Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Textbook Solutions
Chapter 6 Plant Water Relation Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In soil, water available for absorption by root is ……………..
(a) gravitational water
(b) capillary water
(c) hygroscopic water
(d) combined water
Answer:
(b) capillary water
Question 2.
The most widely accepted theory for ascent of sap is ……………..
(a) capillarity theory
(b) root pressure theory
(c) diffusion
(d) transpiration pull theory
Answer:
(d) transpiration pull theory

Question 3.
Water movement between the cells is due to ……………..
(a) T.E
(b) W.P
(c) D.P.D.
(d) incipient plasmolysis
Answer:
(c) D.P.D.
Question 4.
In guard cells, when sugar is converted into starch, the stomata pore ……………..
(a) closes almost completely
(b) opens partially
(c) opens fully
(d) remains unchanged
Answer:
(a) closes almost completely
Question 5.
Surface tension is due to ……………..
(a) diffusion
(b) osmosis
(c) gravitational force
(d) cohesion
Answer:
(d) cohesion
Question 6.
Which of the following type of solution has lower level of solutes than the solution?
(a) Isotonic
(b) Hypotonic
(c) Hypertonic
(d) Anisotonic
Answer:
(b) Hypotonie
Question 7.
During rainy season wooden doors warp and become difficult to open or to close because of ……………..
(a) plasmolysis
(b) imbibition
(c) osmosis
(d) diffusion
Answer:
(b) imbibition
Question 8.
Water absorption takes place through ……………..
(a) lateral root
(b) root cap
(c) root hair
(d) primary root
Answer:
(c) root hair
Question 9.
Due to low atmospheric pressure the rate of transpiration will ……………..
(a) increase
(b) decrease rapidly
(c) decrease slowly
(d) remain unaffected
Answer:
(a) increase
Question 10.
Osmosis is a property of ……………..
(a) solute
(b) solvent
(c) solution
(d) membrane
Answer:
(c) solution
2. Very short answer question
Question 1.
What is osmotic pressure?
Answer:
The pressure exerted due to osmosis is osmotic pressure.
Question 2.
Name the condition in which protoplasm of the plant cell shrinks.
Answer:
Plasmolysis
Question 3.
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Answer:
When a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution then water potential of pure water or solution increases.
Question 4.
Which type of solution will bring about deplasmolysis ?
Answer:
Placing a plasmolysed cell in hypotonic solution will bring about deplasmolysis.

Question 5.
Which type of plants have negative root pressure?
Answer:
Plants showing excessive transpiration have negative root pressure.
Question 6.
In which conditions transpiration pull will be affected?
Answer:
Due to temperature fluctuations during day and night gas bubbles may be formed which affects transpiration pull.
Question 7.
Mention the shape of guard cells in Cyperus.
Answer:
Kidney shaped and dumbbell shaped guard cells are seen.
Question 8.
Why do diurnal changes occur in osmotic potential of guard cells?
Answer:
Enzyme activity of phosphorylase converts starch into sugar during daytime and sugar is converted to starch during night. This causes changes in osmotic potential of guard cells.
Question 9.
What is symplast pathway?
Answer:
When water is absorbed by root hair it passes across from one living cell to other living cell through the plasmodesmatal connections between them, then it is called symplast pathway across the root.
3. Answer the Following Questions
Question 1.
Describe mechanism of absorption of water.
Answer:
Question 2.
Discuss theories of water translocation.
Answer:
Question 3.
What is transpiration? Describe mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Answer:

Question 4.
What is transpiration? Explain role of transpiration.
Answer:
Transpiration : The loss of water from plant body in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
Role of transpiration:
Question 5.
Explain root pressure theory and its limitations.
Answer:
Limitation of this theory:
Question 6.
Explain capillarity theory of water translocation.
Answer:
Question 7.
Why is transpiration called ‘a necessary evil’?
Answer:
Question 8.
Explain movement of water in the root.
Answer:
Question 9.
(i) Osmosis
Answer:
It is a special type of diffusion of solvent through a semipermeable membrane.
(ii) Diffusion
Answer:
It is the movement of ions/ atoms/molecules of a substance from the region of higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration.
(iii) Plasmolysis
Answer:
Exo-osmosis in a living cell when placed in hypertonic solution is called plasmolysis.
(iv) Imbibition
Answer:
It is swelling up of hydrophilic colloids due to adsorption of water.
(v) Guttation
Answer:
The loss of water in the form of liquid is called guttation.
(vi) Transpiration
Answer:
The loss of water from plant body in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
(vii) Ascent of sap
Answer:
The transport of water with dissolved minerals in it from root to other aerial parts of plant against the gravity is called ascent of sap.

(viii) Active absorption
Answer:
Water absorption by activity of root which is against the D.PD. gradient along with expenditure of A.T.E energy generated by respiration is the process of active absorption.
(ix) Diffusion Pressure Deficit (D.P.D.)
Answer:
The difference in the diffusion pressures of pure solvent and the solvent in a solution is called diffusion pressure deficit.
(x) Turgor pressure
Answer:
It is the pressure exerted by turgid cell sap on to the cell membrane and cell wall.
(xi) Water potential
Answer:
Chemical potential of water is called water potential.
(xii) Wall pressure
Answer:
Thick and rigid cell wall exerts a counter pressure to turgor pressure developed on the cell sap is called wall pressure that operates in opposite direction.
(xiii) Root pressure
Answer:
As absorption of water by root hair being a continuous process, a sort of hydrostatic pressure is developed in living cells of root, this is called root pressure.
Question 10.
Osmotic Pressure (O.P) and Turgor Pressure (T.P)
Answer:
Question 11.
How are the minerals absorbed by the plants ?
Answer:
4. Long answer questions
Question 1.
Describe structure of root hair.
Answer:
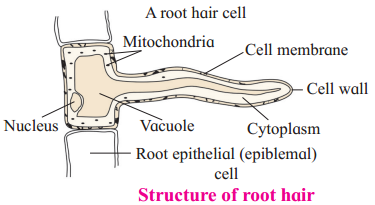
Question 2.
Write on journey of water from soil to xylem in roots.
Answer:

Question 3.
Explain cohesion theory of translocation of water.
Answer:
Question 4.
Write on mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Answer:
Question 5.
What is hydroponics? How is it useful in identifying the role of nutrients?
Answer:
(1) Growing plants in aqueous (soilless) medium is known as hydroponics. [Greek word hudor = water and ponos = work]
(2) It is technique of growing plants by supplying all necessary nutrients in the water supply given to plant.
(3) A nutrient medium is prepared by dissolving necessary salts of micronutrients and macronutricnts In desired quantity and roots of plants are suspended in this liquid with appropriate support.
(4) Hydroponics is of great use in studying the deficiency symptoms of different mineral nutrients.
(5) The plants uptake mineral nutrients in the form of dissolved ions with the help of root hairs from the surrounding medium or nutrient solution supplied.
(6) While preparing the required nutricnt medium particular nutrient can be totally avoided and then the effect of lack of that nutrient can be studied in variation of plant growth.
(7) Any visible change noticed from normal structure and function of the plant is the symptom or hunger sign considered.
(8) For e.g. Yellowing of leaf is observed due to loss of chlorophyll pigments or Chiorosis is noticed if Magnesium is lacking as it is a structural componen of chlorophyll pigment.

Question 6.
Explain the active absorption of minerals.
Answer:
Chapter 6 Plant Water Relation Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In soil, water available for absorption by root is ……………..
(a) gravitational water
(b) capillary water
(c) hygroscopic water
(d) combined water
Answer:
(b) capillary water
Question 2.
The most widely accepted theory for ascent of sap is ……………..
(a) capillarity theory
(b) root pressure theory
(c) diffusion
(d) transpiration pull theory
Answer:
(d) transpiration pull theory

Question 3.
Water movement between the cells is due to ……………..
(a) T.E
(b) W.P
(c) D.P.D.
(d) incipient plasmolysis
Answer:
(c) D.P.D.
Question 4.
In guard cells, when sugar is converted into starch, the stomata pore ……………..
(a) closes almost completely
(b) opens partially
(c) opens fully
(d) remains unchanged
Answer:
(a) closes almost completely
Question 5.
Surface tension is due to ……………..
(a) diffusion
(b) osmosis
(c) gravitational force
(d) cohesion
Answer:
(d) cohesion
Question 6.
Which of the following type of solution has lower level of solutes than the solution?
(a) Isotonic
(b) Hypotonic
(c) Hypertonic
(d) Anisotonic
Answer:
(b) Hypotonie
Question 7.
During rainy season wooden doors warp and become difficult to open or to close because of ……………..
(a) plasmolysis
(b) imbibition
(c) osmosis
(d) diffusion
Answer:
(b) imbibition
Question 8.
Water absorption takes place through ……………..
(a) lateral root
(b) root cap
(c) root hair
(d) primary root
Answer:
(c) root hair
Question 9.
Due to low atmospheric pressure the rate of transpiration will ……………..
(a) increase
(b) decrease rapidly
(c) decrease slowly
(d) remain unaffected
Answer:
(a) increase
Question 10.
Osmosis is a property of ……………..
(a) solute
(b) solvent
(c) solution
(d) membrane
Answer:
(c) solution
2. Very short answer question
Question 1.
What is osmotic pressure?
Answer:
The pressure exerted due to osmosis is osmotic pressure.
Question 2.
Name the condition in which protoplasm of the plant cell shrinks.
Answer:
Plasmolysis
Question 3.
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Answer:
When a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution then water potential of pure water or solution increases.
Question 4.
Which type of solution will bring about deplasmolysis ?
Answer:
Placing a plasmolysed cell in hypotonic solution will bring about deplasmolysis.

