Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Political Science Solutions
Chapter 8 Development Administration Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. State the appropriate concept for the given statement.
Question 1.
State that promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens.
Answer:
Welfare State

Question 2.
Unnecessary delays in administrative work are called.
Answer:
Red Tape
2. Complete the concept maps.
Question 1.
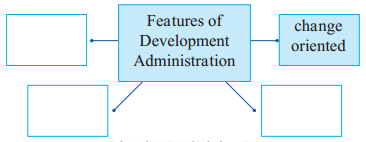
Answer:
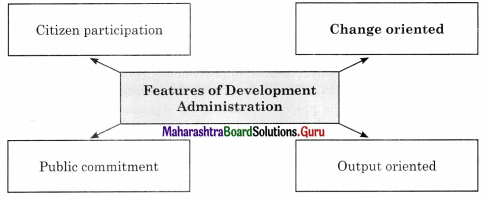
3. State whether the following statements are true or false with reasons.
Question 1.
Change and growth-oriented approaches are called Development Administration.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Question 2.
In post-independent India, the government deliberately invested in the public sector.
Answer:
This statement is True.

Question 3.
The 73rd amendment act gave constitutional status to municipalities.
Answer:
This statement is False.
4. Explain the co-relation between the following.
Question 1.
Planning Commission and NITI Aayog (Traditional public administration and development administration).
Answer:
Development is a complex term that means improvement, growth, or progress. When public administration studies ‘government in action for development’ it becomes development administration. According to Edward Weidner,” development administration is “the process of guiding an organisation toward the achievement of progressive political, economic and social objectives that are authoritatively determined in one manner or the other”.
An approach to have innovative planning towards growth is called development administration. The need for this was felt due to limitations in the traditional approach to public administration, which covered areas such as
The new approach to public administration and public policy focuses on socio-economic development, political modernization, and adaptation of new technologies in administration.
Development administration has two important aspects viz.
5. Answer the following.
Question 1.
Discuss any 4 areas of study in traditional public administration.
Answer:
The main areas of study in traditional public administration include:

Question 2.
Write in brief about NITI Aayog.
Answer:
NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India). After Independence, the Planning Commission was the apex planning body. India adopted Five Year Plans which identified short-term and long-term goals of development in areas such as agriculture, irrigation, industrialization, infrastructure, social security, etc. In 1991, the New Economic Policy focused on economic liberalization.
The Planning Commission has now been replaced by the NITI Aayog (established on 1st January 2015). The Prime Minister is the ex-officio chairman of NITI Aayog. Since India has moved from centralized planning to decentralized planning, this body proposes grassroots level planning from village and district levels to be harmonized with state-level planning and finally with national planning.
NITI Aayog has Governing Council comprising the Chief Ministers of all 29 states and of Delhi and Puducherry and Lt. Governors of Union Territories. As of 2019 Vice-Chairman is Rajiv Kumar and CEO is Amitabh Kant.
6. Express your opinion of the following.
Question 1.
Citizen participation is necessary in development administration.
Answer:
According to Edward Weidner, development administration is “The process of guiding an organisation toward the achievement of progressive political, economic and social objectives that are authoritatively determined in one manner or the other”.
An approach to have innovative planning towards growth is called Development Administration. The need for this was felt due to limitations in the traditional approach to public administration.
The new approach to public administration and public policy focuses on socio-economic development, political modernization, and adaptation of new technologies in administration.

Development Administration has two important aspects viz.
If the process of development is cut off from the grassroots then it eventually fails to materialize the objectives it has set. This necessitates peoples’ participation in the process of planning, implementation, and eventual evaluation.
In a diverse society like India people’s participation is necessary. In India, the needs, requirements, and choices of people may vary vastly according to region. The Indian government had introduced a Community Development Programme in 1952 followed by National Extension Service in 1953. The focus was to promote development in the rural and remote areas. The experience of these programmes helped the government to focus on rural India. The purpose of the participation of the rural and urban citizens was sought through the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts.
Chapter 8 Development Administration Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. State the appropriate concept for the given statement.
Question 1.
State that promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens.
Answer:
Welfare State

Question 2.
Unnecessary delays in administrative work are called.
Answer:
Red Tape
2. Complete the concept maps.
Question 1.

Answer:

3. State whether the following statements are true or false with reasons.
Question 1.
Change and growth-oriented approaches are called Development Administration.
Answer:
This statement is True.
Question 2.
In post-independent India, the government deliberately invested in the public sector.
Answer:
This statement is True.

Question 3.
The 73rd amendment act gave constitutional status to municipalities.
Answer:
This statement is False.
4. Explain the co-relation between the following.
Question 1.
Planning Commission and NITI Aayog (Traditional public administration and development administration).
Answer:
Development is a complex term that means improvement, growth, or progress. When public administration studies ‘government in action for development’ it becomes development administration. According to Edward Weidner,” development administration is “the process of guiding an organisation toward the achievement of progressive political, economic and social objectives that are authoritatively determined in one manner or the other”.
An approach to have innovative planning towards growth is called development administration. The need for this was felt due to limitations in the traditional approach to public administration, which covered areas such as
The new approach to public administration and public policy focuses on socio-economic development, political modernization, and adaptation of new technologies in administration.
Development administration has two important aspects viz.
5. Answer the following.
Question 1.
Discuss any 4 areas of study in traditional public administration.
Answer:
The main areas of study in traditional public administration include:

Question 2.
Write in brief about NITI Aayog.
Answer:
NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India). After Independence, the Planning Commission was the apex planning body. India adopted Five Year Plans which identified short-term and long-term goals of development in areas such as agriculture, irrigation, industrialization, infrastructure, social security, etc. In 1991, the New Economic Policy focused on economic liberalization.
The Planning Commission has now been replaced by the NITI Aayog (established on 1st January 2015). The Prime Minister is the ex-officio chairman of NITI Aayog. Since India has moved from centralized planning to decentralized planning, this body proposes grassroots level planning from village and district levels to be harmonized with state-level planning and finally with national planning.
NITI Aayog has Governing Council comprising the Chief Ministers of all 29 states and of Delhi and Puducherry and Lt. Governors of Union Territories. As of 2019 Vice-Chairman is Rajiv Kumar and CEO is Amitabh Kant.
6. Express your opinion of the following.
Question 1.
Citizen participation is necessary in development administration.
Answer:
According to Edward Weidner, development administration is “The process of guiding an organisation toward the achievement of progressive political, economic and social objectives that are authoritatively determined in one manner or the other”.
An approach to have innovative planning towards growth is called Development Administration. The need for this was felt due to limitations in the traditional approach to public administration.
The new approach to public administration and public policy focuses on socio-economic development, political modernization, and adaptation of new technologies in administration.

Development Administration has two important aspects viz.
If the process of development is cut off from the grassroots then it eventually fails to materialize the objectives it has set. This necessitates peoples’ participation in the process of planning, implementation, and eventual evaluation.
In a diverse society like India people’s participation is necessary. In India, the needs, requirements, and choices of people may vary vastly according to region. The Indian government had introduced a Community Development Programme in 1952 followed by National Extension Service in 1953. The focus was to promote development in the rural and remote areas. The experience of these programmes helped the government to focus on rural India. The purpose of the participation of the rural and urban citizens was sought through the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts.