Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Textbook Solutions
Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
Which factor of an ecosystem includes plants, animals and microorganisms?
(a) Biotic factor
(b) Abiotic factor
(c) Direct factor
(d) Indirect factor
Answer:
(a) Biotic factor
Question 2.
An assemblage of individuals of different species living in the same habitat and having functional interactions is ……………….
(a) Biotic community
(b) Ecological niche
(c) Population
(d) Ecosystem
Answer:
(a) Biotic community

Question 3.
Association between sea anemone and Hermit crab in gastropod shell is that of ………………..
(a) Mutualism
(b) Commensalism
(c) Parasitism
(d) Amensalism
Answer:
(b) Commensalism
Question 4.
Select the statement which explains best parasitism.
(a) One species is benefited.
(b) Both the species are benefited.
(c) One species is benefited, other is not affected.
(d) One species is benefited, other is harmed.
Answer:
(d) One species is benefited, other is harmed.
Question 5.
Growth of bacteria in a newly inoculated agar plate shows ………………….
(a) exponential growth
(b) logistic growth
(c) Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth
(d) zero growth
Answer:
(c) Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth
2. Very short answer questions.
Question 1.
Define the following terms
a. Commensalism
Answer:
The interaction between two species in which one species gets benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited is called commensalism.
b. Parasitism
Answer:
The interaction between two species in which one parasitic species derives benefit from the other host species by harming it is called parasitism.
c. Camouflage
Answer:
Camouflage is the disguising colouration or behaviour to merge with the surrounding so that prey or predator can remain hidden.
Question 2.
Give one example for each
a. Mutualism
b. Interspecific competition
Answer:
a. Lichen is composed of alga (cyanobacteria) and fungus. They cannot survive independently. Their association is mutualistic alga synthesises food by photosynthesis and fungus does the absorption of moisture.
b. Leopard and lion competing for a same prey. Sheep and cow competing for grazing in the same land.

Question 3.
Name the type of association:
a. Clown fish and sea anemone
b. Crow feeding the hatchling of Koel
c. Humming birds and host flowering plants
Answer:
a. Commensalism
b. Brood parasitism
c. Mutualism
Question 4.
What is the ecological process behind the biological control method of managing with pest insects?
Answer:
Protocooperation:
3. Short answer questions.
Question 1.
How is the dormancy of seeds different from hibernation in animals?
Answer:
In dormancy seed is not showing any metabolic activities. It can come back to life if and only if it gets suitable moisture and sunlight. Hibernation is suspended state, in which metabolic reactions do take place but at a very reduced pace. Animal arouses on its own after the winter sleep is over. This arousal is spontaneous and depends upon the ambient temperature. Dormant seed does not show such change unless it is planted or thrown in to moist place.
Question 2.
If a marine fish is placed in a fresh water aquarium, will it be able to survive? Give reason.
Answer:
Marine fish has its own osmoregulation which is different from the osmoregulation seen in fresh water fish. In marine water, the ambient salinity is more than the concentration of ions in the body. But in fresh water reverse is the case. Therefore, marine fish has different machinery to cope up with high saline environment. Therefore, it cannot survive in fresh water as its osmoregulation is not possible in less saline waters.
Question 3.
How is the dormancy of seeds different from hibernation in animals?
Answer:
In dormancy seed is not showing any metabolic activities. It can come back to life if and only if it gets suitable moisture and sunlight. Hibernation is suspended state, in which metabolic reactions do take place but at a very reduced pace. Animal arouses on its own after the winter sleep is over. This arousal is spontaneous and depends upon the ambient temperature. Dormant seed does not show such change unless it is planted or thrown into moist place.

Question 4.
An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and the mango tree?
Answer:
Question 5.
Distinguish between the following:
a. Hibernation and Aestivation
Answer:
E.g. Bats, birds, mammals, insects, etc. show hibernation.
E.g. Bees, snails, earthworms, salamanders, frogs, earthworms, crocodiles, tortoise, etc. show aestivation.
b. Ectotherms and Endotherms
Answer:
E.g. Amphibians and reptiles.
E.g. Mammals and birds
c. Parasitism and Mutualism
Answer:
Question 6.
Write a short note on
a. Adaptations of desert animals
Answer:

b. Adaptations of plants to water scarcity
Or
Adaptations in desert plants.
Answer:
c. Behavioural adaptations in animals
Answer:
Question 7.
Define Population and Community.
Answer:
Population:
Group of organisms belonging to same species that can potentially interbreed with each other and live together in a well-defined geographical area by sharing or competing for similar resources, is called population.
Community:
Several populations of different species in a particular area makes a community.
4. Long answer questions.
Question 1.
With the help of suitable diagram, describe the logistic population growth curve.
Answer:
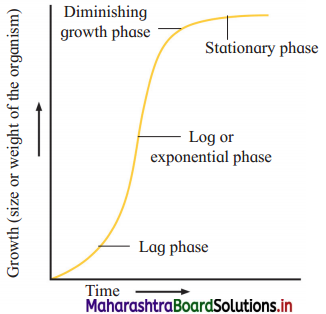

Question 2.
Enlist and explain the important characteristics of a population.
Answer:
Important characteristics of a population are as follows:
1. Natality:
2. Mortality:
3. Density:
The density of a population in a given habitat during a given period fluctuates due to changes in four basic processes, viz.
4. Sex ratio : Ratio of the number of individuals of one sex (male) to that of the other sex (female) is called sex ratio. In nature male, female ratio is always 1 : 1. This 1 : 1 ratio is called evolutionary stable strategy of ESS for each population.
5. Age distribution and age pyramid : This parameter is important for human population. Each population is composed of individuals of different ages. The age distribution is plotted for the population, the resulting structure is called an age pyramid. For making the age pyramid, the entire population is divided into three age groups as Pre-Reproductive (age 0-14 years), Reproductive (age 15-44 years) and Post-reproductive (age 45 -85+ years).
6. Growth : Growth of a population causes rise in its density. The size and density are dynamic parameters as they keep on changing with time, and various factors including food, predation pressure and adverse weather. From the density, one comes to know if the population is flourishing or declining.
Chapter 13 Organisms and Populations Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
Which factor of an ecosystem includes plants, animals and microorganisms?
(a) Biotic factor
(b) Abiotic factor
(c) Direct factor
(d) Indirect factor
Answer:
(a) Biotic factor
Question 2.
An assemblage of individuals of different species living in the same habitat and having functional interactions is ……………….
(a) Biotic community
(b) Ecological niche
(c) Population
(d) Ecosystem
Answer:
(a) Biotic community

Question 3.
Association between sea anemone and Hermit crab in gastropod shell is that of ………………..
(a) Mutualism
(b) Commensalism
(c) Parasitism
(d) Amensalism
Answer:
(b) Commensalism
Question 4.
Select the statement which explains best parasitism.
(a) One species is benefited.
(b) Both the species are benefited.
(c) One species is benefited, other is not affected.
(d) One species is benefited, other is harmed.
Answer:
(d) One species is benefited, other is harmed.
Question 5.
Growth of bacteria in a newly inoculated agar plate shows ………………….
(a) exponential growth
(b) logistic growth
(c) Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth
(d) zero growth
Answer:
(c) Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth
2. Very short answer questions.
Question 1.
Define the following terms
a. Commensalism
Answer:
The interaction between two species in which one species gets benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefited is called commensalism.
b. Parasitism
Answer:
The interaction between two species in which one parasitic species derives benefit from the other host species by harming it is called parasitism.
c. Camouflage
Answer:
Camouflage is the disguising colouration or behaviour to merge with the surrounding so that prey or predator can remain hidden.
Question 2.
Give one example for each
a. Mutualism
b. Interspecific competition
Answer:
a. Lichen is composed of alga (cyanobacteria) and fungus. They cannot survive independently. Their association is mutualistic alga synthesises food by photosynthesis and fungus does the absorption of moisture.
b. Leopard and lion competing for a same prey. Sheep and cow competing for grazing in the same land.

Question 3.
Name the type of association:
a. Clown fish and sea anemone
b. Crow feeding the hatchling of Koel
c. Humming birds and host flowering plants
Answer:
a. Commensalism
b. Brood parasitism
c. Mutualism
Question 4.
What is the ecological process behind the biological control method of managing with pest insects?
Answer:
Protocooperation:
3. Short answer questions.
Question 1.
How is the dormancy of seeds different from hibernation in animals?
Answer:
In dormancy seed is not showing any metabolic activities. It can come back to life if and only if it gets suitable moisture and sunlight. Hibernation is suspended state, in which metabolic reactions do take place but at a very reduced pace. Animal arouses on its own after the winter sleep is over. This arousal is spontaneous and depends upon the ambient temperature. Dormant seed does not show such change unless it is planted or thrown in to moist place.
Question 2.
If a marine fish is placed in a fresh water aquarium, will it be able to survive? Give reason.
Answer:
Marine fish has its own osmoregulation which is different from the osmoregulation seen in fresh water fish. In marine water, the ambient salinity is more than the concentration of ions in the body. But in fresh water reverse is the case. Therefore, marine fish has different machinery to cope up with high saline environment. Therefore, it cannot survive in fresh water as its osmoregulation is not possible in less saline waters.
Question 3.
How is the dormancy of seeds different from hibernation in animals?
Answer:
In dormancy seed is not showing any metabolic activities. It can come back to life if and only if it gets suitable moisture and sunlight. Hibernation is suspended state, in which metabolic reactions do take place but at a very reduced pace. Animal arouses on its own after the winter sleep is over. This arousal is spontaneous and depends upon the ambient temperature. Dormant seed does not show such change unless it is planted or thrown into moist place.

Question 4.
An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and the mango tree?
Answer:
Question 5.
Distinguish between the following:
a. Hibernation and Aestivation
Answer:
| Hibernation | Aestivation |
| 1. Hibernation is winter sleep shown by some warm-blooded and some cold-blooded animals. | 1. Aestivation is the type of summer sleep, shown by cold-blooded animals. |
| 2. It is for the whole winter. | 2. It is of short duration. |
| 3. The animals look out for the warmer place to enter into hibernation. | 3. Animals search for the moist, shady and cool place to sleep. |
| 4. Metabolic activities of hibernators slowdown in this dormant stage. | 4. Metabolic activities of aestivators remain low during aestivation period. |
| 5. Hibernation helps in maintaining the body temperature and prevents any internal body damage due to low temperatures. E.g. Bats, birds, mammals, insects, etc. show hibernation. | 5. Aestivation helps in maintaining the body temperature by avoiding the excessive water loss and thus prevents any internal body damaged due to high temperatures. E.g. Bees, snails, earthworms, salamanders, frogs, earthworms, crocodiles, tortoise, etc. show aestivation. |
E.g. Bees, snails, earthworms, salamanders, frogs, earthworms, crocodiles, tortoise, etc. show aestivation.
b. Ectotherms and Endotherms
Answer:
| Ectotherms | Endotherms |
| 1. Ectotherms do not have ability to generate heat in the body. | 1. Endotherms possess the ability to generate their own body heat. |
| 2. Ectotherms depend on the environmental sources to heat their bodies. E.g sunlight. | 2. Endotherms do not depend upon outside sources to generate heat. |
| 3. Most ectotherms are confined to warmer parts of the world. | 3. Endotherms inhabit coldest parts of the earth. |
| 4. Body temperature of ectotherms fluctuate according to ambient temperature. | 4. Body temperatures of endotherms remain constant and do not show fluctuations as per ambient temperatures. |
| 5. Metabolic rate of ectotherms is low. E.g. Amphibians and reptiles. | 5. Metabolic rate of endotherms is high. E.g. Mammals and birds |
E.g. Mammals and birds
c. Parasitism and Mutualism
Answer:
| Parasitism | Mutualism |
| 1. Parasitism is the relationship where only one organism receive benefits, while the other is harmed in return. | 1. Mutualism is the relationship where both the organisms of distinct species are benefited. |
| 2. Parasite cannot survive without host but if the host is overexploited then parasite too dies. | 2. Both the species are dependent on each other for their benefits and survival. |
| 3. Parasitism can be facultative or obligatory. | 3. Mutualism is obligatory relationship. |
| 4. Parasitism is a negative interaction. | 4. Mutualism is a positive interaction. |
Write a short note on
a. Adaptations of desert animals
Answer:

b. Adaptations of plants to water scarcity
Or
Adaptations in desert plants.
Answer:
c. Behavioural adaptations in animals
Answer:
Question 7.
Define Population and Community.
Answer:
Population:
Group of organisms belonging to same species that can potentially interbreed with each other and live together in a well-defined geographical area by sharing or competing for similar resources, is called population.
Community:
Several populations of different species in a particular area makes a community.
4. Long answer questions.
Question 1.
With the help of suitable diagram, describe the logistic population growth curve.
Answer:


Question 2.
Enlist and explain the important characteristics of a population.
Answer:
Important characteristics of a population are as follows:
1. Natality:
2. Mortality:
3. Density:
The density of a population in a given habitat during a given period fluctuates due to changes in four basic processes, viz.
4. Sex ratio : Ratio of the number of individuals of one sex (male) to that of the other sex (female) is called sex ratio. In nature male, female ratio is always 1 : 1. This 1 : 1 ratio is called evolutionary stable strategy of ESS for each population.
5. Age distribution and age pyramid : This parameter is important for human population. Each population is composed of individuals of different ages. The age distribution is plotted for the population, the resulting structure is called an age pyramid. For making the age pyramid, the entire population is divided into three age groups as Pre-Reproductive (age 0-14 years), Reproductive (age 15-44 years) and Post-reproductive (age 45 -85+ years).
6. Growth : Growth of a population causes rise in its density. The size and density are dynamic parameters as they keep on changing with time, and various factors including food, predation pressure and adverse weather. From the density, one comes to know if the population is flourishing or declining.