Question 5.
Which type of plants have negative root pressure?
Answer:
Plants showing excessive transpiration have negative root pressure.
Question 6.
In which conditions transpiration pull will be affected?
Answer:
Due to temperature fluctuations during day and night gas bubbles may be formed which affects transpiration pull.
Question 7.
Mention the shape of guard cells in Cyperus.
Answer:
Kidney shaped and dumbbell shaped guard cells are seen.
Question 8.
Why do diurnal changes occur in osmotic potential of guard cells?
Answer:
Enzyme activity of phosphorylase converts starch into sugar during daytime and sugar is converted to starch during night. This causes changes in osmotic potential of guard cells.
Question 9.
What is symplast pathway?
Answer:
When water is absorbed by root hair it passes across from one living cell to other living cell through the plasmodesmatal connections between them, then it is called symplast pathway across the root.
3. Answer the Following Questions
Question 1.
Describe mechanism of absorption of water.
Answer:
Question 2.
Discuss theories of water translocation.
Answer:
Question 3.
What is transpiration? Describe mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Answer:

Question 4.
What is transpiration? Explain role of transpiration.
Answer:
Transpiration : The loss of water from plant body in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
Role of transpiration:
Question 5.
Explain root pressure theory and its limitations.
Answer:
Limitation of this theory:
Question 6.
Explain capillarity theory of water translocation.
Answer:
Question 7.
Why is transpiration called ‘a necessary evil’?
Answer:
Question 8.
Explain movement of water in the root.
Answer:
Question 9.
(i) Osmosis
Answer:
It is a special type of diffusion of solvent through a semipermeable membrane.
(ii) Diffusion
Answer:
It is the movement of ions/ atoms/molecules of a substance from the region of higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration.
(iii) Plasmolysis
Answer:
Exo-osmosis in a living cell when placed in hypertonic solution is called plasmolysis.
(iv) Imbibition
Answer:
It is swelling up of hydrophilic colloids due to adsorption of water.
(v) Guttation
Answer:
The loss of water in the form of liquid is called guttation.
(vi) Transpiration
Answer:
The loss of water from plant body in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
(vii) Ascent of sap
Answer:
The transport of water with dissolved minerals in it from root to other aerial parts of plant against the gravity is called ascent of sap.

(viii) Active absorption
Answer:
Water absorption by activity of root which is against the D.PD. gradient along with expenditure of A.T.E energy generated by respiration is the process of active absorption.
(ix) Diffusion Pressure Deficit (D.P.D.)
Answer:
The difference in the diffusion pressures of pure solvent and the solvent in a solution is called diffusion pressure deficit.
(x) Turgor pressure
Answer:
It is the pressure exerted by turgid cell sap on to the cell membrane and cell wall.
(xi) Water potential
Answer:
Chemical potential of water is called water potential.
(xii) Wall pressure
Answer:
Thick and rigid cell wall exerts a counter pressure to turgor pressure developed on the cell sap is called wall pressure that operates in opposite direction.
(xiii) Root pressure
Answer:
As absorption of water by root hair being a continuous process, a sort of hydrostatic pressure is developed in living cells of root, this is called root pressure.
Question 10.
Osmotic Pressure (O.P) and Turgor Pressure (T.P)
Answer:
| Osmotic Pressure (O.R) | Turgor Pressure (T.P.) |
| 1. The pressure exerted due to osmosis is called osmotic pressure. | 1. The pressure exerted by turgid cell sap on cell membrane and cell wall, is called turgor pressure. |
| 2. It is pressure caused by water when it moves by osmosis. | 2. It is pressure caused by content of cell (cell sap). |
| 3. It is generated by the osmotic flow of water through a semipermeable membrane. | 3. It is maintained by osmosis. |
How are the minerals absorbed by the plants ?
Answer:
4. Long answer questions
Question 1.
Describe structure of root hair.
Answer:

Question 2.
Write on journey of water from soil to xylem in roots.
Answer:

Question 3.
Explain cohesion theory of translocation of water.
Answer:
Question 4.
Write on mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Answer:
Question 5.
What is hydroponics? How is it useful in identifying the role of nutrients?
Answer:
(1) Growing plants in aqueous (soilless) medium is known as hydroponics. [Greek word hudor = water and ponos = work]
(2) It is technique of growing plants by supplying all necessary nutrients in the water supply given to plant.
(3) A nutrient medium is prepared by dissolving necessary salts of micronutrients and macronutricnts In desired quantity and roots of plants are suspended in this liquid with appropriate support.
(4) Hydroponics is of great use in studying the deficiency symptoms of different mineral nutrients.
(5) The plants uptake mineral nutrients in the form of dissolved ions with the help of root hairs from the surrounding medium or nutrient solution supplied.
(6) While preparing the required nutricnt medium particular nutrient can be totally avoided and then the effect of lack of that nutrient can be studied in variation of plant growth.
(7) Any visible change noticed from normal structure and function of the plant is the symptom or hunger sign considered.
(8) For e.g. Yellowing of leaf is observed due to loss of chlorophyll pigments or Chiorosis is noticed if Magnesium is lacking as it is a structural componen of chlorophyll pigment.

Question 6.
Explain the active absorption of minerals.
Answer: