Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Biology Textbook Solutions
Chapter 7 Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
Which of the hormone can replace vernalization ?
(a) Auxin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Gibberellins
(d) Ethylene
Answer:
(c) Gibberellins

Question 2.
The principle pathway of water translocation in angiosperms is ………………..
(a) Sieve cells
(b) Sieve tube elements
(c) Xylem
(d) Xylem and phloem
Answer:
(c) Xylem
Question 3.
Abscissic acid controls ………………..
(a) cell division
(b) leaf fall and dormancy
(c) shoot elongation
(d) cell elongation and wall formation
Answer:
(b) leaf fall and dormancy
Question 4.
Which is employed for artificial ripening of banana fruits?
(a) Auxin
(b) Ethylene
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Gibberellin
Answer:
(b) Ethylene
Question 5.
Which of the following is required for stimulation of flowering in plants?
(a) Adequate oxygen
(b) Definite photoperiod
(c) Adequate water
(d) Water and minerals
Answer:
(b) Definite photoperiod
Question 6.
For short day plants, the critical period is ………………..
(a) light
(b) dark/night
(c) UV rays
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(b) dark/night
Question 7.
Which of the following is NOT day neutral plant?
(a) Tomato
(b) Cotton
(c) Sunflower
(d) Soybean
Answer:
(d) Soybean
Question 8.
Essential macro elements are ………………..
(a) manufactured during photosynthesis
(b) produced by enzymes
(c) obtained from soil
(d) produced by growth hormones
Answer:
(c) obtained from soil
Question 9.
Function of Zinc is ………………..
(a) closing of stomata
(b) biosynthesis of 3-IAA
(c) synthesis of chlorophyll
(d) oxidation of carbohydrates
Answer:
(b) biosynthesis of 3-LAA
Question 10.
Necrosis means ………………..
(a) yellow spot on the leaves
(b) death of tissue
(c) darkening of green colour in leaves
(d) wilting of leaves
Answer:
(b) death of tissue
Question 11.
Conversion of nitrates to nitrogen is called ………………..
(a) ammonification
(b) nitrification
(c) nitrogen fixation
(d) denitrification
Answer:
(d) denitrification
Question 12.
How many molecules of ATP are required to fix one molecule of nitrogen?
(a) 12
(b) 20
(c) 6
(d) 16
Answer:
(d) 16
2. Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Enlist the phases of growth in plants.
Answer:
The three phases of growth are phase of cell division, phase of cell enlargement and phase of cell maturation.
Question 2.
Give full form of IAA.
Answer:
Full form is Indole Acetic Acid.

Question 3.
What does it mean by ‘open growth’?
Answer:
In plants the growth is indeterminate and takes place throughout the life at specific regions having meristems.
Question 4.
Plant stress hormone.
Answer:
Abscissic acid.
Question 5.
What is denitrification?
Answer:
Anaerobic bacteria can convert nitrates of soil back into nitrogen gas. That process performed by denitrifying bacteria is denitrification.
Question 6.
Bacteria responsible for conversion of nitrite to nitrate.
Answer:
Nitrobacter.
Question 7.
What is the role of gibberellins in rosette plants?
Answer:
In rosette plants like beet and cabbage, bolting, i.e. elongation of internodes before flowering is observed due to effect of gibberellins.
Question 8.
Vernalization
Answer:
The response of plant to the influence of low temperature on flowering in plants is called vernalization.
Question 9.
Photoperiodism
Answer:
The response of plant to the influence of light for initiation of flowering is known as photoperiodism.
Question 10.
What is grand period of growth?
Answer:
There are three phases of growth and the total time required for all phases to occur is called grand period of growth.
3. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
(i) Differentiation
Answer:
(ii) Redifferentiation
Answer:
Question 2.
Arithmetic growth and Geometric growth
Answer:
Question 3.
Enlist the role and deficiency symptoms of: (a) nitrogen (b) phosphorus (c) potassium.
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen:
Role : Constituent of proteins as amino acids, nucleic acids, vitamins, hormones, coenzymes, ATP and chlorophyll molecule.
Deficiency symptoms : stunted growth and chlorosis.
(b) Phosphorus:
Role : Constituent of cell membrane, certain proteins, nucleic acids and nucleotides, required for all phosphorylation reactions.
Deficiency symptoms : Poor growth, leaves dull green
(c) Potassium :
Role : Determination of anion – cation balance in cell, necessary for protein synthesis, involved in formation of cell membrane, opening and closing of stomata, activates enzymes, helps in maintenance of turgidity of cells.
Deficiency symptom : Yellow edges in leaves, premature death.

Question 4.
What is short day plant? Give any two examples.
Answer:
The plants which flower when the day length or light period is shorter than the critical photoperiod are called short day plants or SDP
SDPs usually flower during winter and late summer.
Examples – Dahlia, Aster, Tobacco, Chrysanthemum, Soybean (Glycine max) and Cocklebur (Xanthium).
Question 5.
What is vernalization? Give its significance.
Answer:
A low temperature or chilling treatment that induces early flowering in plants is known as vernalization.
Significance:
4. Long answer questions
Question 1.
Explain sigmoid growth curve with the help of diagram.
Answer:
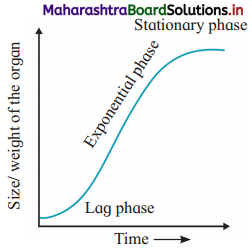
Question 2.
Describe the types of plants on the basis of photoperiod required, with the help of suitable examples.
Answer:
1. Short day plants : Plants that flower under short day length conditions are called short day plants. Plants such as Dahlia, Xanthium, Soybean, Aster, Tobacco and Chrysanthemum are short day plants or SDR. Short day plants require a long uninterrupted dark period for flowering. Therefore, they are also called long night plants.
2. Long day plants : Plants that flower only when they are exposed to light period longer than their critical photoperiod are called long day plants or LDP Long day plants require a short dark or night period for flowering. Hence, they are also called short night plants. Plants such as radish, spinach, wheat, poppy, cabbage, pea, sugar beet, etc. are long day plants.
3. Day neutral plants : Plants in which the flowering is not affected by the day length period are called day neutral plants or DNP or photoneutral plants. Plants such as cucumber, sunflower, cotton, balsam, maize, tomato, etc. are day neutral plants.
Question 3.
Explain biological nitrogen fixation with example.
Answer:

Question 4.
Write on macro and micro nutrients required for plant growth.
Answer:
Chapter 7 Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Multiple choice questions
Question 1.
Which of the hormone can replace vernalization ?
(a) Auxin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Gibberellins
(d) Ethylene
Answer:
(c) Gibberellins

Question 2.
The principle pathway of water translocation in angiosperms is ………………..
(a) Sieve cells
(b) Sieve tube elements
(c) Xylem
(d) Xylem and phloem
Answer:
(c) Xylem
Question 3.
Abscissic acid controls ………………..
(a) cell division
(b) leaf fall and dormancy
(c) shoot elongation
(d) cell elongation and wall formation
Answer:
(b) leaf fall and dormancy
Question 4.
Which is employed for artificial ripening of banana fruits?
(a) Auxin
(b) Ethylene
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Gibberellin
Answer:
(b) Ethylene
Question 5.
Which of the following is required for stimulation of flowering in plants?
(a) Adequate oxygen
(b) Definite photoperiod
(c) Adequate water
(d) Water and minerals
Answer:
(b) Definite photoperiod
Question 6.
For short day plants, the critical period is ………………..
(a) light
(b) dark/night
(c) UV rays
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(b) dark/night
Question 7.
Which of the following is NOT day neutral plant?
(a) Tomato
(b) Cotton
(c) Sunflower
(d) Soybean
Answer:
(d) Soybean
Question 8.
Essential macro elements are ………………..
(a) manufactured during photosynthesis
(b) produced by enzymes
(c) obtained from soil
(d) produced by growth hormones
Answer:
(c) obtained from soil
Question 9.
Function of Zinc is ………………..
(a) closing of stomata
(b) biosynthesis of 3-IAA
(c) synthesis of chlorophyll
(d) oxidation of carbohydrates
Answer:
(b) biosynthesis of 3-LAA
Question 10.
Necrosis means ………………..
(a) yellow spot on the leaves
(b) death of tissue
(c) darkening of green colour in leaves
(d) wilting of leaves
Answer:
(b) death of tissue
Question 11.
Conversion of nitrates to nitrogen is called ………………..
(a) ammonification
(b) nitrification
(c) nitrogen fixation
(d) denitrification
Answer:
(d) denitrification
Question 12.
How many molecules of ATP are required to fix one molecule of nitrogen?
(a) 12
(b) 20
(c) 6
(d) 16
Answer:
(d) 16
2. Very short answer questions
Question 1.
Enlist the phases of growth in plants.
Answer:
The three phases of growth are phase of cell division, phase of cell enlargement and phase of cell maturation.
Question 2.
Give full form of IAA.
Answer:
Full form is Indole Acetic Acid.

Question 3.
What does it mean by ‘open growth’?
Answer:
In plants the growth is indeterminate and takes place throughout the life at specific regions having meristems.
Question 4.
Plant stress hormone.
Answer:
Abscissic acid.
Question 5.
What is denitrification?
Answer:
Anaerobic bacteria can convert nitrates of soil back into nitrogen gas. That process performed by denitrifying bacteria is denitrification.
Question 6.
Bacteria responsible for conversion of nitrite to nitrate.
Answer:
Nitrobacter.
Question 7.
What is the role of gibberellins in rosette plants?
Answer:
In rosette plants like beet and cabbage, bolting, i.e. elongation of internodes before flowering is observed due to effect of gibberellins.
Question 8.
Vernalization
Answer:
The response of plant to the influence of low temperature on flowering in plants is called vernalization.
Question 9.
Photoperiodism
Answer:
The response of plant to the influence of light for initiation of flowering is known as photoperiodism.
Question 10.
What is grand period of growth?
Answer:
There are three phases of growth and the total time required for all phases to occur is called grand period of growth.
3. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
(i) Differentiation
Answer:
(ii) Redifferentiation
Answer:
Question 2.
Arithmetic growth and Geometric growth
Answer:
| Arithmetic growth | Geometric growth |
| 1. In arithmetic growth only one daughter cell continues to divide, while the other undergoes differentiation and maturation. | 1. In geometric growth both the daughter cells continue to divide and redivide again and again. |
| 2. Rate of growth is constant. | 2 Rate growth is initially slow but later on rapid rate. |
| 3. Linear curve is obtained. | 3. Exponential curve is obtained. |
| 4. Mathematical expression is Lt = Lo + rt whereLt = length of time ‘t’ Lo = Length at time zero rt = growth rate, t = time of growth |
4. Mathematical expression is Wt = Woe rt where, Wt = final size, Wo = initial size, r = growth rate, t = time of growth E = base of natural logarithm |
| 5. e.g. Elongation of root | 5. e.g. Divisions of zygote during embryo development. |
Enlist the role and deficiency symptoms of: (a) nitrogen (b) phosphorus (c) potassium.
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen:
Role : Constituent of proteins as amino acids, nucleic acids, vitamins, hormones, coenzymes, ATP and chlorophyll molecule.
Deficiency symptoms : stunted growth and chlorosis.
(b) Phosphorus:
Role : Constituent of cell membrane, certain proteins, nucleic acids and nucleotides, required for all phosphorylation reactions.
Deficiency symptoms : Poor growth, leaves dull green
(c) Potassium :
Role : Determination of anion – cation balance in cell, necessary for protein synthesis, involved in formation of cell membrane, opening and closing of stomata, activates enzymes, helps in maintenance of turgidity of cells.
Deficiency symptom : Yellow edges in leaves, premature death.

Question 4.
What is short day plant? Give any two examples.
Answer:
The plants which flower when the day length or light period is shorter than the critical photoperiod are called short day plants or SDP
SDPs usually flower during winter and late summer.
Examples – Dahlia, Aster, Tobacco, Chrysanthemum, Soybean (Glycine max) and Cocklebur (Xanthium).
Question 5.
What is vernalization? Give its significance.
Answer:
A low temperature or chilling treatment that induces early flowering in plants is known as vernalization.
Significance:
4. Long answer questions
Question 1.
Explain sigmoid growth curve with the help of diagram.
Answer:

Question 2.
Describe the types of plants on the basis of photoperiod required, with the help of suitable examples.
Answer:
1. Short day plants : Plants that flower under short day length conditions are called short day plants. Plants such as Dahlia, Xanthium, Soybean, Aster, Tobacco and Chrysanthemum are short day plants or SDR. Short day plants require a long uninterrupted dark period for flowering. Therefore, they are also called long night plants.
2. Long day plants : Plants that flower only when they are exposed to light period longer than their critical photoperiod are called long day plants or LDP Long day plants require a short dark or night period for flowering. Hence, they are also called short night plants. Plants such as radish, spinach, wheat, poppy, cabbage, pea, sugar beet, etc. are long day plants.
3. Day neutral plants : Plants in which the flowering is not affected by the day length period are called day neutral plants or DNP or photoneutral plants. Plants such as cucumber, sunflower, cotton, balsam, maize, tomato, etc. are day neutral plants.
Question 3.
Explain biological nitrogen fixation with example.
Answer:

Question 4.
Write on macro and micro nutrients required for plant growth.
Answer: