Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Geography Solutions
Chapter 3 Agents of Erosion Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Compete the Chain.
Question 1.
Answer:
2. Choose the correct option by identifying the correct correlation in the sentences.
Question 1.
Water or snow enters the cracks in the rocks and makes it weak. When the glacier passes on these rocks, it pulls the rocks at the bottom along with it. This process is called
(a) Plucking
(b) Abrasion
(c) Attrition
(d) Transportation
Answer:
(d) Transportation

Question 2.
Sometimes, the river starts erosion upstream. This happens when the head stream gets a lot of water in the early stages of river’s flow.
(a) Downcutting
(b) Headward erosion
(c) Lateral erosion
(d) Vertical erosion
Answer:
(b) Headward erosion
Question 3.
Soft rock erodes beneath the hard rock due to sea waves. This results into landforms which further develop as sea arches. The landform is
(a) Sea cave
(b) Sea stack
(c) Sea cliff
(d) Wave cut platform
Answer:
(a) Sea cave
Question 4.
This landform develops due to depositional work of wind. The windward slope of this landform is gentle.
(a) Loess plains
(b) Barchans
(c) Seif
(d) Sand hills
Answer:
(b) Barchans
Question 5.
River, glacier, wind, sea waves and groundwater are the agents of erosion. Following work in the correct order is responsible to form various landforms.
(a) Disintegration, picking up, transportation, weathering
(b) Picking up, disintegration, deposition, weathering
(c) Deposition, transportation, picking up, disintegration
(d) Disintegration, picking up, transportation, deposition
Answer:
(d) Disintegration, picking up, transportation, deposition
3. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
The Eastern coast of India have deltas formed by the rivers but the Western coast has estuaries.
Answer:
The Eastern coast of India have deltas formed by the rivers but the Western coast has estuaries because-

Question 2.
There is direct relationship between the velocity of the agents and process of deposition.
Answer:
There is direct relationship between the velocity of the agents and the process of deposition because-
Question 3.
Compared to all the agents, sea waves work ceaselessly.
Answer:
Compared to all the agents, sea waves work ceaselessly because-
Question 4.
One finds many sheep rocks, horns, Aretes and hanging valleys in the Himalayas.
Answer:
One finds many sheep rocks, horns, Aretes and hanging valleys in the Himalayas because-
1. In Himalayas work of glacier is more predominant due to snow covered peaks and slopes. Sheep rock, horns, Aretes and hanging valleys are formed by glacier. Like other agents of erosion, glaciers too carry out erosion, transportation and deposition.
2. In the Himalayas, glaciers remove rock particles from the surface on which they flow by abrasion which leads to formation of sheep rocks.
3. Ice movement, accompanied by weathering and mass wasting has steepened the walls at the head of the glacier. This has deepened into armchair-shaped depression called cirque.
4. In Himalayas, two of more cirques have developed and the area between them is narrowed and formed arete and further the headward erosion of the glaciers has eroded the summit leading to the formation of typical peak called horn.
5. The Himalayan glaciers too have tributaries like rivers. The rate of erosion is different. The main valley gets eroded faster and becomes deeper than the tributary glacial valley. These appear to be hanging when seen from the main valley. Thus, hanging valleys are formed.

Question 5.
Karst landforms are seen concealed under the surface of the earth.
Answer:
Karst landforms are seen concealed under the surface of the earth because-
Question 6.
Snowline decides the limit of glacier work as an agent of erosion.
Answer:
Snowline decides the limit of glacier work as an agent of erosion because-
4. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
Attrition
Answer:
Question 2.
The work of rivers in hilly areas and human activities :
Answer:
Gorges: River from its source, when it starts flowing the process of erosion starts. In mountainous areas, rivers flow at a higher speed due to steep slope. As a result, bed gets eroded more than banks and gorges are formed with steep banks and narrow beds. Such gorges have also become famous tourist places. For example, Gorge of Narmada river at Jabalpur.
In ‘V’ shaped valleys of river, terraced farming is practiced on valley slopes.
In hilly areas, the river has speed, slope and hence downcutting is on a lower scale. Thus, agriculture, agroforestry, animal husbandry and forestry are the major human occupations in these regions.
Waterfalls: Water flowing over a hilly region comes down a cliff, forming alternate bands of eroded soft and hard rocks, such features are called waterfalls. These waterfalls become a site for tourist attraction. For example, Jog falls on Sharavati river, Chuliya falls on Chambal river and Venna falls in Mahabaleshwar. Hotel industries also developed along these features.

Question 3.
Conditions necessary for work of wind
Answer:
Wind is a significant agent of erosion in the deserts. Following conditions are necessary for wind to become effective:
5. Differentiate between.
Question 1.
Attrition and Abrasion.
Answer:
Question 2.
U shaped valley and V shaped valley.
Answer:

Question 3.
Stalactite and Stalagmite.
Answer:
Question 4.
Tributaries and Distributaries.
Answer:
6. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the landforms formed by different agents through the process of abrasion.
Answer:
Abrasion involves the scratching and polishing of the surface or bedrock by the particles which are moving onto it. Let us study different landforms formed by different agents of erosion through the process of abrasion.
Work of Seas Waves:
Work of Wind:
(i) Ventifacts:
Abrasion carves the windward side of rock into smooth sloping surface. These rocks are called ventifacts.
(ii) Mushroom rocks
(iii) Yardang:
Work of Glaciers
(i) Roche moutonnee:
They are bedrock hills that are smoothly rounded on the upper side by abrasion and plucking on the lower side.
(ii) Cirque
(iii) Arete
(iv) Horn
(v) U-Shaped Valleys
When glaciers move ahead, they erode the sides as well as the bottom of the valleys they flow through. This makes the valley broad at the bottom, forming a ‘U’. This is called a U-shaped valley.

Question 2.
Explain how the depositional work done by River Ganga has been beneficial to human activities.
Answer:
The River Ganga and its tributaries have deposited load of sediments in the northern Ganga region. Features formed are:
Alluvial Plain Region : The River Ganga and its tributaries bring loads of sediments – organic sediments like dead remains of plants and animals, skin, hide, bones etc., and inorganic sediments like sand, silt, clay, gravel, etc., and deposits at the foothills of the Himalayan family, Northern Ganga Plain region. It is a fertile land and agriculture is the major human occupation. Along with agriculture river transportation and fishing is also done on a large scale. Fertile plains are in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana.
Delta: Ganga-Brahmaputra delta, world’s largest delta has been formed at the mouth of the River Ganga. This delta is known as Sundarbans and is located in West Bengal. It is one of the most fertile regions in the world. Most delta is composed of alluvial soil. Thus, agriculture is the occupation followed in this region too.
Question 3.
Which agents of erosion can you see on the cover page of the textbook? Which landforms can you see there? Write the process of formation of any one.
Answer:
Every bend is made more and more pronounced by dashing of water on outer bank which gets eroded while inner banks have deposition. In due course of time they develop into circular loops, they are called meanders.
7. Draw neat and labelled diagrams for
Question 1.
Deflation
Answer:

Question 2.
Wave-cut platform
Answer:
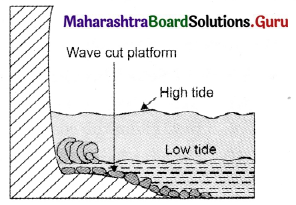

Question 3.
Mushroom rocks
Answer:

11th Geography Digest Chapter 3 Agents of Erosion Intext Questions and Answers
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 27)
1. The names of many places may have some relation with the landforms located there. The names of few of them are given below as example. You are expected to find out the particular landforms to which they are associated. Find about them and try to locate them on a map using an atlas. Make a list of similar examples from India.
Answer:
2. Look at the figure below and answer the questions. (Textbook Page No. 32)
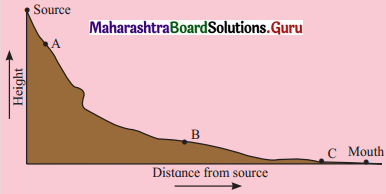
Question 1.
What features are formed in the upper course of the river? What processes will play an important role?
Answer:
Features formed in the upper course of the river are V-shaped valleys, gorges and canyons, potholes, waterfalls and rapids.
Processes responsible for the formation of these landforms are – downcutting, drilling.
Question 2.
Can you mark the location where waterfall may form?
Answer:
Waterfall may form at location ‘A’

Question 3.
Why is there a change in slope from A to B? How will it influence the flow of the river?
Answer:
There will be a change in slope from A to B when river enters the plains at the foothills of a mountain. The flow of the river decreases, the velocity reduces abruptly.
Question 4.
Which human activities can be conducted in the region around A and B?
Answer:
Around region A terraced farming can be practised. Around region B there is rich with alluvium brough down by the rivers, the plain is extensive and useful for agriculture. As the river widens around the source B, fishing and transportation is also found.
Question 5.
In which area will the process of deposition overtake erosion?
Answer:
Deposition will be found at B and C.
Question 6.
Alluvial fans and deltas are both features formed due to deposition but at different locations. Identify their regions of formation and reason behind their different locations.
Answer:
Alluvial fans will be formed at source ‘B’ at the foothills of the mountains, as there is change in slope and the velocity of the river reduces abruptly. Now the river is unable to carry heavy load. A delta will be formed at the mouth of the river. In this region, which is an extensively flat region, and where the sediments supply is high but velocity is low. So, the river deposits the sediments and branches out to meet ocean or sea.
3. Look at the figure and identify landforms at A, B, C, D, E, F, G. (Textbook Page No. 34)
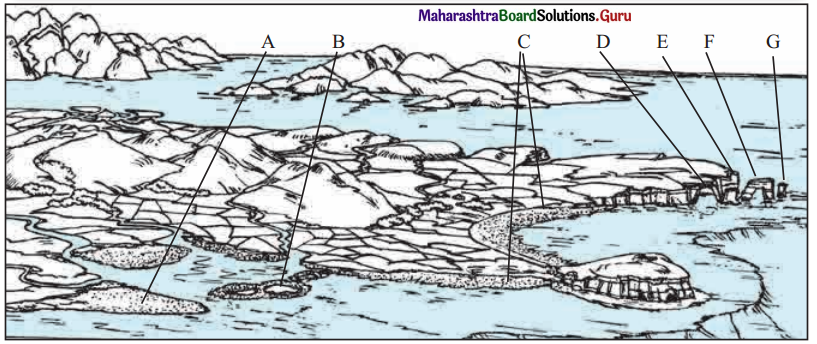
Answer:
A – Headland
B – Lagoon
C – Beach
D – Sea Cave
E – Sea Cliff
F – Sea Arch
G – Sea Stack
Let’s recall. (Textbook Page No. 30)
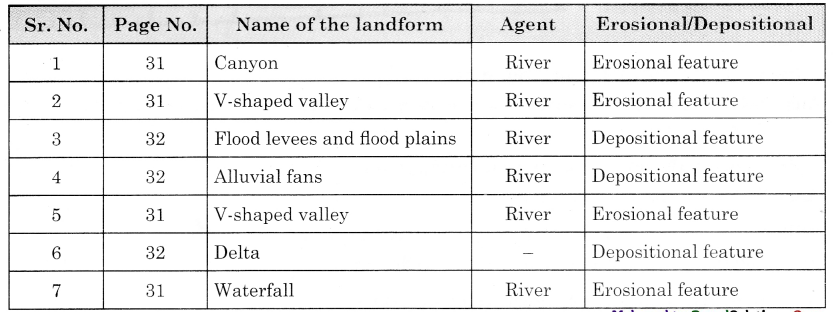
You have already learnt about various landforms formed by the agents of erosion in Class IX. Identify the landforms given in class IX textbook from page no. 30 to 38. Identify the agent which is responsible for their formation. Also, state whether they are erosional or depositional landforms. Complete the table accordingly.
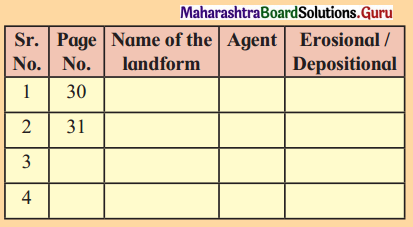
Answer:
Think about it. (Textbook Page No. 30)
Have you ever been to a river and seen its bed? Discuss in the class about your observation about the river, its banks, its bed and its velocity.
Answer:
[Students will discuss their experiences with teachers.]

Find out! (Textbook Page No. 31)
Find out famous examples of gorges and canyons.
Answer:
Following are the famous examples of gorges and canyons of the world.
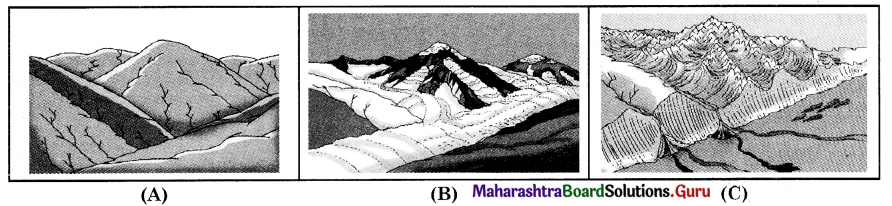
1. Study figure given below and answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 38)
Question 1.
Which rocks are mainly found here?
Answer:
Soluble rock like limestone, a sedimentary rock composed of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) are found.
Question 2.
Identify the spot where stream disappears.
Answer:
Steam will disappear below the sink hole.
Question 3.
Which major erosional process works in this area?
Answer:
Solution is the major erosional process in this area.
Question 4.
Identify the landforms formed by deposition.
Answer:
Stalactite, Stalagmite, columns or pillars are the landforms formed by deposition.
Question 5.
Why do depositional landforms not form on the surface in areas of Karst terrain?
Answer:
In Karst terrain groundwater dissolves minerals like calcium carbonate present in the rocks. The dripping water leaves behind a deposit of calcium carbonate. The water saturated with calcium carbonate dripping on the floor of a cave deposits calcium carbonate on the floor. Thus, depositional landforms do not form on the surface in the areas of Karst terrain.

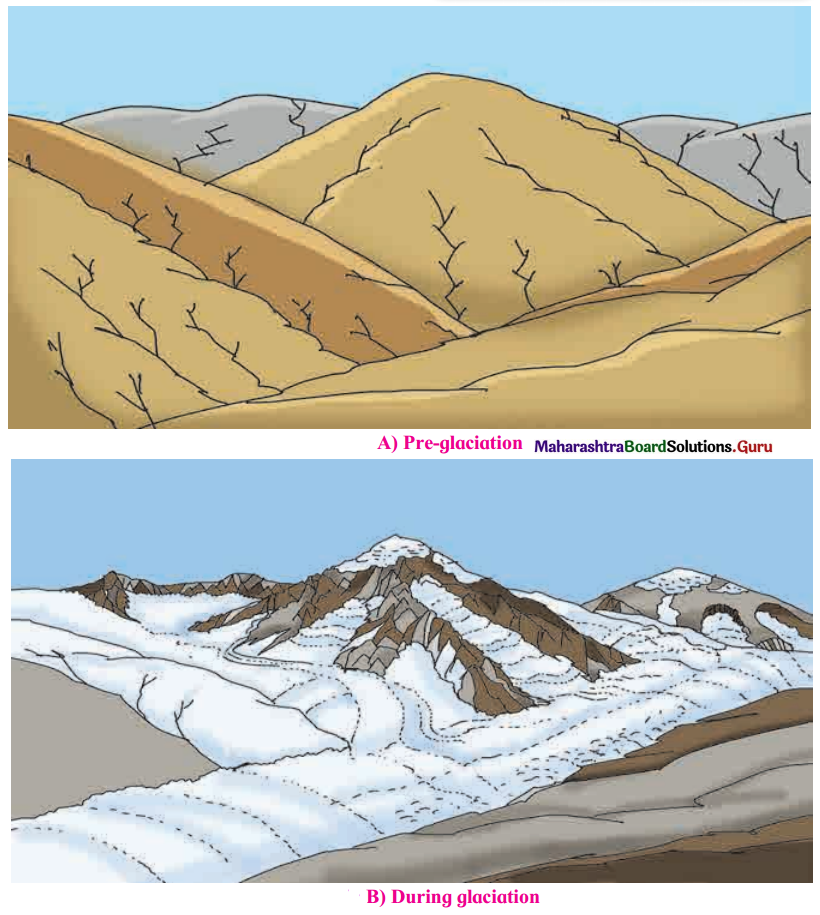
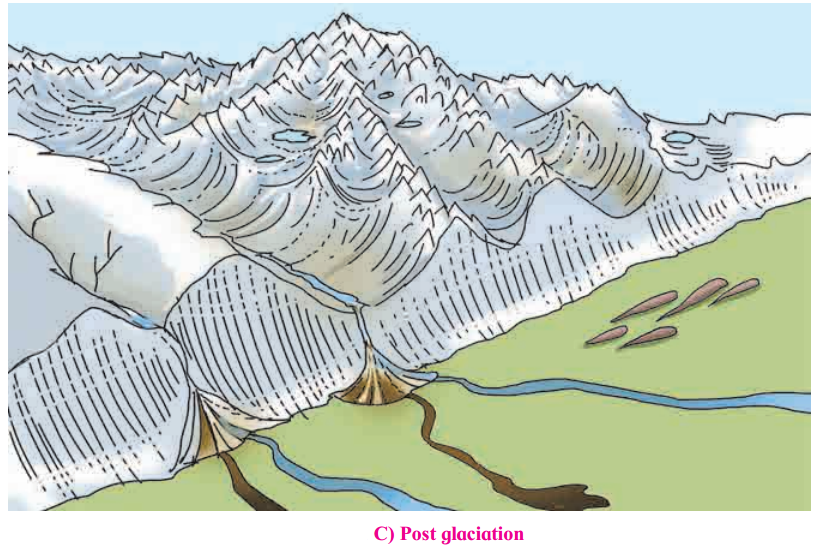
2. See the figure give below A, B, C. Answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 40)
Img 8
Question 1.
What difference do you find in the three figures?
Answer:
Fig A shows the regions before glacier formed.
Fig B showed the regions covered by snow during glaciation.
Fig C shows different erosional and depositional features formed by glaciers after glaciation period.
Question 2.
Identify the landforms formed due to erosion by glaciers.
Answer:
Cirques, horn, U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys are formed due to erosion by glaciers.
Question 3.
Where can U-Shaped valleys be formed?
Answer:
U- Shaped valley is formed in the pre-existing valley.
Question 4.
In which region will deposition occur?
Answer:
Deposition starts generally along the side and front of ice.
Question 5.
Identify the landforms formed by deposition by glaciers.
Answer:
Drumlins, eskers, moraines are the depositional features formed by glaciers.
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No. 41)
In which diagram of the three will you find end moraines? See fig. 3.5 A, B, C.
Answer:
We will find end moraines in Fig. C
Chapter 3 Agents of Erosion Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Compete the Chain.
Question 1.
| Agent | Erosional/Depositional features | Places / Regions |
| (1) River | (1) Caves | (1) China |
| (2) Wind | (2) Beach | (2) Jog |
| (3) Sea waves | (3) Waterfalls | (3) Meghalaya |
| (4) Glaciers | (4) Loess | (4) Diveagar |
| (5) Ground water | (5) Matterhorn | (5) Swiss Alps |
| Agent | Erosional/Depositional features | Places / Regions |
| (1) River | (1) Waterfalls | (1) Jog |
| (2) Wind | (2) Loess | (2) China |
| (3) Sea waves | (3) Beach | (3) Diveagar |
| (4) Glaciers | (4) Matterhorn | (4) Swiss Alps |
| (5) Ground water | (5) Caves | (5) Meghalaya |
Question 1.
Water or snow enters the cracks in the rocks and makes it weak. When the glacier passes on these rocks, it pulls the rocks at the bottom along with it. This process is called
(a) Plucking
(b) Abrasion
(c) Attrition
(d) Transportation
Answer:
(d) Transportation

Question 2.
Sometimes, the river starts erosion upstream. This happens when the head stream gets a lot of water in the early stages of river’s flow.
(a) Downcutting
(b) Headward erosion
(c) Lateral erosion
(d) Vertical erosion
Answer:
(b) Headward erosion
Question 3.
Soft rock erodes beneath the hard rock due to sea waves. This results into landforms which further develop as sea arches. The landform is
(a) Sea cave
(b) Sea stack
(c) Sea cliff
(d) Wave cut platform
Answer:
(a) Sea cave
Question 4.
This landform develops due to depositional work of wind. The windward slope of this landform is gentle.
(a) Loess plains
(b) Barchans
(c) Seif
(d) Sand hills
Answer:
(b) Barchans
Question 5.
River, glacier, wind, sea waves and groundwater are the agents of erosion. Following work in the correct order is responsible to form various landforms.
(a) Disintegration, picking up, transportation, weathering
(b) Picking up, disintegration, deposition, weathering
(c) Deposition, transportation, picking up, disintegration
(d) Disintegration, picking up, transportation, deposition
Answer:
(d) Disintegration, picking up, transportation, deposition
3. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
The Eastern coast of India have deltas formed by the rivers but the Western coast has estuaries.
Answer:
The Eastern coast of India have deltas formed by the rivers but the Western coast has estuaries because-

Question 2.
There is direct relationship between the velocity of the agents and process of deposition.
Answer:
There is direct relationship between the velocity of the agents and the process of deposition because-
Question 3.
Compared to all the agents, sea waves work ceaselessly.
Answer:
Compared to all the agents, sea waves work ceaselessly because-
Question 4.
One finds many sheep rocks, horns, Aretes and hanging valleys in the Himalayas.
Answer:
One finds many sheep rocks, horns, Aretes and hanging valleys in the Himalayas because-
1. In Himalayas work of glacier is more predominant due to snow covered peaks and slopes. Sheep rock, horns, Aretes and hanging valleys are formed by glacier. Like other agents of erosion, glaciers too carry out erosion, transportation and deposition.
2. In the Himalayas, glaciers remove rock particles from the surface on which they flow by abrasion which leads to formation of sheep rocks.
3. Ice movement, accompanied by weathering and mass wasting has steepened the walls at the head of the glacier. This has deepened into armchair-shaped depression called cirque.
4. In Himalayas, two of more cirques have developed and the area between them is narrowed and formed arete and further the headward erosion of the glaciers has eroded the summit leading to the formation of typical peak called horn.
5. The Himalayan glaciers too have tributaries like rivers. The rate of erosion is different. The main valley gets eroded faster and becomes deeper than the tributary glacial valley. These appear to be hanging when seen from the main valley. Thus, hanging valleys are formed.

Question 5.
Karst landforms are seen concealed under the surface of the earth.
Answer:
Karst landforms are seen concealed under the surface of the earth because-
Question 6.
Snowline decides the limit of glacier work as an agent of erosion.
Answer:
Snowline decides the limit of glacier work as an agent of erosion because-
4. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
Attrition
Answer:
Question 2.
The work of rivers in hilly areas and human activities :
Answer:
Gorges: River from its source, when it starts flowing the process of erosion starts. In mountainous areas, rivers flow at a higher speed due to steep slope. As a result, bed gets eroded more than banks and gorges are formed with steep banks and narrow beds. Such gorges have also become famous tourist places. For example, Gorge of Narmada river at Jabalpur.
In ‘V’ shaped valleys of river, terraced farming is practiced on valley slopes.
In hilly areas, the river has speed, slope and hence downcutting is on a lower scale. Thus, agriculture, agroforestry, animal husbandry and forestry are the major human occupations in these regions.
Waterfalls: Water flowing over a hilly region comes down a cliff, forming alternate bands of eroded soft and hard rocks, such features are called waterfalls. These waterfalls become a site for tourist attraction. For example, Jog falls on Sharavati river, Chuliya falls on Chambal river and Venna falls in Mahabaleshwar. Hotel industries also developed along these features.

Question 3.
Conditions necessary for work of wind
Answer:
Wind is a significant agent of erosion in the deserts. Following conditions are necessary for wind to become effective:
5. Differentiate between.
Question 1.
Attrition and Abrasion.
Answer:
| Attrition | Abrasion |
| (i) Attrition is the process of erosion in which rocks and pebbles bump into each other. | (i) Abrasion is the process of erosion which involves scratching and polishing of the surface of bedrock. |
| (ii) In attrition, the rocks and pebbles break up into smaller fragments. | (ii) In abrasion, the rock particles rub against and wear away the surface. |
| (iii) The eroded bedrock on surface have a smooth side. | (iii) The pebbles or rocks become smooth and rounded. |
| (iv) Attrition relates to the material that moves. | (iv) Abrasion affects the surface along which the material moves. |
U shaped valley and V shaped valley.
Answer:
| U shaped valley | V shaped valley |
| (i) It is an erosional feature formed by glaciers as an agent of erosion. | (i) It is an erosional feature formed by river as an agent of erosion. |
| (ii) The glacier moves through pre-existing valley to form U-shaped valleys. | (ii) The river carves out its own valleys. |
| (iii) Due to lateral erosion the valley becomes broad at the bottom. | (iii) Due to vertical downcutting, the valley deepens. |

Question 3.
Stalactite and Stalagmite.
Answer:
| Stalactite | Stalagmite |
| (i) Water saturated with calcium carbonate drips onto the floor from the ceiling. This dripping water dries and builds massive structures. These structures growing from the ceiling are called stalactites. | (i) Water saturated with calcium carbonate drips onto the floor from the ceiling. This dripping water deposited on the floor dries forming structures are called stalagmite. |
Tributaries and Distributaries.
Answer:
| Tributaries | Distributaries |
| (i) When a number of small rivers join the main river, those are called tributaries. | (i) When the main river breaks up into smaller streams, those the called distributaries. |
| (ii) It may originate from glaciers, lakes or springs. | (ii) It is formed from the main river. |
| (iii) Generally, it does not change its course. | (iii) It diverts from the main river in the delta region. |
| (iv) Tributaries add water to the main river. | (iv) Distributaries (take away) divert water from the main river. |
| (v) River Yamuna is a tributary of river Ganga. | (v) River Hooghly is the distributary of River Ganga. |
Question 1.
Explain the landforms formed by different agents through the process of abrasion.
Answer:
Abrasion involves the scratching and polishing of the surface or bedrock by the particles which are moving onto it. Let us study different landforms formed by different agents of erosion through the process of abrasion.
Work of Seas Waves:
Work of Wind:
(i) Ventifacts:
Abrasion carves the windward side of rock into smooth sloping surface. These rocks are called ventifacts.
(ii) Mushroom rocks
(iii) Yardang:
Work of Glaciers
(i) Roche moutonnee:
They are bedrock hills that are smoothly rounded on the upper side by abrasion and plucking on the lower side.
(ii) Cirque
(iii) Arete
(iv) Horn
(v) U-Shaped Valleys
When glaciers move ahead, they erode the sides as well as the bottom of the valleys they flow through. This makes the valley broad at the bottom, forming a ‘U’. This is called a U-shaped valley.

Question 2.
Explain how the depositional work done by River Ganga has been beneficial to human activities.
Answer:
The River Ganga and its tributaries have deposited load of sediments in the northern Ganga region. Features formed are:
Alluvial Plain Region : The River Ganga and its tributaries bring loads of sediments – organic sediments like dead remains of plants and animals, skin, hide, bones etc., and inorganic sediments like sand, silt, clay, gravel, etc., and deposits at the foothills of the Himalayan family, Northern Ganga Plain region. It is a fertile land and agriculture is the major human occupation. Along with agriculture river transportation and fishing is also done on a large scale. Fertile plains are in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab and Haryana.
Delta: Ganga-Brahmaputra delta, world’s largest delta has been formed at the mouth of the River Ganga. This delta is known as Sundarbans and is located in West Bengal. It is one of the most fertile regions in the world. Most delta is composed of alluvial soil. Thus, agriculture is the occupation followed in this region too.
Question 3.
Which agents of erosion can you see on the cover page of the textbook? Which landforms can you see there? Write the process of formation of any one.
Answer:
Every bend is made more and more pronounced by dashing of water on outer bank which gets eroded while inner banks have deposition. In due course of time they develop into circular loops, they are called meanders.
7. Draw neat and labelled diagrams for
Question 1.
Deflation
Answer:

Question 2.
Wave-cut platform
Answer:


Question 3.
Mushroom rocks
Answer:

11th Geography Digest Chapter 3 Agents of Erosion Intext Questions and Answers
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 27)
1. The names of many places may have some relation with the landforms located there. The names of few of them are given below as example. You are expected to find out the particular landforms to which they are associated. Find about them and try to locate them on a map using an atlas. Make a list of similar examples from India.
| Name of the place | Landform associated with the name | Location |
| Revdanda | Sand bar | Raigad, Maharashtra |
| Ganpati Pule | Beach | Ratnagiri, Maharashtra |
| Pravara Sangam | Confluence of rivers | Ahmednagar Maharashtra |
| Name of the place | Landform associated with the name | Location |
| Sundarbans | Delta | West Bengal |
| Triveni Sangam | Confluence of Ganga, Yamuna and Saraswati | Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh |
| Chilika lake | Lagoon | Orrisa |
| Calangute | Beach | Goa |

Question 1.
What features are formed in the upper course of the river? What processes will play an important role?
Answer:
Features formed in the upper course of the river are V-shaped valleys, gorges and canyons, potholes, waterfalls and rapids.
Processes responsible for the formation of these landforms are – downcutting, drilling.
Question 2.
Can you mark the location where waterfall may form?
Answer:
Waterfall may form at location ‘A’

Question 3.
Why is there a change in slope from A to B? How will it influence the flow of the river?
Answer:
There will be a change in slope from A to B when river enters the plains at the foothills of a mountain. The flow of the river decreases, the velocity reduces abruptly.
Question 4.
Which human activities can be conducted in the region around A and B?
Answer:
Around region A terraced farming can be practised. Around region B there is rich with alluvium brough down by the rivers, the plain is extensive and useful for agriculture. As the river widens around the source B, fishing and transportation is also found.
Question 5.
In which area will the process of deposition overtake erosion?
Answer:
Deposition will be found at B and C.
Question 6.
Alluvial fans and deltas are both features formed due to deposition but at different locations. Identify their regions of formation and reason behind their different locations.
Answer:
Alluvial fans will be formed at source ‘B’ at the foothills of the mountains, as there is change in slope and the velocity of the river reduces abruptly. Now the river is unable to carry heavy load. A delta will be formed at the mouth of the river. In this region, which is an extensively flat region, and where the sediments supply is high but velocity is low. So, the river deposits the sediments and branches out to meet ocean or sea.
3. Look at the figure and identify landforms at A, B, C, D, E, F, G. (Textbook Page No. 34)

Answer:
A – Headland
B – Lagoon
C – Beach
D – Sea Cave
E – Sea Cliff
F – Sea Arch
G – Sea Stack
Let’s recall. (Textbook Page No. 30)
You have already learnt about various landforms formed by the agents of erosion in Class IX. Identify the landforms given in class IX textbook from page no. 30 to 38. Identify the agent which is responsible for their formation. Also, state whether they are erosional or depositional landforms. Complete the table accordingly.

Answer:

Think about it. (Textbook Page No. 30)
Have you ever been to a river and seen its bed? Discuss in the class about your observation about the river, its banks, its bed and its velocity.
Answer:
[Students will discuss their experiences with teachers.]

Find out! (Textbook Page No. 31)
Find out famous examples of gorges and canyons.
Answer:
Following are the famous examples of gorges and canyons of the world.
1. Study figure given below and answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 38)

Question 1.
Which rocks are mainly found here?
Answer:
Soluble rock like limestone, a sedimentary rock composed of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) are found.
Question 2.
Identify the spot where stream disappears.
Answer:
Steam will disappear below the sink hole.
Question 3.
Which major erosional process works in this area?
Answer:
Solution is the major erosional process in this area.
Question 4.
Identify the landforms formed by deposition.
Answer:
Stalactite, Stalagmite, columns or pillars are the landforms formed by deposition.
Question 5.
Why do depositional landforms not form on the surface in areas of Karst terrain?
Answer:
In Karst terrain groundwater dissolves minerals like calcium carbonate present in the rocks. The dripping water leaves behind a deposit of calcium carbonate. The water saturated with calcium carbonate dripping on the floor of a cave deposits calcium carbonate on the floor. Thus, depositional landforms do not form on the surface in the areas of Karst terrain.

2. See the figure give below A, B, C. Answer the following questions. (Textbook Page No. 40)
Img 8
Question 1.
What difference do you find in the three figures?
Answer:
Fig A shows the regions before glacier formed.
Fig B showed the regions covered by snow during glaciation.
Fig C shows different erosional and depositional features formed by glaciers after glaciation period.
Question 2.
Identify the landforms formed due to erosion by glaciers.
Answer:
Cirques, horn, U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys are formed due to erosion by glaciers.
Question 3.
Where can U-Shaped valleys be formed?
Answer:
U- Shaped valley is formed in the pre-existing valley.
Question 4.
In which region will deposition occur?
Answer:
Deposition starts generally along the side and front of ice.
Question 5.
Identify the landforms formed by deposition by glaciers.
Answer:
Drumlins, eskers, moraines are the depositional features formed by glaciers.
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No. 41)
In which diagram of the three will you find end moraines? See fig. 3.5 A, B, C.


Answer:
We will find end moraines in Fig. C