Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Textbook Solutions
Chapter 9 Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Choose correct option.
Question A.
Which of the following is not an allotrope of carbon ?
a. buckyball
b. diamond
c. graphite
d. emerald
Answer:
d. emerald
Question B.
………… is inorganic graphite.
a. borax
b. diborane
c. boron nitride
d. colemanite
Answer:
c. boron nitride
Question C.
Haber’s process is used for preparation of ………….
a. HNO3
b. NH3
c. NH2CONH2
d. NH4OH
Answer:
b. NH3
Question D.
Thallium shows different oxidation state because ……………
a. of inert pair effect
b. it is inner transition element
c. it is metal
d. of its high electronegativity
Answer:
a. of inert pair effect
Question E.
Which of the following shows most prominent inert pair effect ?
a. C
b. Si
c. Ge
d. Pb
Answer:
d. Pb

2. Identify the group 14 element that best fits each of the following description.
A. Non-metallic element
B. Form the most acidic oxide
C. They prefer +2 oxidation state.
D. Forms strong π bonds.
Answer:
i. Carbon (C)
ii. Carbon
iii. Tin (Sn) and lead (Pb)
iv. Carbon
3. Give reasons.
A. Ga3+ salts are better reducing agent while Tl3+ salts are better oxidising agent.
B. PbCl4 is less stable than PbCl2
Answer:
A. i. Both gallium (Ga) and thallium (Tl) belong to group 13.
ii. Ga is lighter element compared to thallium Tl. Therefore, its +3 oxidation state is stable. Thus, Ga+ loses two electrons and get oxidized to Ga3+. Hence, Ga+ salts are better reducing agent.
iii. Thallium is a heavy element. Therefore, due to the inert pair effect, Tl forms stable compounds in +1 oxidation state. Thus, Tl3+ salts get easily reduced to Tl1+ by accepting two electrons. Hence, Tl3+ salts are better oxidizing agent.
[Note: This question is modified so as to apply the appropriate textual concept.]
B. i. Pb has electronic configuration [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p2.
ii. Due to poor shielding of 6s2 electrons by inner d and f electrons, it is difficult to remove 6s2 electrons (inert pair).
iii. Thus, due to inert pair effect, +2 oxidation state is more stable than +4 oxidation state.
Hence, PbCl4 is less stable than PbCl2.

4. Give the formula of a compound in which carbon exhibit an oxidation state of
A. +4
B. +2
C. -4
Answer:
A. CCl4
B. CO
C. CH4
5. Explain the trend of the following in group 13 elements :
A. atomic radii
B. ionization enthalpy
C. electron affinity
Answer:
A. Atomic radii:
B. Ionization enthalpy:
C. Electron affinity:
a. Electron affinity shows irregular trend. It first increases from B to A1 and then decreases. The less electron affinity of boron is due to its smaller size. Adding an electron to the 2p orbital in boron leads to a greater repulsion than adding an electron to the larger 3p orbital of aluminium.
b. From Al to Tl, electron affinity decreases. This is because, nuclear charge increases but simultaneously the number of shells in the atoms also increases. As a result, the effective nuclear charge decreases down the group resulting in increased atomic size and thus, it becomes difficult to add an electron to a larger atom. The electron affinity of Ga and In is same.
Note: Electron affinity of group 13 elements:
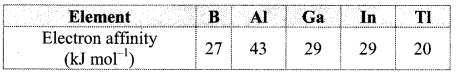
6. Answer the following
Question A.
What is hybridization of Al in AlCl3?
Answer:
Al is sp2 hybridized in AlCl3.
Question B.
Name a molecule having banana bond.
Answer:
Diborane (B2H6)

7. Draw the structure of the following
Question A.
Orthophosphoric acid
Answer:
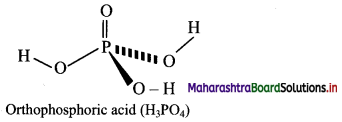
Question B.
Resonance structure of nitric acid
Answer:
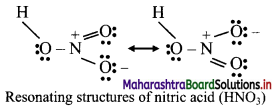
8. Find out the difference between
Question A.
Diamond and Graphite
Answer:
Diamond:
Graphite:
Question B.
White phosphorus and Red phosphorus
Answer:
White phosphorus:
Red phosphorus:

9. What are silicones? Where are they used?
Answer:
i. a. Silicones are organosilicon polymers having R2SiO (where, R = CH3 or C6H5 group) as a repeating unit held together by
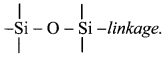
b. Since the empirical formula R2SiO (where R = CH3 or C6H5 group) is similar to that of ketones (R2CO), these compounds are named as silicones.
ii. Applications: They are used as
10. Explain the trend in oxidation state of elements from nitrogen to bismuth.
Answer:
11. Give the test that is used to detect borate radical is qualitative analysis.
Answer:
i. Borax when heated with ethyl alcohol and concentrated H2SO4, produces volatile vapours of triethyl borate, which bum with green edged flame.
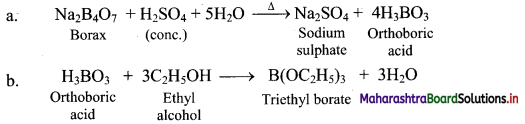
ii. The above reaction is Used as a test for the detection and removal of borate radical \(\left(\mathrm{BO}_{3}^{3-}\right)\) in qualitative analysis.

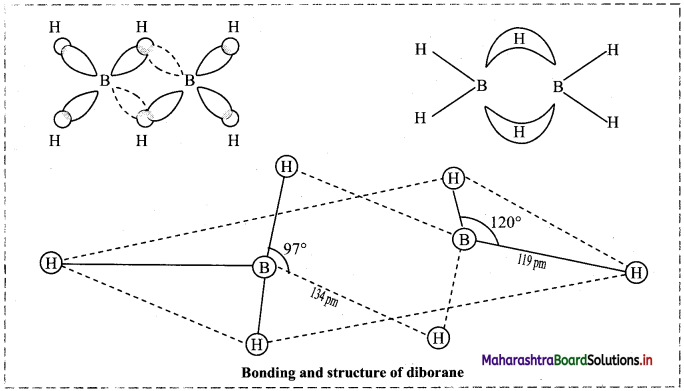
12. Explain structure and bonding of diborane.
Answer:
13. A compound is prepared from the mineral colemanite by boiling it with a solution of sodium carbonate. It is white crystalline solid and used for inorganic qualitative analysis.
a. Name the compound produced.
b. Write the reaction that explains its formation.
Answer:
a. Borax
b. Borax is obtained from its mineral colemanite by boiling it with a solution of sodium carbonate.
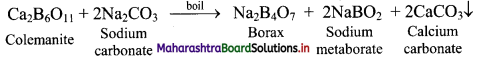
14. Ammonia is a good complexing agent. Explain.
Answer:
i. The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom facilitates complexation of ammonia with transition metal ions. Thus, ammonia is a good complexing agent as it forms complex by donating its lone pair of electrons.
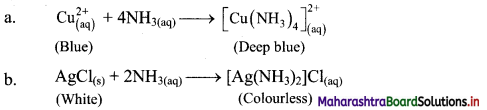
ii. This reaction is used for the detection of metal ions such as Cu2+ and Ag+.
15. State true or false. Correct the false statement.
A. The acidic nature of oxides of group 13 increases down the graph.
B. The tendency for catenation is much higher for C than for Si.
Answer:
A. False
The acidic nature of oxides of group 13 decreases down the group. It changes from acidic through amphoteric to basic.
B. True

16. Match the pairs from column A and B.
Answer:
i – d,
ii – c,
iii – b
17. Give the reactions supporting basic nature of ammonia.
Answer:
In the following reactions ammonia reacts with acids to form the corresponding ammonium salts which indicates basic nature of ammonia.
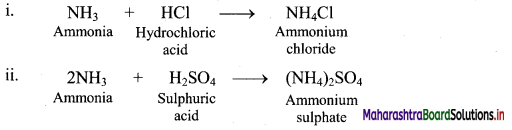
18. Shravani was performing inorganic qualitative analysis of a salt. To an aqueous solution of that salt, she added silver nitrate. When a white precipitate was formed. On adding ammonium hydroxide to this, she obtained a clear solution. Comment on her observations and write the chemical reactions involved.
Answer:
i. When silver nitrate (AgNO3) is added to an aqueous solution of salt sodium chloride (NaCl), a white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) is formed.
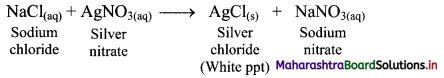
ii. On adding ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) to this, the white precipitate of silver chloride gets dissolved and thus, a clear solution is obtained.
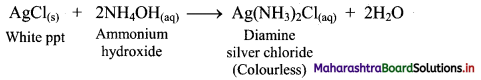

11th Chemistry Digest Chapter 9 Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15 Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 123)
Question 1.
If the valence shell electronic configuration of an element is 3s2 3p1, in which block of the periodic table is it placed?
Answer:
The element having valence shell electronic configuration 3s2 3p1 must be placed in the p-block of the periodic table as its last electron enters in p-subshell (3p).
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 127)
Question 1.
What is common between diamond and graphite?
Answer:
Both diamond and graphite are made up of carbon atoms as they are two allotropes of carbon.
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 129)
Question i.
Which element from the following pairs has higher ionization enthalpy?
B and TI, N and Bi
Answer:
Among B and Tl, boron has higher ionization enthalpy while, among N and Bi, nitrogen has higher ionization enthalpy.
Question ii.
Does boron form covalent compound or ionic?
Answer:
Yes, boron forms covalent compound.

Try this. (Textbook Page No. 131)
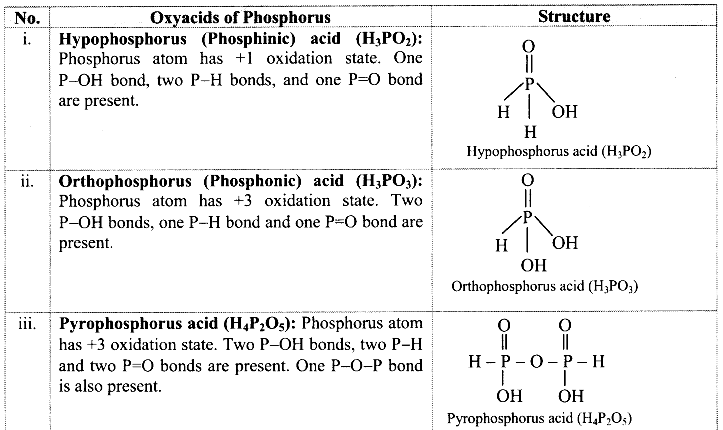
Question 1.
Find out the structural formulae of various oxyacids of phosphorus.
Answer:
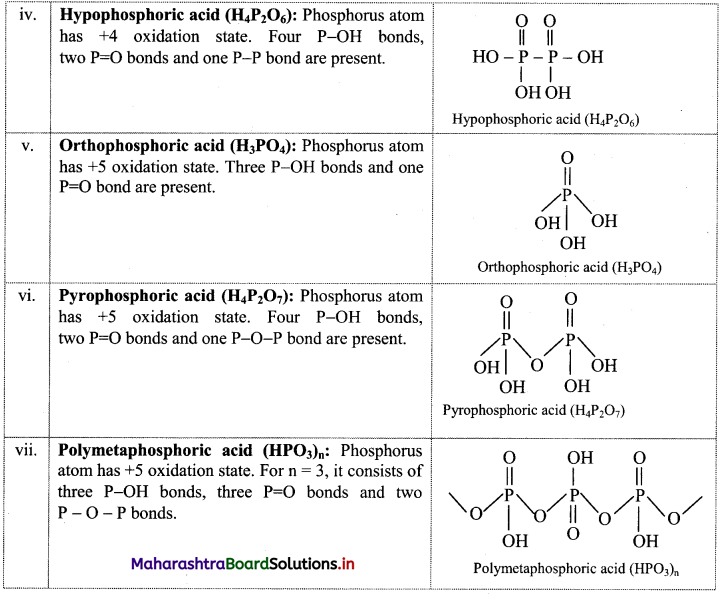
Chapter 9 Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Choose correct option.
Question A.
Which of the following is not an allotrope of carbon ?
a. buckyball
b. diamond
c. graphite
d. emerald
Answer:
d. emerald
Question B.
………… is inorganic graphite.
a. borax
b. diborane
c. boron nitride
d. colemanite
Answer:
c. boron nitride
Question C.
Haber’s process is used for preparation of ………….
a. HNO3
b. NH3
c. NH2CONH2
d. NH4OH
Answer:
b. NH3
Question D.
Thallium shows different oxidation state because ……………
a. of inert pair effect
b. it is inner transition element
c. it is metal
d. of its high electronegativity
Answer:
a. of inert pair effect
Question E.
Which of the following shows most prominent inert pair effect ?
a. C
b. Si
c. Ge
d. Pb
Answer:
d. Pb

2. Identify the group 14 element that best fits each of the following description.
A. Non-metallic element
B. Form the most acidic oxide
C. They prefer +2 oxidation state.
D. Forms strong π bonds.
Answer:
i. Carbon (C)
ii. Carbon
iii. Tin (Sn) and lead (Pb)
iv. Carbon
3. Give reasons.
A. Ga3+ salts are better reducing agent while Tl3+ salts are better oxidising agent.
B. PbCl4 is less stable than PbCl2
Answer:
A. i. Both gallium (Ga) and thallium (Tl) belong to group 13.
ii. Ga is lighter element compared to thallium Tl. Therefore, its +3 oxidation state is stable. Thus, Ga+ loses two electrons and get oxidized to Ga3+. Hence, Ga+ salts are better reducing agent.
iii. Thallium is a heavy element. Therefore, due to the inert pair effect, Tl forms stable compounds in +1 oxidation state. Thus, Tl3+ salts get easily reduced to Tl1+ by accepting two electrons. Hence, Tl3+ salts are better oxidizing agent.
[Note: This question is modified so as to apply the appropriate textual concept.]
B. i. Pb has electronic configuration [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p2.
ii. Due to poor shielding of 6s2 electrons by inner d and f electrons, it is difficult to remove 6s2 electrons (inert pair).
iii. Thus, due to inert pair effect, +2 oxidation state is more stable than +4 oxidation state.
Hence, PbCl4 is less stable than PbCl2.

4. Give the formula of a compound in which carbon exhibit an oxidation state of
A. +4
B. +2
C. -4
Answer:
A. CCl4
B. CO
C. CH4
5. Explain the trend of the following in group 13 elements :
A. atomic radii
B. ionization enthalpy
C. electron affinity
Answer:
A. Atomic radii:
B. Ionization enthalpy:
C. Electron affinity:
a. Electron affinity shows irregular trend. It first increases from B to A1 and then decreases. The less electron affinity of boron is due to its smaller size. Adding an electron to the 2p orbital in boron leads to a greater repulsion than adding an electron to the larger 3p orbital of aluminium.
b. From Al to Tl, electron affinity decreases. This is because, nuclear charge increases but simultaneously the number of shells in the atoms also increases. As a result, the effective nuclear charge decreases down the group resulting in increased atomic size and thus, it becomes difficult to add an electron to a larger atom. The electron affinity of Ga and In is same.
Note: Electron affinity of group 13 elements:

6. Answer the following
Question A.
What is hybridization of Al in AlCl3?
Answer:
Al is sp2 hybridized in AlCl3.
Question B.
Name a molecule having banana bond.
Answer:
Diborane (B2H6)

7. Draw the structure of the following
Question A.
Orthophosphoric acid
Answer:

Question B.
Resonance structure of nitric acid
Answer:

8. Find out the difference between
Question A.
Diamond and Graphite
Answer:
Diamond:
Graphite:
Question B.
White phosphorus and Red phosphorus
Answer:
White phosphorus:
Red phosphorus:

9. What are silicones? Where are they used?
Answer:
i. a. Silicones are organosilicon polymers having R2SiO (where, R = CH3 or C6H5 group) as a repeating unit held together by
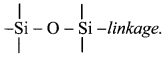
b. Since the empirical formula R2SiO (where R = CH3 or C6H5 group) is similar to that of ketones (R2CO), these compounds are named as silicones.
ii. Applications: They are used as
10. Explain the trend in oxidation state of elements from nitrogen to bismuth.
Answer:
11. Give the test that is used to detect borate radical is qualitative analysis.
Answer:
i. Borax when heated with ethyl alcohol and concentrated H2SO4, produces volatile vapours of triethyl borate, which bum with green edged flame.

ii. The above reaction is Used as a test for the detection and removal of borate radical \(\left(\mathrm{BO}_{3}^{3-}\right)\) in qualitative analysis.

12. Explain structure and bonding of diborane.
Answer:

13. A compound is prepared from the mineral colemanite by boiling it with a solution of sodium carbonate. It is white crystalline solid and used for inorganic qualitative analysis.
a. Name the compound produced.
b. Write the reaction that explains its formation.
Answer:
a. Borax
b. Borax is obtained from its mineral colemanite by boiling it with a solution of sodium carbonate.
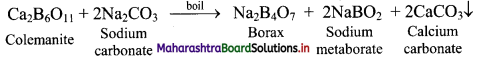
14. Ammonia is a good complexing agent. Explain.
Answer:
i. The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom facilitates complexation of ammonia with transition metal ions. Thus, ammonia is a good complexing agent as it forms complex by donating its lone pair of electrons.

ii. This reaction is used for the detection of metal ions such as Cu2+ and Ag+.
15. State true or false. Correct the false statement.
A. The acidic nature of oxides of group 13 increases down the graph.
B. The tendency for catenation is much higher for C than for Si.
Answer:
A. False
The acidic nature of oxides of group 13 decreases down the group. It changes from acidic through amphoteric to basic.
B. True

16. Match the pairs from column A and B.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| i. | BCl3 | a. | Angular molecule |
| ii. | SiO2 | b. | Linear covalent molecule |
| iii. | CO2 | c. | Tetrahedral molecule |
| d. | Planar trigonal molecule |
i – d,
ii – c,
iii – b
17. Give the reactions supporting basic nature of ammonia.
Answer:
In the following reactions ammonia reacts with acids to form the corresponding ammonium salts which indicates basic nature of ammonia.

18. Shravani was performing inorganic qualitative analysis of a salt. To an aqueous solution of that salt, she added silver nitrate. When a white precipitate was formed. On adding ammonium hydroxide to this, she obtained a clear solution. Comment on her observations and write the chemical reactions involved.
Answer:
i. When silver nitrate (AgNO3) is added to an aqueous solution of salt sodium chloride (NaCl), a white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) is formed.

ii. On adding ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) to this, the white precipitate of silver chloride gets dissolved and thus, a clear solution is obtained.


11th Chemistry Digest Chapter 9 Elements of Group 13, 14 and 15 Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 123)
Question 1.
If the valence shell electronic configuration of an element is 3s2 3p1, in which block of the periodic table is it placed?
Answer:
The element having valence shell electronic configuration 3s2 3p1 must be placed in the p-block of the periodic table as its last electron enters in p-subshell (3p).
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 127)
Question 1.
What is common between diamond and graphite?
Answer:
Both diamond and graphite are made up of carbon atoms as they are two allotropes of carbon.
Can you recall? (Textbook Page No. 129)
Question i.
Which element from the following pairs has higher ionization enthalpy?
B and TI, N and Bi
Answer:
Among B and Tl, boron has higher ionization enthalpy while, among N and Bi, nitrogen has higher ionization enthalpy.
Question ii.
Does boron form covalent compound or ionic?
Answer:
Yes, boron forms covalent compound.

Try this. (Textbook Page No. 131)
Question 1.
Find out the structural formulae of various oxyacids of phosphorus.
Answer:

