Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Solutions
Chapter 2 Weathering and Mass Wasting Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Complete the Chain.
Question 1.
Answer:

2. Identify the correct correlation.
A : Assertion
R : Reasoning
Question 1.
A – In areas of high rainfall, slides are very common.
R – Types of mass wasting movements are dependent on a region’s climate.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
A – Gravity is a major factor in mass wasting.
R – Gravity pulls all things down to the earth’s surface.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 3.
A – Freeze and thaw weathering is common in desert areas.
R – Water gets into cracks and breaks the rocks.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 4.
A – Surface water helps solifluction.
R – Water table is responsible for the same.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(a) Only A is correct.
3. Identify the correct group.
Question 1.
Answer:
C

4. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
Temperature is the main factor behind granular weathering.
Answer:
Temperature is the main factor behind granular weathering because-
Question 2.
Human is an agent of weathering.
Answer:
Human is an agent of weathering because-
Question 3.
Slope is a major factor in mass wasting.
Answer:
Slope is a major factor in mass wasting because-
Question 4.
Oxidation changes the size and colour of the rocks.
Answer:
Oxidation changes the size and colour of the rocks because-

Question 5.
Effect of mass movement will be greater along the western slope of the Sahyadri’s than the eastern slope.
Answer:
Effect of the mass movement will be greater along the western slope of the Sahyadri’s than the eastern slope because-
5. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
Gravity and Solifluction
Answer:
Gravity:
Solifluction:
Question 2.
Role of water in mass wasting
Answer:
Question 3.
Exfoliation
Answer:

Question 4.
Weathering and homogeneity in rocks
Answer:
Question 5.
Carbonation
Answer:
6. Draw a neat and labelled diagram for
Question 1.
Freeze and thaw weathering
Answer:
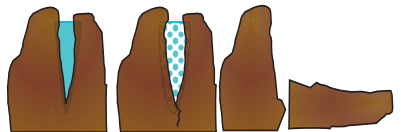
Question 2.
Block disintegration
Answer:


Question 3.
Biological Weathering
Answer:

7. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Explain with examples the process of weathering happening in Konkan.
Answer:

Question 2.
Explain the correlation between Himalayas and mass movements. Give examples wherever necessary.
Answer:
11th Geography Digest Chapter 2 Weathering and Mass Wasting Intext Questions and Answers
Let’s recall (Textbook Page No. 15)
1. Study the diagram in fig 2.1 and answer the following questions.
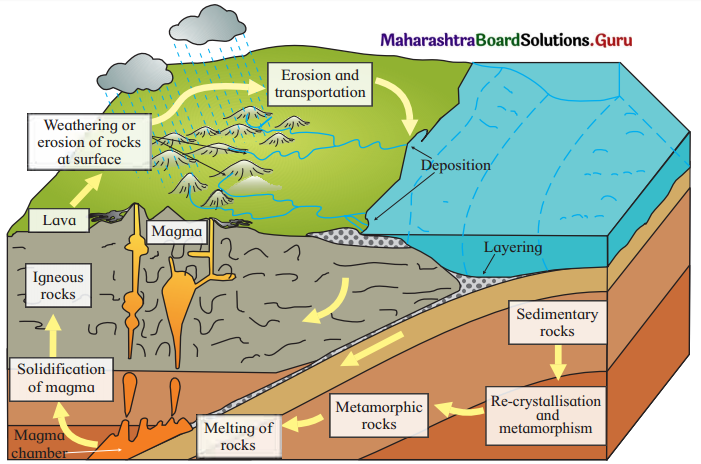
Question 1.
Identify the types of rocks shown in the diagram.
Answer:
Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks are shown in the diagram.
Question 2.
Arrange the rocks according to their chronology of origin.
Answer:
Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.
Question 3.
Explain how sedimentary rocks are formed.
Answer:
Sedimentary rocks are formed from layering upon layering of all the organic (dead remains of plants and animals) and in organic (sand, silt, clay, gravel, etc.) material in a depression or on low lying area. If there are cementing material like limestone, hardening and compaction takes place, then sedimentary rocks are formed.

Question 4.
Think of all the factors which may break the rocks into smaller pieces.
Answer:
Heat, pressure, water, wind, animals, plants etc., can break rocks into smaller pieces.
Question 5.
Which type of rock will break easily as compared to others? Why?
Answer:
Think about it.
Question 1.
In which regions will freeze-thaw weathering not be effective? (Textbook Page No. 17)
Answer:
Freeze-thaw weathering will not be effective on the cold polar regions as the soil cover and rocks are very little on the polar areas and moreover, there is snow everywhere.
Question 2.
Besides climatic factors, rock type and structure, can you think of some more factors that affect weathering? (Textbook Page No. 19)
Answer:
Plants, animals, micro-organisms, humans are some more factors that affect weathering.
Question 3.
Can tectonic forces be responsible for mass movement? (Textbook Page No. 25)
Answer:

Question 4.
There is a shift of materials in mass movement as well as in transportation from one place to the other. So, why can’t both not be treated as one and the same? (Textbook Page No. 25)
Answer:
Mass movement is caused by abrupt movement and freefall of loosened rock particles because of gravity and friction falling towards the surface, whereas transportation is carrying of rock materials with the help of agents of erosion such as water, wind, air, ice, etc. Thus, they are not same.
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Can animals and plants also influence weathering? Will that be physical or chemical weathering? Which type of weathering does stone quarrying cause? (Textbook Page No. 19)
Answer:
Yes, burrowing animals widen the fissures in the rocks. Rocks become weak and disintegrate.
The roots of the trees and other plants penetrate in the soil, they grow in size, exert pressure on rocks, widen cracks in the rocks and rocks break. Many microscopic organisms such as algae, lichens, bacteria, moss etc produce chemicals and they break down the outer layer of the rock. These chemicals are responsible for physical and chemical weathering of rocks. The stone quarrying causes the anthropogenic weathering.
2. A region is having an annual mean temperature of 5° C and an annual rainfall of 1000 mm. Can you comment upon the weathering and the type with the help of following questions? (Textbook Page No. 20)
Question 1.
Which type of weathering will be dominant here?
Answer:
Physical weathering will be dominant here.
Question 2.
Where will such a region be found?
Answer:
Such a region will be found in permafrost conditions, alpine and periglacial region.

Question 1.
Complete the table by using the words: intense, moderate, slight and very slight or no weathering. (Textbook Page No. 20)
Answer:
Rate of Physical Weathering:
Rate of Chemical Weathering:
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 21)
1. See the diagram given in fig 2.10 and answer the following questions.
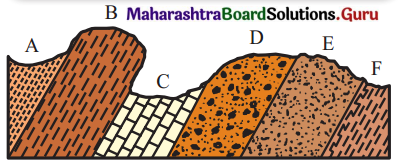
Question 1.
Which rock layer has experienced the most weathering?
Answer:
Rock layer C has experienced the most weathering.
Question 2.
Which rock layer has experienced the least weathering?
Answer:
Rock layer B has experienced the least weathering.

Question 3.
What could be the reason behind difference in weathering?
Answer:
Rock C has lot of fractures and joints so it got weathered easily.
Rock B might have been a hard rock, more resistant, so weathering process is slow.
2. The satellite images given in fig. 2.11 A and B belong to the same location but different timeline. Study the images and answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 21)
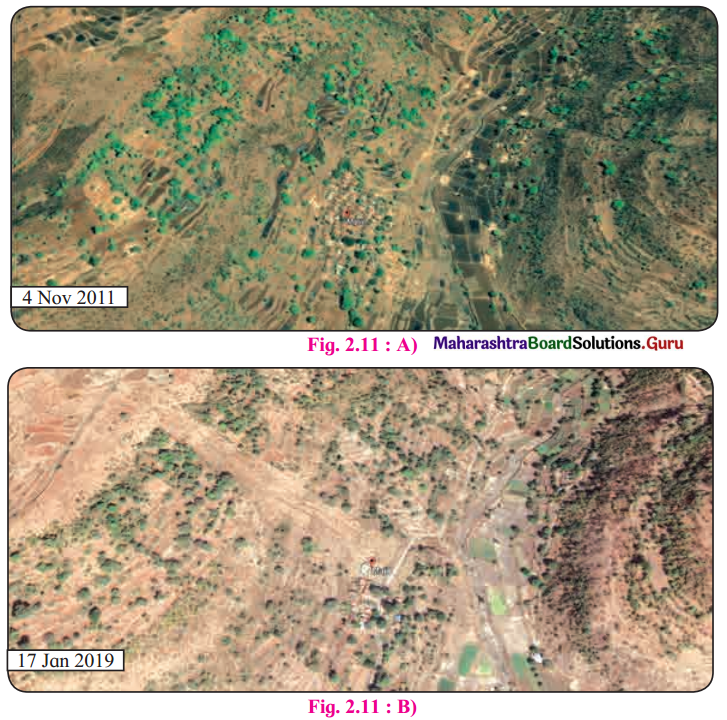
Question 1.
Compare the images and tell what differences do you find in these images?
Answer:
Image 2.11 (A) shows maximum area under vegetation. Image 2.11 (B) shows development in form of settlements and transportation routes.
Question 2.
In 2019, what does the patch of land going from north-west to south-east signify? Why was it not there in 2011 image?
Answer:
The sweeping portion from north-west to south-east is visible in satellite image of 2019. This is because the village is located at the foothills. The rain and slope were responsible for the mudslide. Heavy rainfall and absence of vegetation aggravated the situation. In 2011, vegetation was thick but in 2019 deforestation has been done extensively for farming practices.
Question 3.
To what extent is the climate of a place responsible for this disaster?
Answer:
Climate plays an important role for the disaster. Heavy rainfall makes soil to move from the surface of the mountain towards the foothills.
Question 4.
Which other factors are responsible for the disaster?
Answer:
Deforestation and absence of vegetation are responsible for this.

Give it a try.
1. Study the following schematic diagram. It shows the relationship between speed of material and moisture content. Read the index, and answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 23)
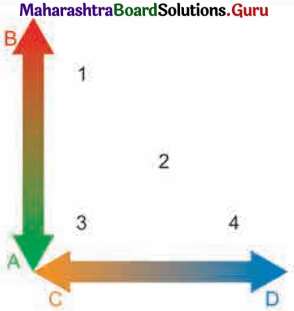
(A) Fast (B) Slow (C) Dry (D) Wet
(1) Creep (2) Slide (3) Fall (4) Flow
Question i.
What will happen when the weather conditions are dry?
Answer:
There will not be moisture content hence speed of material will be low.
Question ii.
When will a flow occur?
Answer:
Flow will occur when the moisture content as well as speed of material will be high.
Question iii.
When will a creep occur?
Answer:
Creep will occur when speed of material will be slow.
Question iv.
Now can you enumerate the factors which affect mass wasting?
Answer:
Factors such as gravity, slope of land, climate of region, amount of water, material and structure of the rock affect mass wasting.
Question 2.
On the basis of given points, differentiate between weathering and erosion. (Textbook Page No. 25)
Answer:
Table
Think a little. (Textbook Page No. 24)
Think of the reason why landslides should be more frequent in foothill zone of the Himalayas and Western Ghats region. Why do landslides not occur in Marathwada in Maharashtra or Maidan area in Karnataka?
Answer:
Himalayas are one of the youngest fold mountains of the world. They are formed due to convergent movement of the Indian plate and erosion plate. They are still rising in height. These tectonic movements cause frequent earthquakes in the region resulting into landslides whereas western Ghats lie in the stable Deccan shield less prone to landslides.
Himalayas are greater in height than the western Ghats. The slopes are comparatively steep and hence landslides are common in Himalayas whereas, the western Ghats are much lesser in height than the Himalayas hence less prone to landslides as compared to Himalayas.
The perennial rivers in Himalayas carry lots of sediments during rainfall and due to melting of glaciers in the summer thus leading to landslides, whereas, in Western Ghats many rivers are non-perennial and hence less amount of silt and debris in carried as compared to Himalayan rivers. Thus, there is reduction in the chances of landslides, only during the rainy season, landslides occur in Western Ghats region.

Try this. (Textbook Page No. 24)
Question 1.
Different types of materials flow down the slope. Types of mass wasting depend on their speed. Observe the pictures given in figure 2.12. Match the explanation given below with the diagrams. Identify them as slow or rapid movements.
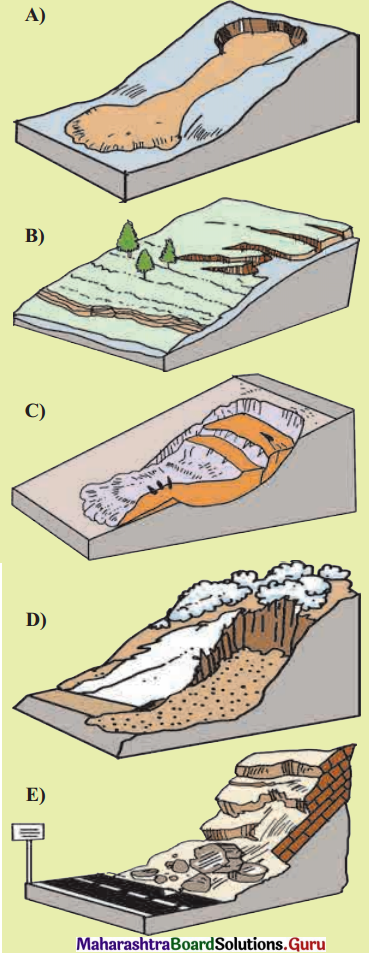
Answer:
A – Earth flow – Rapid or slow movement
B – Creep – Slowest movement
C – Land slide – Rapid movement
D – Solifluction – Slow movement
E – Rock fall – Rapid movement

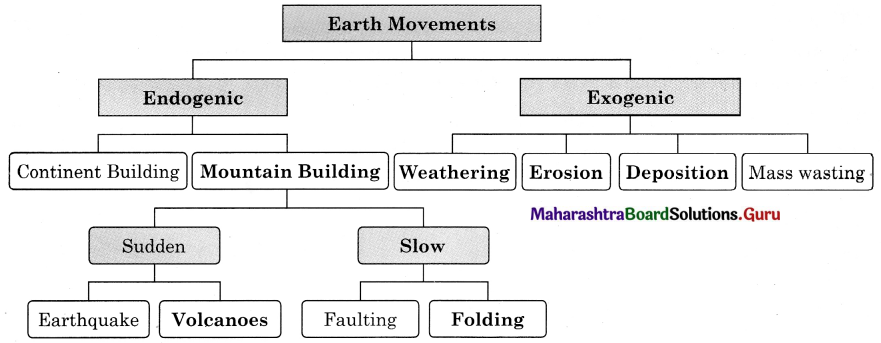
Question 2.
Complete the following flow chart. (Textbook Page No. 25)
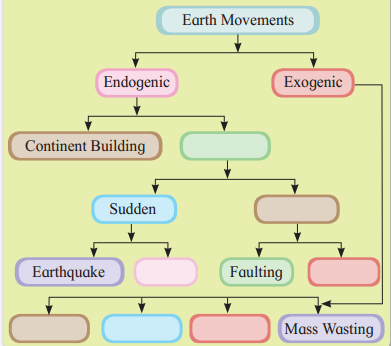
Answer:
Chapter 2 Weathering and Mass Wasting Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Complete the Chain.
Question 1.
| Rock type | Name of the rock | Dominant type of weathering |
| (1) Igneous | (1) Dolomite | (1) Physical Weathering |
| (2) Sedimentary | (2) Slate | (2) Chemical Weathering |
| (3) Metamorphic | (3) Basalt | |
| (4) Limestone | ||
| (5) Granite |
| Rock type | Name of the rock | Dominant type of weathering |
| (1) Igneous | (1) Basalt Granite | (1) Physical Weathering Physical Weathering |
| (2) Sedimentary | (2) Dolomite Limestone | (2) Chemical Weathering Chemical Weathering |
| (3) Metamorphic | (3) Slate | (3) Physical Weathering |

2. Identify the correct correlation.
A : Assertion
R : Reasoning
Question 1.
A – In areas of high rainfall, slides are very common.
R – Types of mass wasting movements are dependent on a region’s climate.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
A – Gravity is a major factor in mass wasting.
R – Gravity pulls all things down to the earth’s surface.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 3.
A – Freeze and thaw weathering is common in desert areas.
R – Water gets into cracks and breaks the rocks.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 4.
A – Surface water helps solifluction.
R – Water table is responsible for the same.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(a) Only A is correct.
3. Identify the correct group.
Question 1.
| A | B | C | D |
| (1) Oxidation | (1) Solution | (1) Fall | (1) Pressure |
| (2) Carbonation | (2) Salt weathering | (2) Creep | (2) Temperature |
| (3) Freeze thaw weathering | (3) Oxidation | (3) Slide | (3) Slope |
| (4) Shattering | (4) Carbonation | (4) Flow | (4) Rainfall |
C

4. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
Temperature is the main factor behind granular weathering.
Answer:
Temperature is the main factor behind granular weathering because-
Question 2.
Human is an agent of weathering.
Answer:
Human is an agent of weathering because-
Question 3.
Slope is a major factor in mass wasting.
Answer:
Slope is a major factor in mass wasting because-
Question 4.
Oxidation changes the size and colour of the rocks.
Answer:
Oxidation changes the size and colour of the rocks because-

Question 5.
Effect of mass movement will be greater along the western slope of the Sahyadri’s than the eastern slope.
Answer:
Effect of the mass movement will be greater along the western slope of the Sahyadri’s than the eastern slope because-
5. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
Gravity and Solifluction
Answer:
Gravity:
Solifluction:
Question 2.
Role of water in mass wasting
Answer:
Question 3.
Exfoliation
Answer:

Question 4.
Weathering and homogeneity in rocks
Answer:
Question 5.
Carbonation
Answer:
6. Draw a neat and labelled diagram for
Question 1.
Freeze and thaw weathering
Answer:

Question 2.
Block disintegration
Answer:


Question 3.
Biological Weathering
Answer:

7. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Explain with examples the process of weathering happening in Konkan.
Answer:

Question 2.
Explain the correlation between Himalayas and mass movements. Give examples wherever necessary.
Answer:
11th Geography Digest Chapter 2 Weathering and Mass Wasting Intext Questions and Answers
Let’s recall (Textbook Page No. 15)
1. Study the diagram in fig 2.1 and answer the following questions.

Question 1.
Identify the types of rocks shown in the diagram.
Answer:
Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks are shown in the diagram.
Question 2.
Arrange the rocks according to their chronology of origin.
Answer:
Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.
Question 3.
Explain how sedimentary rocks are formed.
Answer:
Sedimentary rocks are formed from layering upon layering of all the organic (dead remains of plants and animals) and in organic (sand, silt, clay, gravel, etc.) material in a depression or on low lying area. If there are cementing material like limestone, hardening and compaction takes place, then sedimentary rocks are formed.

Question 4.
Think of all the factors which may break the rocks into smaller pieces.
Answer:
Heat, pressure, water, wind, animals, plants etc., can break rocks into smaller pieces.
Question 5.
Which type of rock will break easily as compared to others? Why?
Answer:
Think about it.
Question 1.
In which regions will freeze-thaw weathering not be effective? (Textbook Page No. 17)
Answer:
Freeze-thaw weathering will not be effective on the cold polar regions as the soil cover and rocks are very little on the polar areas and moreover, there is snow everywhere.
Question 2.
Besides climatic factors, rock type and structure, can you think of some more factors that affect weathering? (Textbook Page No. 19)
Answer:
Plants, animals, micro-organisms, humans are some more factors that affect weathering.
Question 3.
Can tectonic forces be responsible for mass movement? (Textbook Page No. 25)
Answer:

Question 4.
There is a shift of materials in mass movement as well as in transportation from one place to the other. So, why can’t both not be treated as one and the same? (Textbook Page No. 25)
Answer:
Mass movement is caused by abrupt movement and freefall of loosened rock particles because of gravity and friction falling towards the surface, whereas transportation is carrying of rock materials with the help of agents of erosion such as water, wind, air, ice, etc. Thus, they are not same.
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Can animals and plants also influence weathering? Will that be physical or chemical weathering? Which type of weathering does stone quarrying cause? (Textbook Page No. 19)
Answer:
Yes, burrowing animals widen the fissures in the rocks. Rocks become weak and disintegrate.
The roots of the trees and other plants penetrate in the soil, they grow in size, exert pressure on rocks, widen cracks in the rocks and rocks break. Many microscopic organisms such as algae, lichens, bacteria, moss etc produce chemicals and they break down the outer layer of the rock. These chemicals are responsible for physical and chemical weathering of rocks. The stone quarrying causes the anthropogenic weathering.
2. A region is having an annual mean temperature of 5° C and an annual rainfall of 1000 mm. Can you comment upon the weathering and the type with the help of following questions? (Textbook Page No. 20)
Question 1.
Which type of weathering will be dominant here?
Answer:
Physical weathering will be dominant here.
Question 2.
Where will such a region be found?
Answer:
Such a region will be found in permafrost conditions, alpine and periglacial region.

Question 1.
Complete the table by using the words: intense, moderate, slight and very slight or no weathering. (Textbook Page No. 20)
Answer:
Rate of Physical Weathering:
| High rainfall | Moderate rainfall | Low rainfall | |
| High temperature | Intense | Moderate | Intense |
| Moderate temperature | Intense | Moderate | Slight |
| Low temperature | Moderate | Slight | No weathering |
| High rainfall | Moderate rainfall | Low rainfall | |
| High temperature | Intense | Moderate | Moderate |
| Moderate temperature | Intense | Moderate | Slight |
| Low temperature | Moderate | Slight | Slight |
1. See the diagram given in fig 2.10 and answer the following questions.

Question 1.
Which rock layer has experienced the most weathering?
Answer:
Rock layer C has experienced the most weathering.
Question 2.
Which rock layer has experienced the least weathering?
Answer:
Rock layer B has experienced the least weathering.

Question 3.
What could be the reason behind difference in weathering?
Answer:
Rock C has lot of fractures and joints so it got weathered easily.
Rock B might have been a hard rock, more resistant, so weathering process is slow.
2. The satellite images given in fig. 2.11 A and B belong to the same location but different timeline. Study the images and answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 21)

Question 1.
Compare the images and tell what differences do you find in these images?
Answer:
Image 2.11 (A) shows maximum area under vegetation. Image 2.11 (B) shows development in form of settlements and transportation routes.
Question 2.
In 2019, what does the patch of land going from north-west to south-east signify? Why was it not there in 2011 image?
Answer:
The sweeping portion from north-west to south-east is visible in satellite image of 2019. This is because the village is located at the foothills. The rain and slope were responsible for the mudslide. Heavy rainfall and absence of vegetation aggravated the situation. In 2011, vegetation was thick but in 2019 deforestation has been done extensively for farming practices.
Question 3.
To what extent is the climate of a place responsible for this disaster?
Answer:
Climate plays an important role for the disaster. Heavy rainfall makes soil to move from the surface of the mountain towards the foothills.
Question 4.
Which other factors are responsible for the disaster?
Answer:
Deforestation and absence of vegetation are responsible for this.

Give it a try.
1. Study the following schematic diagram. It shows the relationship between speed of material and moisture content. Read the index, and answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 23)

(A) Fast (B) Slow (C) Dry (D) Wet
(1) Creep (2) Slide (3) Fall (4) Flow
Question i.
What will happen when the weather conditions are dry?
Answer:
There will not be moisture content hence speed of material will be low.
Question ii.
When will a flow occur?
Answer:
Flow will occur when the moisture content as well as speed of material will be high.
Question iii.
When will a creep occur?
Answer:
Creep will occur when speed of material will be slow.
Question iv.
Now can you enumerate the factors which affect mass wasting?
Answer:
Factors such as gravity, slope of land, climate of region, amount of water, material and structure of the rock affect mass wasting.
Question 2.
On the basis of given points, differentiate between weathering and erosion. (Textbook Page No. 25)
Answer:
Table
Think a little. (Textbook Page No. 24)
Think of the reason why landslides should be more frequent in foothill zone of the Himalayas and Western Ghats region. Why do landslides not occur in Marathwada in Maharashtra or Maidan area in Karnataka?
Answer:
Himalayas are one of the youngest fold mountains of the world. They are formed due to convergent movement of the Indian plate and erosion plate. They are still rising in height. These tectonic movements cause frequent earthquakes in the region resulting into landslides whereas western Ghats lie in the stable Deccan shield less prone to landslides.
Himalayas are greater in height than the western Ghats. The slopes are comparatively steep and hence landslides are common in Himalayas whereas, the western Ghats are much lesser in height than the Himalayas hence less prone to landslides as compared to Himalayas.
The perennial rivers in Himalayas carry lots of sediments during rainfall and due to melting of glaciers in the summer thus leading to landslides, whereas, in Western Ghats many rivers are non-perennial and hence less amount of silt and debris in carried as compared to Himalayan rivers. Thus, there is reduction in the chances of landslides, only during the rainy season, landslides occur in Western Ghats region.

Try this. (Textbook Page No. 24)
Question 1.
Different types of materials flow down the slope. Types of mass wasting depend on their speed. Observe the pictures given in figure 2.12. Match the explanation given below with the diagrams. Identify them as slow or rapid movements.

Answer:
A – Earth flow – Rapid or slow movement
B – Creep – Slowest movement
C – Land slide – Rapid movement
D – Solifluction – Slow movement
E – Rock fall – Rapid movement

Question 2.
Complete the following flow chart. (Textbook Page No. 25)

Answer:
