Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Textbook Solutions
Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Griffith worked on ………………..
(a) Bacteriophage
(b) Drosophila
(c) Frog eggs
(d) Streptococci
Answer:
(d) Streptococci
Question 2.
The molecular knives of DNA are ………………..
(a) Ligases
(b) Polymerases
(c) Endonucleases
(d) Transcriptase
Answer:
(c) Endonucleases

Question 3.
Translation occurs in the ………………..
(a) Nucleus
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Nucleolus
(d) Lysosomes
Answer:
(b) Cytoplasm
Question 4.
The enzyme required for transcription is ………………..
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) RNApolymerase
(c) Restriction enzyme
(d) RNase
Answer:
(b) RNA polymerase
Question 5.
Transcription is the transfer of genetic information from ………………..
(a) DNA to RNA
(b) t-RNA to m-RNA
(c) DNA to m-RNA
(d) m-RNA to t-RNA
Answer:
(a) DNA to RNA
Question 6.
Which of the following is NOT part of protein synthesis?
(a) Replication
(b) Translation
(c) Transcription
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Replication
Question 7.
In the RNA molecule, which nitrogen base is found in place of thymine?
(a) Guanine
(b) Cytosine
(c) Thymine
(d) Uracil
Answer:
(d) Uracil
Question 8.
How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids?
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 9
(d) 12
Answer:
(a) 3
Question 9.
Which out of the following is NOT an example of inducible operon?
(a) Lactose operon
(b) Histidine operon
(c) Arabinose operon
(d) Tryptophan operon
Answer:
(d) Tryptophan operon
Question 10.
Place the following event of translation in the correct sequence ………………..
i. Binding of met-t-RNA to the start codon.
ii. Covalent bonding between two amino acids.
iii. Binding of second t-RNA.
iv. Joining of small and large ribosome subunits.
(a) iii, iv, i, ii
(b) i, iv, iii, ii
(c) iv, iii, ii, i
(d) ii, iii, iv, i
Answer:
(b) i, iv, iii, ii
2. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the function of an RNA primer during protein synthesis?
Answer:
During DNA replication, RNA primer provides 3’ OH to which DNA polymerase enzyme can add nucleotides to synthesize new strand using parental strand of DNA as template.
[Note : RNA primer has no direct role in protein synthesis.]
Question 2.
Why is the genetic code considered as commaless?
Answer:
The triplet codon are arranged one after the other on m-RNA molecule without any gap or space and therefore genetic code is considered as commaless.
Question 3
Genome
Answer:
Genome is the total genetic constitution of an organism or a complete copy of genetic information (DNA) or one complete set of chromosomes (monoploid or haploid) of an organism.
Question 4.
Which enzyme does remove supercoils from replicating DNA?
Answer:
Super-helix relaxing enzyme (Topoisomerase) removes supercoils from replicating DNA.
Question 5.
Why are Okazaki fragments formed on lagging strand only?
Answer:
Okazaki fragments are formed only on lagging template as only short stretch of lagging template becomes available for replication at one time.
Question 6.
When does DNA replication take place?
Answer:
In eukaryotes DNA-replication takes place during S-phase of interphase of cell cycle and in prokaryotes. DNA replicates prior to cell division.
Question 7.
Define term Codogen and Codon
Answer:
Codogen is a triplet of nucleotides present on the DNA which specifies one particular amino acid.
Codon is a triplet of nucleotides present on the m-RNA which specifies one particular amino acid.

Question 8.
What is degeneracy of genetic code?
Answer:
Genetic code is degenerate as 61 codons code for 20 amino acids, that is two or more codons can specify the same amino acid. E.g. Cysteine has two codons, while isoleucine has three codons.
Question 9.
Which are the nucleosomal ‘core’ histones?
Answer:
Two molecules each of histone proteins, viz. H2A. H2B, H3 and H4 are the nucleosomal ‘core’ histones.
3. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
DNA packaging in eukaryotic cell.
Answer:
Question 2.
Enlist the characteristics of genetic code.
Answer:
The characteristics of genetic code are
Question 3.
Applications of DNA fingerprinting.
Answer:
Applications of DNA fingerprinting are as follows:
Question 4.
Explain the role of lactose in ‘Lac Operon’.
Answer:
4. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Human genome project.
Answer:
1. Human Genome Project (HGP) was initiated in 1990 under the International administration of the Human Genome Organization (HUGO) and it was completed r in 2003.
2. The main aims:
3. Significance:
Question 2.
Describe the structure of operon.
Answer:
Question 3.
In the figure below A, B and C are three types of
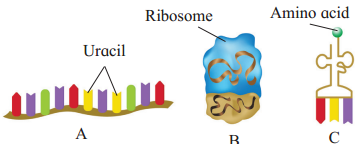
Answer:
Answer: A, B and C are A : m-RNA, B : r-RNA, C : t-RNA
Question 4.
Identify the labelled structures on the following diagram of translation.
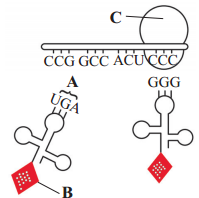
Part A is the ………………
Part B is the ………………
Part C is the ………………
Answer:
Part A is the anti-codon.
Part B is the amino acid.
Part C is the larger subunit of ribosome.

Question 5.
Match the entries in Column I with those of Column II and choose the correct answer.
Answer:
5. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the process of DNA replication.
Answer:
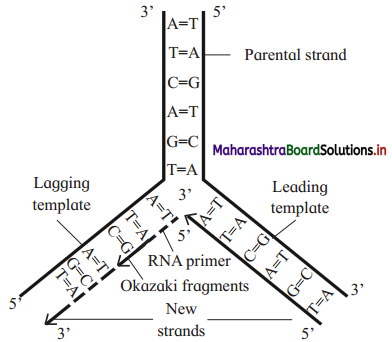
DNA replication is semi-conservative replication. It involves following steps:
Activation of Nucleotides:
Point of Origin or Initiation point:
Unwinding of DNA molecule:
Replicating fork:
Synthesis of new strands:
Leading and Lagging strand:
Formation of two daughter DNA molecules:
Question 2.
Describe the process of transcription in protein synthesis.
Answer:
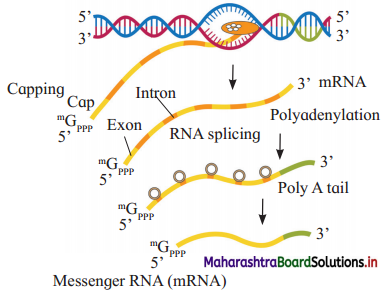
Transcription involves three stages, viz. Initiation, Elongation and Termination.
(1) Initiation:
(2) Elongation:
(3) Termination:
When RNA polymerase reaches the terminator site on the DNA, both enzyme and newly formed m-RNA (primary transcript) gets released.
Question 3.
Describe the process of translation in protein synthesis.
Answer:
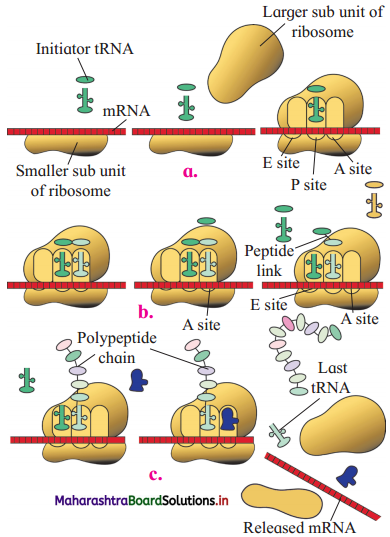
Translation involves the following steps:
1. Activation of amino acids and formation of charged t-RNA (t-RNA – amino acid complex):
i. In the presence of an enzyme amino acyl t-RNA synthetase, the amino acid is activated and then attached to the specific t-RNA molecule at 3’ end to form charged t-RNA (t-RNA – amino acid complex).
ii. ATP is essential for the reaction.
2. Initiation of Polypeptide chain:

3. Elongations of polypeptide chain:
Addition of amino acid occurs in 3 Step cycle-
i. Codon recognition.
Anticodon of second (and subsequent) amino acyl t-RNA molecule recognizes and binds with codon at A-site by hydrogen bonds.
ii. Peptide bond formation.
iii. Translocation.
4. Termination and release of polypeptide:
When stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) gets exposed at the A-site, the release factor binds to the stop codon, thereby terminating the translation process
The polypeptide gets released in the cytoplasm.
Two subunits of ribosome dissociate and last t-RNA and m-RNA are released in the cytoplasm.
m-RNA gets denatured by nucleases immediately.
Question 4.
Describe Lac ‘Operon’.
Answer:
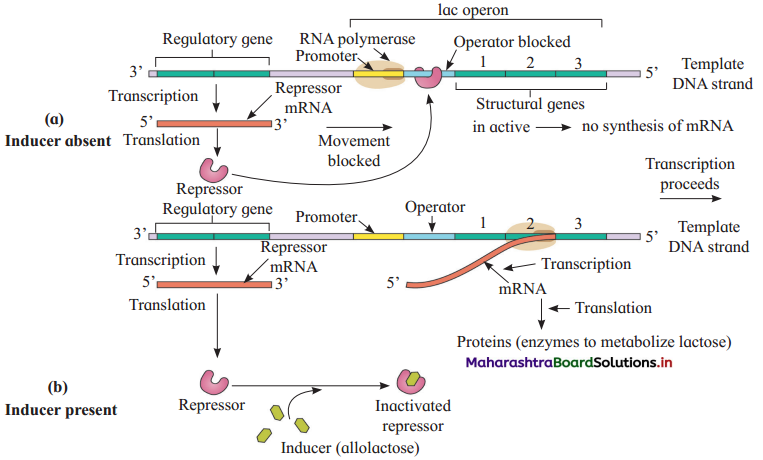
Lac operon consists of the following components:
(1) Regulator gene:
(2) Promoter gene:
(3) Operator gene:
(4) Structural gene:
Question 5.
Justify the statements. If the answer is false, change the underlined word(s) to make the statement true.
(i) The DNA molecule is double stranded and the RNA molecule is single stranded.
Answer:
(ii) The process of translation occurs at the ribosome.
Answer:

(iii) The job of m-RNA is to pick up amino acids and transport them to the ribosomes.
Answer:
The job of t-RNA is to pick up amino acids and transport them to ribosomes. t-RNA is an adapter molecule. It reads the codons of m-RNA and also simultaneously transfer specific amino acid to m-RNA Ribosome complex. It binds with amino acid at its 3′ end.
(iv) Transcription must occur before translation may occur.
Answer:
In prokaryotes, translation can start before transcription is complete, as both these processes occur in the same compartment, i.e. cytoplasm. But in eukaryotes, transcription and processing of hnRNA occurs in nucleus. hnRNA then comes out of the nucleus through nuclear pores and then it is translated at ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Question 6.
Guess
(i) the possible locations of DNA on the collected evidence from a crime scene and
(ii) the possible sources of DNA.
Answer:
Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Griffith worked on ………………..
(a) Bacteriophage
(b) Drosophila
(c) Frog eggs
(d) Streptococci
Answer:
(d) Streptococci
Question 2.
The molecular knives of DNA are ………………..
(a) Ligases
(b) Polymerases
(c) Endonucleases
(d) Transcriptase
Answer:
(c) Endonucleases

Question 3.
Translation occurs in the ………………..
(a) Nucleus
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Nucleolus
(d) Lysosomes
Answer:
(b) Cytoplasm
Question 4.
The enzyme required for transcription is ………………..
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) RNApolymerase
(c) Restriction enzyme
(d) RNase
Answer:
(b) RNA polymerase
Question 5.
Transcription is the transfer of genetic information from ………………..
(a) DNA to RNA
(b) t-RNA to m-RNA
(c) DNA to m-RNA
(d) m-RNA to t-RNA
Answer:
(a) DNA to RNA
Question 6.
Which of the following is NOT part of protein synthesis?
(a) Replication
(b) Translation
(c) Transcription
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Replication
Question 7.
In the RNA molecule, which nitrogen base is found in place of thymine?
(a) Guanine
(b) Cytosine
(c) Thymine
(d) Uracil
Answer:
(d) Uracil
Question 8.
How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids?
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 9
(d) 12
Answer:
(a) 3
Question 9.
Which out of the following is NOT an example of inducible operon?
(a) Lactose operon
(b) Histidine operon
(c) Arabinose operon
(d) Tryptophan operon
Answer:
(d) Tryptophan operon
Question 10.
Place the following event of translation in the correct sequence ………………..
i. Binding of met-t-RNA to the start codon.
ii. Covalent bonding between two amino acids.
iii. Binding of second t-RNA.
iv. Joining of small and large ribosome subunits.
(a) iii, iv, i, ii
(b) i, iv, iii, ii
(c) iv, iii, ii, i
(d) ii, iii, iv, i
Answer:
(b) i, iv, iii, ii
2. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the function of an RNA primer during protein synthesis?
Answer:
During DNA replication, RNA primer provides 3’ OH to which DNA polymerase enzyme can add nucleotides to synthesize new strand using parental strand of DNA as template.
[Note : RNA primer has no direct role in protein synthesis.]
Question 2.
Why is the genetic code considered as commaless?
Answer:
The triplet codon are arranged one after the other on m-RNA molecule without any gap or space and therefore genetic code is considered as commaless.
Question 3
Genome
Answer:
Genome is the total genetic constitution of an organism or a complete copy of genetic information (DNA) or one complete set of chromosomes (monoploid or haploid) of an organism.
Question 4.
Which enzyme does remove supercoils from replicating DNA?
Answer:
Super-helix relaxing enzyme (Topoisomerase) removes supercoils from replicating DNA.
Question 5.
Why are Okazaki fragments formed on lagging strand only?
Answer:
Okazaki fragments are formed only on lagging template as only short stretch of lagging template becomes available for replication at one time.
Question 6.
When does DNA replication take place?
Answer:
In eukaryotes DNA-replication takes place during S-phase of interphase of cell cycle and in prokaryotes. DNA replicates prior to cell division.
Question 7.
Define term Codogen and Codon
Answer:
Codogen is a triplet of nucleotides present on the DNA which specifies one particular amino acid.
Codon is a triplet of nucleotides present on the m-RNA which specifies one particular amino acid.

Question 8.
What is degeneracy of genetic code?
Answer:
Genetic code is degenerate as 61 codons code for 20 amino acids, that is two or more codons can specify the same amino acid. E.g. Cysteine has two codons, while isoleucine has three codons.
Question 9.
Which are the nucleosomal ‘core’ histones?
Answer:
Two molecules each of histone proteins, viz. H2A. H2B, H3 and H4 are the nucleosomal ‘core’ histones.
3. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
DNA packaging in eukaryotic cell.
Answer:
Question 2.
Enlist the characteristics of genetic code.
Answer:
The characteristics of genetic code are
Question 3.
Applications of DNA fingerprinting.
Answer:
Applications of DNA fingerprinting are as follows:
Question 4.
Explain the role of lactose in ‘Lac Operon’.
Answer:
4. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Human genome project.
Answer:
1. Human Genome Project (HGP) was initiated in 1990 under the International administration of the Human Genome Organization (HUGO) and it was completed r in 2003.
2. The main aims:
3. Significance:
Question 2.
Describe the structure of operon.
Answer:
Question 3.
In the figure below A, B and C are three types of

Answer:
Answer: A, B and C are A : m-RNA, B : r-RNA, C : t-RNA
Question 4.
Identify the labelled structures on the following diagram of translation.

Part A is the ………………
Part B is the ………………
Part C is the ………………
Answer:
Part A is the anti-codon.
Part B is the amino acid.
Part C is the larger subunit of ribosome.

Question 5.
Match the entries in Column I with those of Column II and choose the correct answer.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Alkali treatment | i. Separation of DNA fragments on gel slab |
| B. Southern blotting | ii. Splits DNA fragments into single strands |
| C. Electrophoresis | iii. DNA transferred to nitrocellulose sheet |
| D. PCR | iv. X-ray photography |
| E. Autoradiography | v. Produce fragments different sizes |
| F. DNA treated with REN | vi. DNA amplification |
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Alkali treatment | ii. Splits DNA fragments into single strands |
| B. Southern blotting | iii. DNA transferred to nitrocellulose sheet |
| C. Electrophoresis | i. Separation of DNA fragments on gel slab |
| D. PCR | vi. DNA amplification |
| E. Autoradiography | iv. X-ray photography |
| F. DNA treated with REN | v. Produce fragments different sizes |
Question 1.
Explain the process of DNA replication.
Answer:

DNA replication is semi-conservative replication. It involves following steps:
Activation of Nucleotides:
Point of Origin or Initiation point:
Unwinding of DNA molecule:
Replicating fork:
Synthesis of new strands:
Leading and Lagging strand:
Formation of two daughter DNA molecules:
Question 2.
Describe the process of transcription in protein synthesis.
Answer:

Transcription involves three stages, viz. Initiation, Elongation and Termination.
(1) Initiation:
(2) Elongation:
(3) Termination:
When RNA polymerase reaches the terminator site on the DNA, both enzyme and newly formed m-RNA (primary transcript) gets released.
Question 3.
Describe the process of translation in protein synthesis.
Answer:

Translation involves the following steps:
1. Activation of amino acids and formation of charged t-RNA (t-RNA – amino acid complex):
i. In the presence of an enzyme amino acyl t-RNA synthetase, the amino acid is activated and then attached to the specific t-RNA molecule at 3’ end to form charged t-RNA (t-RNA – amino acid complex).
ii. ATP is essential for the reaction.
2. Initiation of Polypeptide chain:

3. Elongations of polypeptide chain:
Addition of amino acid occurs in 3 Step cycle-
i. Codon recognition.
Anticodon of second (and subsequent) amino acyl t-RNA molecule recognizes and binds with codon at A-site by hydrogen bonds.
ii. Peptide bond formation.
iii. Translocation.
4. Termination and release of polypeptide:
When stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) gets exposed at the A-site, the release factor binds to the stop codon, thereby terminating the translation process
The polypeptide gets released in the cytoplasm.
Two subunits of ribosome dissociate and last t-RNA and m-RNA are released in the cytoplasm.
m-RNA gets denatured by nucleases immediately.
Question 4.
Describe Lac ‘Operon’.
Answer:

Lac operon consists of the following components:
(1) Regulator gene:
(2) Promoter gene:
(3) Operator gene:
(4) Structural gene:
Question 5.
Justify the statements. If the answer is false, change the underlined word(s) to make the statement true.
(i) The DNA molecule is double stranded and the RNA molecule is single stranded.
Answer:
(ii) The process of translation occurs at the ribosome.
Answer:

(iii) The job of m-RNA is to pick up amino acids and transport them to the ribosomes.
Answer:
The job of t-RNA is to pick up amino acids and transport them to ribosomes. t-RNA is an adapter molecule. It reads the codons of m-RNA and also simultaneously transfer specific amino acid to m-RNA Ribosome complex. It binds with amino acid at its 3′ end.
(iv) Transcription must occur before translation may occur.
Answer:
In prokaryotes, translation can start before transcription is complete, as both these processes occur in the same compartment, i.e. cytoplasm. But in eukaryotes, transcription and processing of hnRNA occurs in nucleus. hnRNA then comes out of the nucleus through nuclear pores and then it is translated at ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Question 6.
Guess
(i) the possible locations of DNA on the collected evidence from a crime scene and
(ii) the possible sources of DNA.
| Evidence | Possible location of DNA on the evidence | Sources of DNA |
| e.g. Eyeglasses | e.g. Earpieces | e.g. Sweat, Skin |
| Bottle, Can, Glass | Sides, mouthpiece | —————- |
| ————– | Handle | Sweat, skin, blood |
| Used cigarette | Cigarette butt | —————– |
| Bite mark | —————– | Saliva |
| ————- | Surface area | Hair, semen, sweat, urine |
| Evidence | Possible location of DNA on the evidence | Sources of DNA |
| e.g. Eyeglasses | e.g. Earpieces | e.g. Sweat, Skin |
| Bottle, Can, Glass | Sides, mouthpiece | Saliva |
| Door | Handle | Sweat, skin, blood |
| Used cigarette | Cigarette butt | Saliva |
| Bite mark | Teeth impression | Saliva |
| Clothes | Surface area | Hair, semen, sweat, urine |