Balbharati Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce Maths Solution Book Pdf
Chapter 1 Mathematical Logic Ex 1.6 Questions and Answers.
Question 1.
Prepare the truth tables for the following statement patterns:
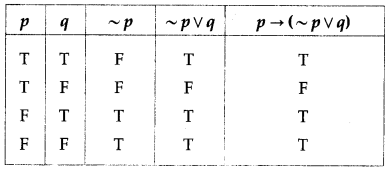
(i) p → (~p ∨ q)
Solution:
Here are two statements and three connectives.
∴ there are 2 × 2 = 4 rows and 2 + 3 = 5 columns in the truth table.
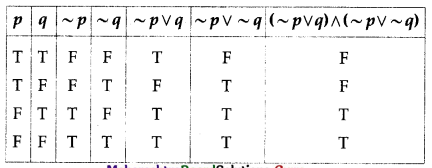
(ii) (~p ∨ q) ∧ (~p ∨ ~q)
Solution:

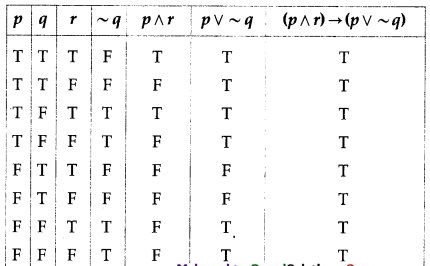
(iii) (p ∧ r) → (p ∨ ~q)
Solution:
Here are three statements and 4 connectives.
∴ there are 2 × 2 × 2 = 8 rows and 3 + 4 = 7 columns in the truth table.
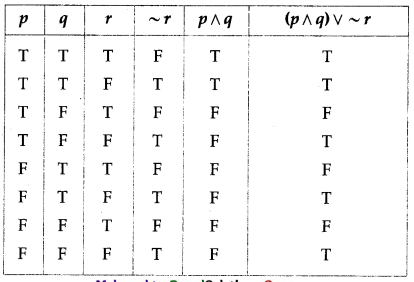
(iv) (p ∧ q) ∨ ~r
Solution:
Question 2.
Examine, whether each of the following statement patterns is a tautology or a contradiction or a contingency:
(i) q ∨ [~(p ∧ q)]
Solution:
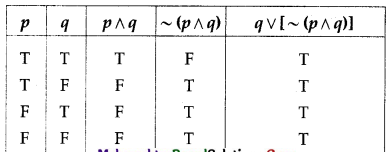
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ q ∨ [~(p ∧ q)] is a tautology.
(ii) (~q ∧ p) ∧ (p ∧ ~p)
Solution:
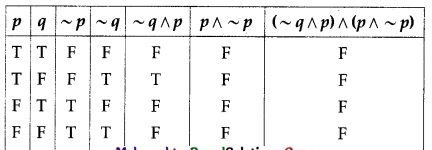
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (~q ∧ p) ∧ (p ∧ ~p) is a contradiction.

(iii) (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q)
Solution:
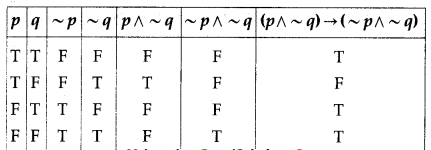
The entries in the last column are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q) is a contingency.
(iv) ~p → (p → ~q)
Solution:
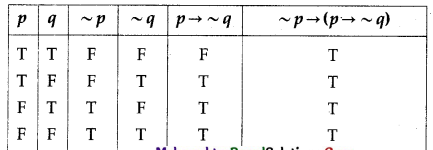
All the entries in the last column of the truth table are T.
∴ p → (p → ~q) is a tautology.
Question 3.
Prove that each of the following statement pattern is a tautology:
(i) (p ∧ q) → q
Solution:
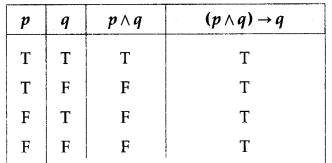
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (p ∧ q) → q is a tautology.
(ii) (p → q) ↔ (~q → ~p)
Solution:
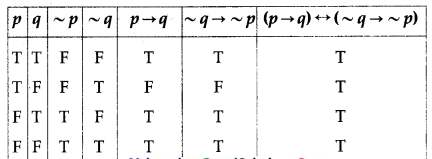
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (p → q) ↔ (~q → ~p) is a tautology.
(iii) (~p ∧ ~q) → (p → q)
Solution:
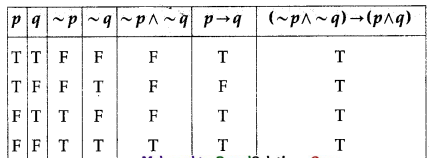
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (~p ∧ ~q) → (p → q) is a tautology.

(iv) (~p ∨ ~q) ↔ ~(p ∧ q)
Solution:
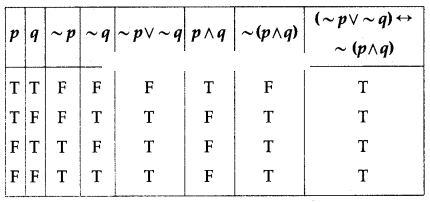
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (~p ∨ ~q) ↔ ~(p ∧ q) is a tautology.
Question 4.
Prove that each of the following statement pattern is a contradiction:
(i) (p ∨ q) ∧ (~p ∧ ~q)
Solution:
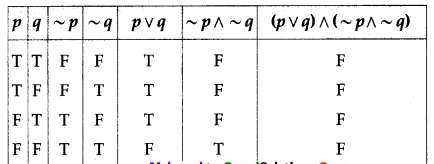
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (p ∨ q) ∧ (~p ∧ ~q) is a contradiction.
(ii) (p ∧ q) ∧ ~p
Solution:
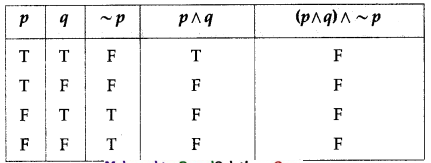
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (p ∧ q) ∧ ~p is a contradiction.
(iii) (p ∧ q) ∧ (~p ∨ ~q)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (p ∧ q) ∧ (~p ∨ ~q) is a contradiction.

(iv) (p → q) ∧ (p ∧ ~q)
Solution:
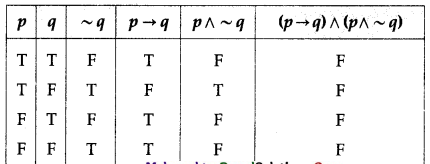
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (p → q) ∧ (p ∧ ~q) is a contradiction.
Question 5.
Show that each of the following statement pattern is a contingency:
(i) (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q)
Solution:
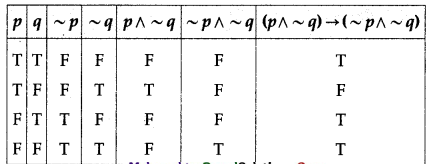
The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q) is a contingency.
(ii) (p → q) ↔ (~p ∧ q)
Solution:
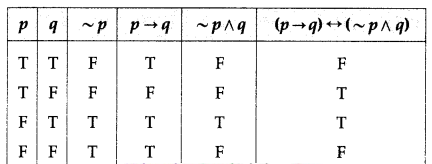
The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p → q) ↔ (~p ∧ q) is a contingency.
(iii) p ∧ [(p → ~q) → q]
Solution:
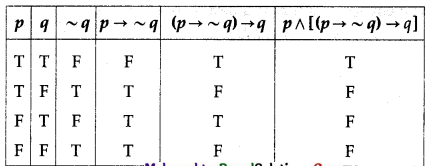
The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ p ∧ [(p → ~q) → q] is a contingency.
(iv) (p → q) ∧ (p → r)
Solution:
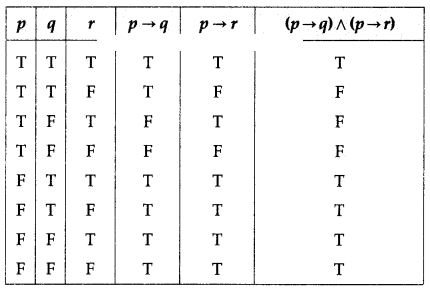
The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p → q) ∧ (p → r) is a contingency.

Question 6.
Using the truth table, verify:
(i) p ∨ (q ∧ r) = (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r)
Solution:
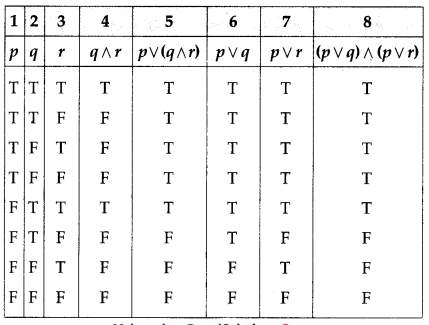
The entries in columns 5 and 8 are identical.
∴ p ∨ (q ∧ r) ≡ (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r).
(ii) p → (p → q) ≡ ~q → (p → q)
Solution:
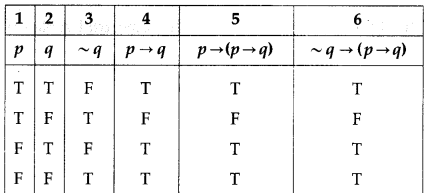
The entries in columns 5 and 6 are identical.
∴ p → (p → q) ≡ ~q → (p → q)
(iii) ~(p → ~q) ≡ p ∧ ~(~q) ≡ p ∧ q
Solution:
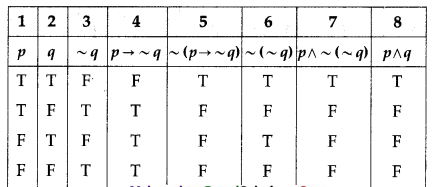
The entries in columns 5, 7 and 8 are identical.
∴ ~(p → ~q) ≡ p ∧ ~(~q) ≡ p ∧ q.
(iv) ~(p ∨ q) ∨ (~p ∧ q) ≡ ~p
Solution:
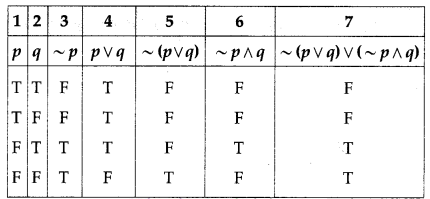
The entries in columns 3 and 7 are identical.
∴ ~(p ∨ q) ∨ (~p ∧ q) ≡ ~p.

Question 7.
Prove that the following pairs of statement patterns are equivalent:
(i) p ∨ (q ∧ r) and (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r)
Solution:
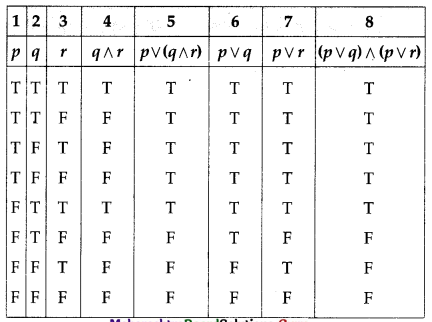
The entries in columns 5 and 8 are identical.
∴ p ∨ (q ∧ r) ≡ (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r)
(ii) p ↔ q and (p → q) ∧ (q → p)
Solution:
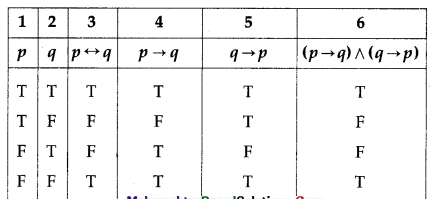
The entries in columns 3 and 6 are identical.
∴ p ↔ q ≡ (p → q) ∧ (q → p)
(iii) p → q and ~q → ~p and ~p ∨ q
Solution:
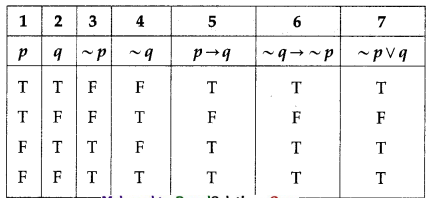
The entries in columns 5, 6 and 7 are identical.
∴ p → q ≡ ~q → ~p ≡ ~p ∨ q.

(iv) ~(p ∧ q) and ~p ∨ ~q
Solution:

The entries in columns 6 and 7 are identical.
∴ ~(p ∧ q) ≡ ~p ∨ ~q.
Chapter 1 Mathematical Logic Ex 1.6 Questions and Answers.
Question 1.
Prepare the truth tables for the following statement patterns:
(i) p → (~p ∨ q)
Solution:
Here are two statements and three connectives.
∴ there are 2 × 2 = 4 rows and 2 + 3 = 5 columns in the truth table.

(ii) (~p ∨ q) ∧ (~p ∨ ~q)
Solution:


(iii) (p ∧ r) → (p ∨ ~q)
Solution:
Here are three statements and 4 connectives.
∴ there are 2 × 2 × 2 = 8 rows and 3 + 4 = 7 columns in the truth table.

(iv) (p ∧ q) ∨ ~r
Solution:

Question 2.
Examine, whether each of the following statement patterns is a tautology or a contradiction or a contingency:
(i) q ∨ [~(p ∧ q)]
Solution:
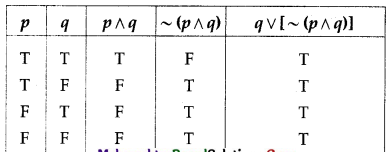
All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ q ∨ [~(p ∧ q)] is a tautology.
(ii) (~q ∧ p) ∧ (p ∧ ~p)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (~q ∧ p) ∧ (p ∧ ~p) is a contradiction.

(iii) (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q)
Solution:

The entries in the last column are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q) is a contingency.
(iv) ~p → (p → ~q)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the truth table are T.
∴ p → (p → ~q) is a tautology.
Question 3.
Prove that each of the following statement pattern is a tautology:
(i) (p ∧ q) → q
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (p ∧ q) → q is a tautology.
(ii) (p → q) ↔ (~q → ~p)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (p → q) ↔ (~q → ~p) is a tautology.
(iii) (~p ∧ ~q) → (p → q)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (~p ∧ ~q) → (p → q) is a tautology.

(iv) (~p ∨ ~q) ↔ ~(p ∧ q)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (~p ∨ ~q) ↔ ~(p ∧ q) is a tautology.
Question 4.
Prove that each of the following statement pattern is a contradiction:
(i) (p ∨ q) ∧ (~p ∧ ~q)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (p ∨ q) ∧ (~p ∧ ~q) is a contradiction.
(ii) (p ∧ q) ∧ ~p
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are T.
∴ (p ∧ q) ∧ ~p is a contradiction.
(iii) (p ∧ q) ∧ (~p ∨ ~q)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (p ∧ q) ∧ (~p ∨ ~q) is a contradiction.

(iv) (p → q) ∧ (p ∧ ~q)
Solution:

All the entries in the last column of the above truth table are F.
∴ (p → q) ∧ (p ∧ ~q) is a contradiction.
Question 5.
Show that each of the following statement pattern is a contingency:
(i) (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q)
Solution:

The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p ∧ ~q) → (~p ∧ ~q) is a contingency.
(ii) (p → q) ↔ (~p ∧ q)
Solution:

The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p → q) ↔ (~p ∧ q) is a contingency.
(iii) p ∧ [(p → ~q) → q]
Solution:

The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ p ∧ [(p → ~q) → q] is a contingency.
(iv) (p → q) ∧ (p → r)
Solution:

The entries in the last column of the above truth table are neither all T nor all F.
∴ (p → q) ∧ (p → r) is a contingency.

Question 6.
Using the truth table, verify:
(i) p ∨ (q ∧ r) = (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r)
Solution:

The entries in columns 5 and 8 are identical.
∴ p ∨ (q ∧ r) ≡ (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r).
(ii) p → (p → q) ≡ ~q → (p → q)
Solution:

The entries in columns 5 and 6 are identical.
∴ p → (p → q) ≡ ~q → (p → q)
(iii) ~(p → ~q) ≡ p ∧ ~(~q) ≡ p ∧ q
Solution:

The entries in columns 5, 7 and 8 are identical.
∴ ~(p → ~q) ≡ p ∧ ~(~q) ≡ p ∧ q.
(iv) ~(p ∨ q) ∨ (~p ∧ q) ≡ ~p
Solution:

The entries in columns 3 and 7 are identical.
∴ ~(p ∨ q) ∨ (~p ∧ q) ≡ ~p.

Question 7.
Prove that the following pairs of statement patterns are equivalent:
(i) p ∨ (q ∧ r) and (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r)
Solution:

The entries in columns 5 and 8 are identical.
∴ p ∨ (q ∧ r) ≡ (p ∨ q) ∧ (p ∨ r)
(ii) p ↔ q and (p → q) ∧ (q → p)
Solution:

The entries in columns 3 and 6 are identical.
∴ p ↔ q ≡ (p → q) ∧ (q → p)
(iii) p → q and ~q → ~p and ~p ∨ q
Solution:

The entries in columns 5, 6 and 7 are identical.
∴ p → q ≡ ~q → ~p ≡ ~p ∨ q.

(iv) ~(p ∧ q) and ~p ∨ ~q
Solution:

The entries in columns 6 and 7 are identical.
∴ ~(p ∧ q) ≡ ~p ∨ ~q.