Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Textbook Solutions
Chapter 13 Respiration and Energy Transfer Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Choose Correct option
Question (A)
The reactions of the TCA cycle occur in
(A) ribosomes
(B) grana
(C) mitochondria
(D) endoplasmic reticulum
Answer:
(C) mitochondria

Question (B)
In eukaryotes the complete oxidation of a molecule of glucose results in the net gain of
(A) 2 molecules of ATP
(B) 36 molecules of ATP
(C) 4 molecules of ATP
(D) 38 molecules of ATP
Answer:
(D) 38 molecules of ATP
Question (C)
Which step of Krebs cycle operates substrate-level phosphorylation?
(A) ∝-ketoglutarate → succinyl CoA.
(B) Succinyl CoA → succinate
(C) Succinate → fumarate
(D) Fumarate → malate
Answer:
(B) Succinyl CoA → succinate
2. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
Question 1.
A. Acetyl CoA is formed from __________ and co-enzyme A.
B. In the prokaryotes ________ molecules of ATP are formed per molecule of glucose oxidised.
C. Glycolysis takes place in ________ .
D. F1 – F0 particles participate in the synthesis of _________ .
E. During glycolysis _________ molecules of NADH+H+ are formed.
Answer:
A. pyruvic acid
B. 2/38
C. cytoplasm
D. ATP
E. 2
[Note: ii. In prokaryotes, during anaerobic respiration 2 ATPs are formed per glucose and 38 ATPs are formed during aerobic respiration.]
3. Answer the following questions
Question (A)
When and where does anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
Answer:
1. In absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration takes place in skeletal muscles of man during vigorous exercise.
2. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm of the yeast cell.
Question (B)
Why is less energy produced during anaerobic respiration than in aerobic respiration?
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration produces less energy because:

Question (C)
Which is the site for ETS in mitochondrial respiration?
Answer:
The inner mitochondrial membrane is the site for ETS in mitochondrial respiration.
Question (D)
Which compound is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration?
Answer:
Molecular oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration.
Question (E)
What is RQ.? What is its value for fats?
Answer:
1. Respiratory quotient (R.Q.) or respiratory ratio is the ratio of volume of CO2 released to the volume of O2 consumed in respiration.
2. R.Q. = Volume of CO2 released / Volume of O2 consumed
Question (F)
What are respiratory substrates? Name the most common respiratory substrate.
Answer:
Respiratory substrates are the molecules that are oxidized during respiration to release energy which can be used for ATP synthesis. Carbohydrates, fats and proteins are the common respiratory substrate. Glucose is the most common respiratory substrate.
Question (G)
Write explanatory notes on:
Question (i)
Glycolysis
Answer:
Glycolysis is a process where glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid, hence called glycolysis (glucose-breaking). It is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves ten steps.
Glycolysis consists of two major phases:
1. Preparatory phase (1-5 steps).
2. Payoff phase (6-10 steps).
1. Preparatory phase:
a. In this phase, glucose is phosphorylated twice by using two ATP molecules and a molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is formed.
b. It is then cleaved into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate. These two molecules are 3-carbon carbohydrates (trioses) and are isomers of each other.
c. Dihydroxy acetone phosphate is isomerised to second molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
d. Therefore, two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are formed.
e. Preparatory phase of glycolysis ends.
2. Payoff phase:
a. In this phase, both molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are converted to two molecules of 1,3- bisphoglycerate by oxidation and phosphorylation. Here, the phosphorylation is brought about by inorganic phosphate instead of ATP.
b. Both molecules of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate are converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid through series of reactions accompanied with release of energy. This released energy is used to produce ATP (4 molecules) by substrate-level phosphorylation.

