and Joseph.
Solution:
Let the speeds of Hamid and Joseph be x km/hr andy km/hr respectively.
Distance travelled by Hamid in 20 minutes

According to the first condition,

∴ The speeds of Hamid and Joseph 50 km/hr and 40 km/hr respectively.
covers the Problem Set 1 Algebra 10th Class Maths Part 1 Answers Solutions Chapter 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables.
Choose correct alternative for each of the following questions.
Question 1.
To draw graph of 4x + 5y = 19, find y when x = 1.
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) -3
Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
For simultaneous equations in variables x and y, Dx = 49, Dy = – 63, D = 7 then what is x?
(a) 7
(b) -7
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 } \)
(d) \(\frac { -1 }{ 7 } \)
Answer:
(a)
Question 3.
Find the value of
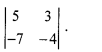
(a) -1
(b) -41
(c) 41
(d) 1
Answer:
(d)
Question 4.
To solvex + y = 3; 3x – 2y – 4 = 0 by determinant method find D.
(a) 5
(b) 1
(c) -5
(d) -1
Answer:
(c)
Question 5.
ax + by = c and mx + n y = d and an ≠ bm then these simultaneous equations have-
(a) Only one common solution
(b) No solution
(c) Infinite number of solutions
(d) Only two solutions.
Answer:
(a)
Question 2.
Complete the following table to draw the graph of 2x – 6y = 3.
Answer:

Question 3.
Solve the following simultaneous equations graphically.
i. 2x + 3y = 12 ; x – y = 1
ii. x – 3y = 1 ; 3x – 2y + 4 = 0
iii. 5x – 6y + 30 = 0; 5x + 4y – 20 = 0
iv. 3x – y – 2 = 0 ; 2x + y = 8
v. 3x + y= 10 ; x – y = 2
Answer:
i. The given simultaneous equations are

The two lines interest at point (3,2).
∴ x = 3 and y = 2 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 2x + 3y = 12 and x – y = 1.
ii. The given simultaneous equations are

The two lines intersect at point (-2, -1).
∴ x = -2 and y = -1 is the solution of the simultaneous equations x – 3y = 1 and 3x – 2p + 4 = 0.
iii. The given simultaneous equations are


The two lines intersect at point (0, 5).
∴ x = 0 and y = 5 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 5x – 6y + 30 = 0 and 5x + 4y – 20 = 0.
iv. The given simultaneous equations are


The two lines intersect at point (2, 4).
∴ x = 2 and y = 4 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 3x – y – 2 = 0 and 2x + y = 8.
v. The given simultaneous equations are


The two lines intersect at point (3, 1).
∴ x = 3 and y = 1 is the solution of the simultaneous equations 3x + y = 10 and x – y = 2.
Question 4.
Find the values of each of the following determinants.

Solution:
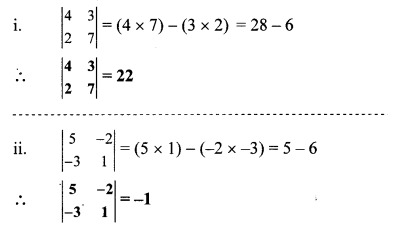
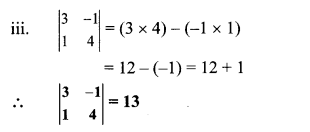
Question 5.
Solve the following equations by Cramer’s method.
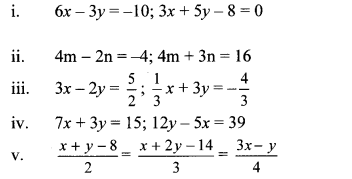
Solution:
i. The given simultaneous equations are
6x – 3y = -10 …(i)
3x + 5y – 8 = 0
∴ 3x + 5y = 8 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form. Comparing the given equations with a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 6, b1 = -3, c1 = 10 and
a2 = 3, b2 = 5, c2 = 8
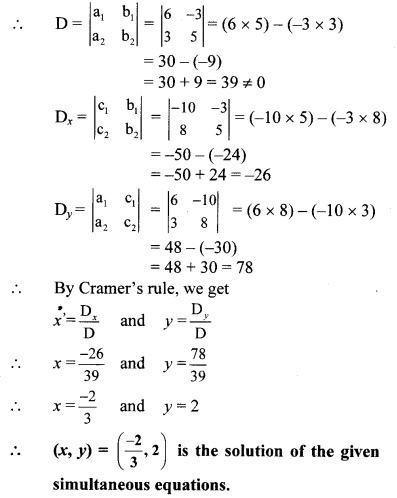
ii. The given simultaneous equations are
4m – 2n = -4 …(i)
4m + 3n = 16 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in am + bn = c form.
Comparing the given equations with a1m + b1n = c1 and a2m + b2n = c2, we get
a1 = 4, b1 = -2, c1 = -4 and
a2 = 4, b2 = 3, c2 = 16
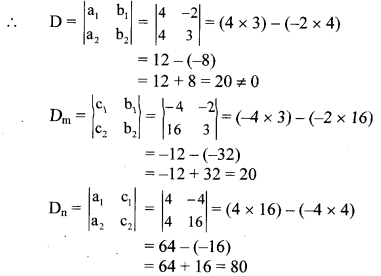

∴ (m, n) = (1, 4) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
iii. The given simultaneous equations are
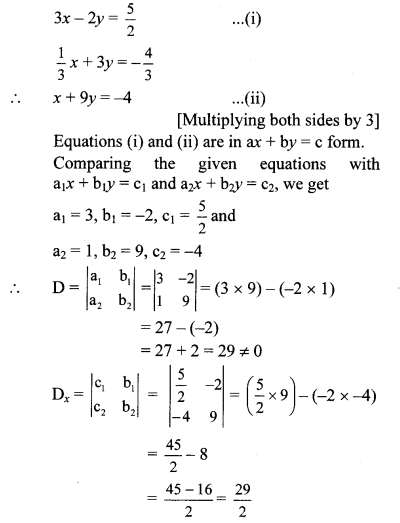

iv. The given simultaneous equations are
7x + 3y = 15 …(i)
12y – 5x = 39
i.e. -5x + 12y = 39 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 7, b1 = 3, c1 = 15 and
a2 = -5, b2 = 12, c2 = 39
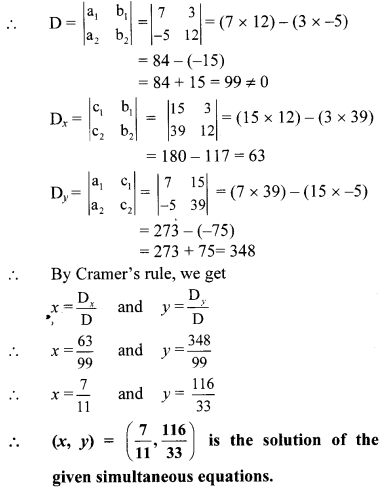
v. The given simultaneous equations are
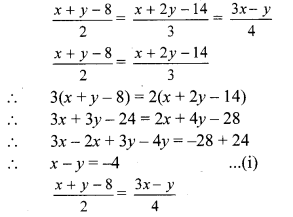
∴ 4(x + y – 8) = 2(3x – y)
∴ 4x + 4y – 32 = 6x – 2y
∴ 6x – 4x – 2y – 4y = -32
∴ 2x – 6y = -32
∴ x – 3y = -16 …(ii)[Dividing both sides by 2]
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form. Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 1, b1 = -1, c1 = -4 and
a2 = 1, b2 = -3, c2 = -16
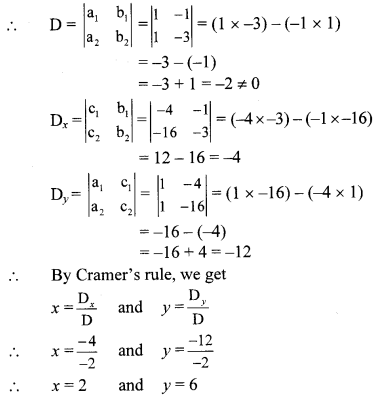
∴ (x, y) = (2, 6) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
Question 6.
Solve the following simultaneous equations:
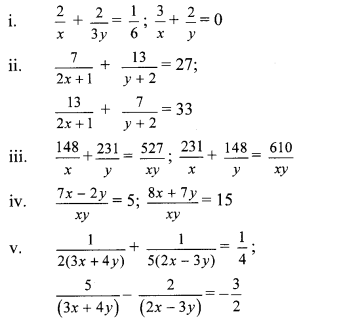
Answer:
i. The given simultaneous equations are

Subtracting equation (iv) from (iii), we get

∴ (x, y) = (6, – 4) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
ii. The given simultaneous equations are

Adding equations (v) and (vi), we get

iii. The given simultaneous equations are

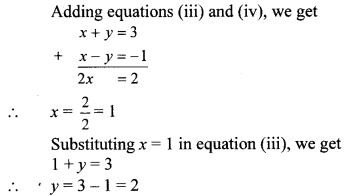
∴ (x, y) = (1, 2) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
iv. The given simultaneous equations are
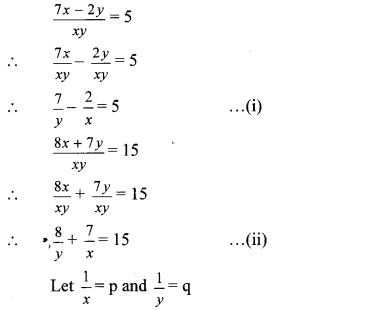
∴ Equations (i) and (ii) become 7q – 2p = 5 …(iii)
8q + 7p = 15 …(iv)
Multiplying equation (iii) by 7, we get
49q – 14p = 35 …(v)
Multiplying equation (iv) by 2, we get
16q + 14p = 30 …(vi)
Adding equations (v) and (vi), we get
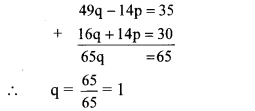
Substituting q = 1 in equation (iv), we get
8(1) + 7p = 15
∴ 8 + 7p = 15
∴ 7p = 15 – 8
∴ 7p = 7
∴ p = \(\frac { 7 }{ 7 } \) = 1
∴ (P, q) = (1,1)
Resubstituting the values of p and q, we get
1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ x } \) and 1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ y } \)
∴ x = 1 and y = 1
∴ (x, y) = (1, 1) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
v. The given simultaneous equations are

Resubstituting the values of p and q, we get
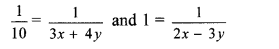
∴ 3x + 4y = 10 …(v)
and 2x – 3y = 1 …(vi)
Multiplying equation (v) by 3, we get
9x + 12y = 30 …(vii)
Multiplying equation (vi) by 4, we get
8x – 12y = 4 …(viii)
Adding equations (vii) and (viii), we get
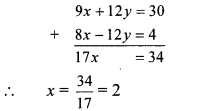
Substituting x = 2 in equation (v), we get
3(2) + 4y = 10
⇒ 6 + 4y = 10
⇒ 4y = 10 – 6
⇒ y = 4/4 = 1
∴ y = 1
∴ (x, y) = (2, 1) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
Question 7.
Solve the following word problems, i. A two digit number and the number with digits interchanged add up to 143. In the given number the digit in unit’s place is 3 more than the digit in the ten’s place. Find the original number.
Solution:
Let the digit in unit’s place be x
and that in the ten’s place be y.

ii. Kantabai bought 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) kg tea and 5 kg sugar from a shop. She paid ₹ 50 as return fare for rickshaw. Total expense was ₹ 700. Then she realised that by ordering online the goods can be bought with free home delivery at the same price. So, next month she placed the order online for 2 kg tea and 7 kg sugar. She paid ₹ 880 for that. Find the rate of sugar and tea per kg.
Solution:
Let the rate of tea be ₹ x per kg and that of sugar be ₹ y per kg.
According to the first condition,
cost of 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) kg tea + cost of 5 kg sugar + fare for rickshaw = total expense
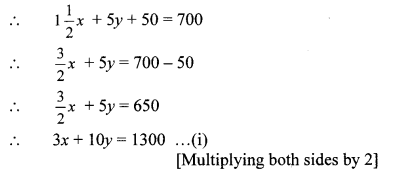
According to the second condition,
cost of 2 kg tea + cost of 7 kg sugar = total expense
2x + 7y = 880 …(ii)
Multiplying equation (i) by 2, we get
6x + 20y = 2600 …(iii)
Multiplying equation (ii) by 3, we get
6x + 21y = 2640 …(iv)
Subtracting equation (iii) from (iv), we get
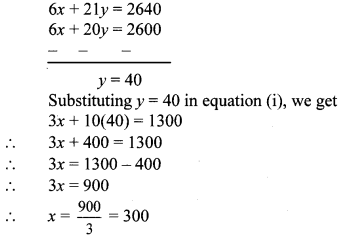
∴ The rate of tea is ₹ 300 per kg and that of sugar is ₹ 40 per kg.
iii. To find number of notes that Anushka had, complete the following activity.

Solution:
Anushka had x notes of ₹ 100 and y notes of ₹ 50.
According to the first condition,
100x + 50y = 2500
∴ 2x + y = 50 …(i) [Dividing both sides by 50]
According to the second condition,
100y + 50x = 2000
∴ 2y + x = 40 … [Dividing both sides by 50]
i.e. x + 2y = 40
∴ 2x + 4y = 80 …(ii) [Multiplying both sides by 2]
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii), we get
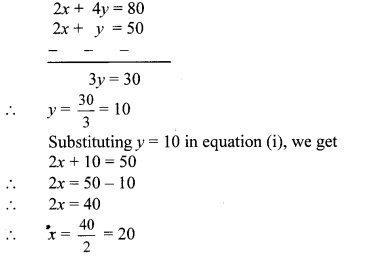
∴ Anushka had 20 notes of ₹ 100 and 10 notes of ₹ 50.
iv. Sum of the present ages of Manish and Savita is 31, Manish’s age 3 years ago was 4 times the age of Savita. Find their present ages.
Solution:
Let the present ages of Manish and Savita be x years and y years respectively.
According to the first condition,
x + y = 31 …(i)
3 years ago,
Manish’s age = (x – 3) years
Savita’s age = (y – 3) years
According to the second condition,
(x – 3) = 4 (y – 3)
∴ x – 3 = 4y – 12
∴ x – 4y = -12 + 3
∴ x – 4y = -9 …(ii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from (i), we get
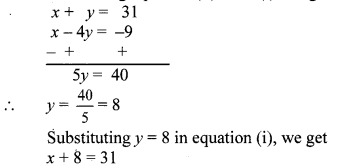
∴ x = 31 – 8
∴ x = 23
The present ages of Manish and Savita are 23 years and 8 years respectively.
v. In a factory the ratio of salary of skilled and unskilled workers is 5 : 3. Total salary of one day of both of them is ₹ 720. Find daily wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
Solution:
Let the daily wages of skilled workers be ₹ x
that of unskilled workers be ₹ y.
According to the first condition,

∴ The daily wages of skilled workers is ₹ 450 and that of unskilled workers is ₹ 270.
vi. Places A and B are 30 km apart and they are on a straight road. Hamid travels from A to B on bike. At the same time Joseph starts from B on bike, travels towards A. They meet each other after 20 minutes. If Joseph would have started from B at the same time but in the opposite direction (instead of towards A), Hamid would have caught him after 3 hours. Find the speed of Hamid and Joseph.
Solution:
Let the speeds of Hamid and Joseph be x km/hr andy km/hr respectively.
Distance travelled by Hamid in 20 minutes

According to the first condition,

∴ The speeds of Hamid and Joseph 50 km/hr and 40 km/hr respectively.