Question (ii)
Write explanatory notes on: Fermentation by yeast
Answer:
Alcoholic fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration where the pyruvate is decarboxylated to acetaldehyde. The acetaldehyde is then reduced by NADH+H+ to ethanol and Carbon dioxide. Since ethanol is produced during the process, it is termed alcoholic fermentation.
Question (iii)
Write explanatory notes on: Electron transport chain
Answer:
Significance of ETS:
Question (H)
How are glycolysis, TCA cycle and electron transport chain-linked? Explain.
Answer:
Glycolysis, TCA cycle and electron transport chain are linked in the following manner:

Question (I)
How would you demonstrate that yeast can respire both aerobically and anaerobically?
Answer:
Respiration in yeast can be demonstrated with the help of an experiment.
Anaerobic respiration in yeast:
Aerobic respiration in yeast: Experiment explained can be carried out for demonstrating aerobic respiration in yeast.
Question (J)
What is the advantage of step wise energy release in respiration?
Answer:
In ETS energy is released in step wise manner to prevent damage of cells.
Question (K)
Explain ETS.
Answer:

Question (L)
Discuss “The respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway”.
OR
Question (M)
Why is Krebs cycle referred as amphibolic pathway?
Answer:
Question (N)
The common pathway for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration is
(A) Krebs cycle
(B) Glycolysis
(C) ETS
(D) Terminal oxidation
Answer:
(B) Glycolysis
4. Compare
Question (A)
Photosynthesis and respiration.
Answer:

Question (B)
Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration
Answer:
5. Differentiate between
Question (A)
Respiration and combustion.
Answer:
Question (B)
Distinguish between Glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
Answer:

Question (C)
Aerobic respiration and fermentation.
Answer:
Question 6.
Identify the cycle given below. Correct it and fill in the blanks and write description of it in your own
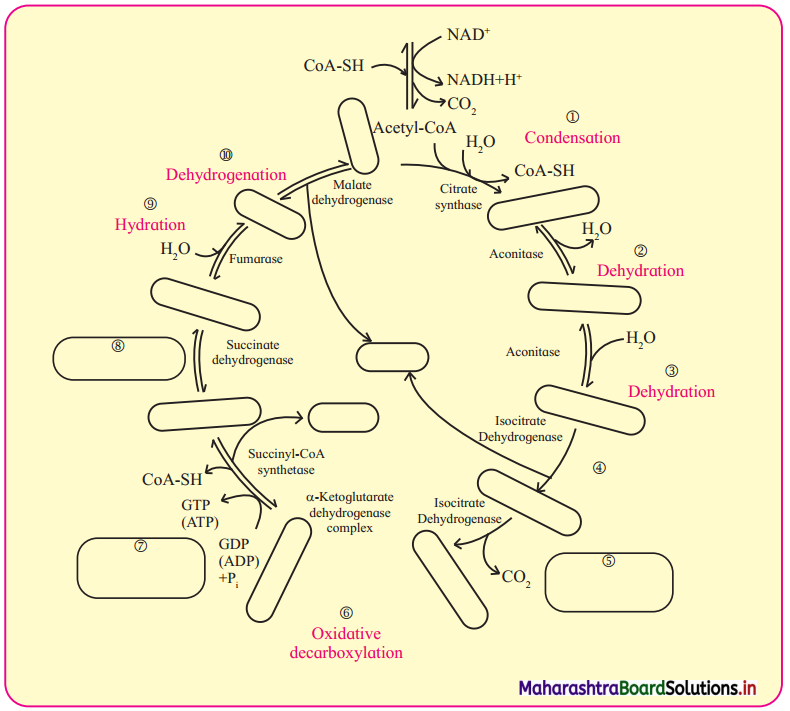 Answer:
Answer:

Practical / Project:
Question 1.
Make Powerpoint Presentation on Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle and Conduct the group discussion on it in classroom.
[Note: Students are expected to perform above activity on their own.]
11th Biology Digest Chapter 13 Respiration and Energy Transfer Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
(i) Which nutrients are used for energy production?
Answer:
Nutrients like carbohydrates, fats and proteins are used for energy production.
(ii) Why do organisms take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide?
Answer:
a. At cellular level, organisms require energy to carry out different metabolic activities.
b. The energy is made available by oxidizing/breaking the food.
Therefore, oxygen is required by aerobic organisms for breaking the food and carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct of oxidation.

Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 152)
Why is glycolysis considered as biochemical proof of evolution?
Answer:
Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 152)
(i) What is role of Mg++, Zn++ in various steps of glycolysis?
Answer:
a. Mg++ and Zn++ are the cofactors that are tightly bound to enzymes and helps the enzymes to perform their functions.
b. They regulate the activity of the most important enzymes like Hexokinase, Phosphoffuctokinase, Triose phosphate dehydrogenase, Phosphoglycerate kinase, Enolase, Pyruvate kinase.
(ii) Why some reactions of glycolysis are reversible and some irreversible?
Answer:
Irreversible chemical reactions:
Some chemical reactions can occur in only one direction i.e. these reactions are irreversible reactions. The reactants can change to the products, but the products cannot change back to the reactants.
Reversible chemical reactions:

Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 152)
Why do athletes like sprinters have higher proportion of white muscle fibers?
Answer:
1. The white muscle fibres produce energy in a very short period of time that is required for fast and severe work. Thus, the energy becomes immediately available to the athletes.
2. On the other hand, the red muscle produce energy over a prolonged period of time, hence athletes have higher proportion of white muscle fibers.
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
Which steps are involved in aerobic respiration?
Answer:
It involves glycolysis, acetyl CoA formation (connecting link reaction), Krebs cycle, electron transfer chain reaction and terminal oxidation.
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
What is aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
For anaerobic respiration: Anaerobic respiration is the cellular respiration that does not involve the atmospheric oxygen. It is also called as fermentation. It involves glycolysis where the product of glycolysis i.e. pyruvate is converted to either lactic acid or ethanol and for aerobic respiration.
1. Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of free molecular oxygen during oxidation of glucose.
2. In this type of respiration, the glucose is completely oxidized to C02 and H20 with release of large amount of energy. It involves glycolysis, acetyl CoA formation (connecting link reaction), Krebs cycle, electron transfer chain reaction and terminal oxidation.
Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 157)
Do the plants breath like animals? If yes, how and why?
Answer:

Internet my friend (Textbook Page No. 155)
What is effect of carbon monoxide poisoning on cytochromes?
Answer:
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
Which is most preferred nutrient among carbohydrate, protein and fat for energy production? Why?
Answer:
Internet my friend (Textbook Page No. 158)
Calculate the RQ for different respiratory substrates using appropriate formula.
Answer:
The RQ for different respiratory substrates are:
1. Carbohydrates (R.Q. is 1)
When carbohydrates are used as substrate, equal volumes of C02 and 02 are released and consumed respectively, thus its R.Q. is 1.
C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 → 6 C02 + 6H20
R.Q. = 6C02 / 602 = 1.0
2. Fats (R.Q. is less than 1)
Substrates like fats are poorer in oxygen than carbohydrates. Thus, more oxygen is utilized for its complete oxidation.
2(C51 H98 O6) + 145O2 → 102CO2 + 98H2O + Energy
R.Q. = C02 / 02 = 102 / 145 = 0.7
3. Protein respiration (R.Q. is less than 1)

Chapter 13 Respiration and Energy Transfer Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Choose Correct option
Question (A)
The reactions of the TCA cycle occur in
(A) ribosomes
(B) grana
(C) mitochondria
(D) endoplasmic reticulum
Answer:
(C) mitochondria

Question (B)
In eukaryotes the complete oxidation of a molecule of glucose results in the net gain of
(A) 2 molecules of ATP
(B) 36 molecules of ATP
(C) 4 molecules of ATP
(D) 38 molecules of ATP
Answer:
(D) 38 molecules of ATP
Question (C)
Which step of Krebs cycle operates substrate-level phosphorylation?
(A) ∝-ketoglutarate → succinyl CoA.
(B) Succinyl CoA → succinate
(C) Succinate → fumarate
(D) Fumarate → malate
Answer:
(B) Succinyl CoA → succinate
2. Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
Question 1.
A. Acetyl CoA is formed from __________ and co-enzyme A.
B. In the prokaryotes ________ molecules of ATP are formed per molecule of glucose oxidised.
C. Glycolysis takes place in ________ .
D. F1 – F0 particles participate in the synthesis of _________ .
E. During glycolysis _________ molecules of NADH+H+ are formed.
Answer:
A. pyruvic acid
B. 2/38
C. cytoplasm
D. ATP
E. 2
[Note: ii. In prokaryotes, during anaerobic respiration 2 ATPs are formed per glucose and 38 ATPs are formed during aerobic respiration.]
3. Answer the following questions
Question (A)
When and where does anaerobic respiration occur in man and yeast?
Answer:
1. In absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration takes place in skeletal muscles of man during vigorous exercise.
2. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm of the yeast cell.
Question (B)
Why is less energy produced during anaerobic respiration than in aerobic respiration?
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration produces less energy because:

Question (C)
Which is the site for ETS in mitochondrial respiration?
Answer:
The inner mitochondrial membrane is the site for ETS in mitochondrial respiration.
Question (D)
Which compound is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration?
Answer:
Molecular oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration.
Question (E)
What is RQ.? What is its value for fats?
Answer:
1. Respiratory quotient (R.Q.) or respiratory ratio is the ratio of volume of CO2 released to the volume of O2 consumed in respiration.
2. R.Q. = Volume of CO2 released / Volume of O2 consumed
Question (F)
What are respiratory substrates? Name the most common respiratory substrate.
Answer:
Respiratory substrates are the molecules that are oxidized during respiration to release energy which can be used for ATP synthesis. Carbohydrates, fats and proteins are the common respiratory substrate. Glucose is the most common respiratory substrate.
Question (G)
Write explanatory notes on:
Question (i)
Glycolysis
Answer:
Glycolysis is a process where glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid, hence called glycolysis (glucose-breaking). It is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves ten steps.
Glycolysis consists of two major phases:
1. Preparatory phase (1-5 steps).
2. Payoff phase (6-10 steps).
1. Preparatory phase:
a. In this phase, glucose is phosphorylated twice by using two ATP molecules and a molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is formed.
b. It is then cleaved into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate. These two molecules are 3-carbon carbohydrates (trioses) and are isomers of each other.
c. Dihydroxy acetone phosphate is isomerised to second molecule of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
d. Therefore, two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate are formed.
e. Preparatory phase of glycolysis ends.
2. Payoff phase:
a. In this phase, both molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are converted to two molecules of 1,3- bisphoglycerate by oxidation and phosphorylation. Here, the phosphorylation is brought about by inorganic phosphate instead of ATP.
b. Both molecules of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate are converted into two molecules of pyruvic acid through series of reactions accompanied with release of energy. This released energy is used to produce ATP (4 molecules) by substrate-level phosphorylation.

Question (ii)
Write explanatory notes on: Fermentation by yeast
Answer:
Alcoholic fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration where the pyruvate is decarboxylated to acetaldehyde. The acetaldehyde is then reduced by NADH+H+ to ethanol and Carbon dioxide. Since ethanol is produced during the process, it is termed alcoholic fermentation.
Question (iii)
Write explanatory notes on: Electron transport chain
Answer:
Significance of ETS:
Question (H)
How are glycolysis, TCA cycle and electron transport chain-linked? Explain.
Answer:
Glycolysis, TCA cycle and electron transport chain are linked in the following manner:

Question (I)
How would you demonstrate that yeast can respire both aerobically and anaerobically?
Answer:
Respiration in yeast can be demonstrated with the help of an experiment.
Anaerobic respiration in yeast:
Aerobic respiration in yeast: Experiment explained can be carried out for demonstrating aerobic respiration in yeast.
Question (J)
What is the advantage of step wise energy release in respiration?
Answer:
In ETS energy is released in step wise manner to prevent damage of cells.
Question (K)
Explain ETS.
Answer:

Question (L)
Discuss “The respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway”.
OR
Question (M)
Why is Krebs cycle referred as amphibolic pathway?
Answer:
Question (N)
The common pathway for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration is
(A) Krebs cycle
(B) Glycolysis
(C) ETS
(D) Terminal oxidation
Answer:
(B) Glycolysis
4. Compare
Question (A)
Photosynthesis and respiration.
Answer:
| Photosynthesis | Respiration |
| (a) It takes place in the cells containing chlomplasts. | It takes place in all living cells of higher organisms. |
| (b) It occurs in chloroplast. | It occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria. |
| (c) It is an energc trapping process. | It is an energy releasing process. |
| (d) It is an anabolic process. | It is a catabolic process. |
| (e) This process requires C02 and FLO. | This process requires sugar and 02. |
| (f) Light is necessary for photosynthesis. | Light is not necessary for aerobic respiration. |
| (g) End products are carbohydrates and oxygen. | End products can be C02 and H20 or ethanol or lactic acid and energy. |

Question (B)
Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration
Answer:
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| (a) It takes place in higher organisms. | It takes place in lower organisms. |
| (b) It takes place in cytoplasm and mitochondria. | It takes place in cytoplasm. |
| (c) It involves the participation of free molecular oxygen. | It does not involve participation of free molecular oxygen. |
| (d) Oxidation of food is complete. | Oxidation of food is incomplete. |
| (e) It produces C02 and H20. | It produces C02 and C2H5OH. |
| (f) It releases more energy, i.e. 38 ATP. | It releases less energy, i.e. 2 ATP. |
| (g) Overall equation: C6H1206 + 602 → 6C02 + 6H20 + Energy |
Overall equation: C6H1206 → 2C2H5 OH + 2C02 + Energy |
Question (A)
Respiration and combustion.
Answer:
| Respiration | Combustion |
| (a) It is a biochemical and stepwise process. | It is physiochemical and spontaneous process. |
| (b) It occurs inside the cells. | It is a non-cellular process. |
| (c) Energy is released in steps. | Large amount of energy is released at a time. |
| (d) No light is produced in respiration. | Light may be produced in combustion. |
| (e) It is controlled by enzymes. | It is not controlled by enzymes. |
| (f) A number of intermediates are produced. | No intermediates are produced. |
Distinguish between Glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
Answer:
| Glycolysis/EMP pathway | Krebs cycle/TCA cycle/ Citric acid cycle |
| 1. Glycolysis is common in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. | Krebs cycle occurs only in aerobic respiration. |
| 2. It takes place in the cytoplasm. | It takes place in the mitochondria. |
| 3. C02 is not released. | C02 is released. |
| 4. Total amount of energy produced = 8 ATP. | Total amount of energy produced = 24 ATP. |
| 5. It is linear pathway. | It is cyclic pathway. |
| 6. Pyruvic acid is the end product. | C02 and H2Q are the end products. |

Question (C)
Aerobic respiration and fermentation.
Answer:
| Aerobic respiration | Fermentation |
| 1. It takes place in higher organisms. | It takes place in both higher and lower organisms. |
| 2. It takes place in cytoplasm and mitochondria | It takes place in cytoplasm. |
| 3. It involves the participation of free molecular oxygen. | It does not involve participation of free molecular oxygen. |
| 4. It involves many steps – glycolysis, link reaction, Krebs cycle and ETS. | It involves only glycolysis, decarboxylation and reduction, (alcoholic fermentation) |
| 5. Oxidation of food is complete. | Oxidation of food is incomplete. |
| 6. It produces C02 and H20. | It produces either ethanol or lactic acid and C02 depending upon the type of fermentation. |
| 7. It releases more energy, i.e. 38 ATP. | It releases less energy, i.e. 2 ATP. |
Identify the cycle given below. Correct it and fill in the blanks and write description of it in your own
 Answer:
Answer:
Practical / Project:
Question 1.
Make Powerpoint Presentation on Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle and Conduct the group discussion on it in classroom.
[Note: Students are expected to perform above activity on their own.]
11th Biology Digest Chapter 13 Respiration and Energy Transfer Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
(i) Which nutrients are used for energy production?
Answer:
Nutrients like carbohydrates, fats and proteins are used for energy production.
(ii) Why do organisms take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide?
Answer:
a. At cellular level, organisms require energy to carry out different metabolic activities.
b. The energy is made available by oxidizing/breaking the food.
Therefore, oxygen is required by aerobic organisms for breaking the food and carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct of oxidation.

Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 152)
Why is glycolysis considered as biochemical proof of evolution?
Answer:
Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 152)
(i) What is role of Mg++, Zn++ in various steps of glycolysis?
Answer:
a. Mg++ and Zn++ are the cofactors that are tightly bound to enzymes and helps the enzymes to perform their functions.
b. They regulate the activity of the most important enzymes like Hexokinase, Phosphoffuctokinase, Triose phosphate dehydrogenase, Phosphoglycerate kinase, Enolase, Pyruvate kinase.
(ii) Why some reactions of glycolysis are reversible and some irreversible?
Answer:
Irreversible chemical reactions:
Some chemical reactions can occur in only one direction i.e. these reactions are irreversible reactions. The reactants can change to the products, but the products cannot change back to the reactants.
Reversible chemical reactions:

Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 152)
Why do athletes like sprinters have higher proportion of white muscle fibers?
Answer:
1. The white muscle fibres produce energy in a very short period of time that is required for fast and severe work. Thus, the energy becomes immediately available to the athletes.
2. On the other hand, the red muscle produce energy over a prolonged period of time, hence athletes have higher proportion of white muscle fibers.
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
Which steps are involved in aerobic respiration?
Answer:
It involves glycolysis, acetyl CoA formation (connecting link reaction), Krebs cycle, electron transfer chain reaction and terminal oxidation.
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
What is aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
For anaerobic respiration: Anaerobic respiration is the cellular respiration that does not involve the atmospheric oxygen. It is also called as fermentation. It involves glycolysis where the product of glycolysis i.e. pyruvate is converted to either lactic acid or ethanol and for aerobic respiration.
1. Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of free molecular oxygen during oxidation of glucose.
2. In this type of respiration, the glucose is completely oxidized to C02 and H20 with release of large amount of energy. It involves glycolysis, acetyl CoA formation (connecting link reaction), Krebs cycle, electron transfer chain reaction and terminal oxidation.
Use your brainpower (Textbook Page No. 157)
Do the plants breath like animals? If yes, how and why?
Answer:

Internet my friend (Textbook Page No. 155)
What is effect of carbon monoxide poisoning on cytochromes?
Answer:
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 151)
Which is most preferred nutrient among carbohydrate, protein and fat for energy production? Why?
Answer:
Internet my friend (Textbook Page No. 158)
Calculate the RQ for different respiratory substrates using appropriate formula.
Answer:
The RQ for different respiratory substrates are:
1. Carbohydrates (R.Q. is 1)
When carbohydrates are used as substrate, equal volumes of C02 and 02 are released and consumed respectively, thus its R.Q. is 1.
C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 → 6 C02 + 6H20
R.Q. = 6C02 / 602 = 1.0
2. Fats (R.Q. is less than 1)
Substrates like fats are poorer in oxygen than carbohydrates. Thus, more oxygen is utilized for its complete oxidation.
2(C51 H98 O6) + 145O2 → 102CO2 + 98H2O + Energy
R.Q. = C02 / 02 = 102 / 145 = 0.7
3. Protein respiration (R.Q. is less than 1)
