Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Textbook Solutions
Chapter 10 Halogen Derivatives Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Choose the most correct option.
Question i.
The development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own need is known as
a. Continuous development
b. Sustainable development
c. True development
d. Irrational development
Answer:
b. Sustainable development

Question ii.
Which of the following is ϒ-isomer of BHC?
a. DDT
b. lindane
c. Chloroform
d. Chlorobenzene
Answer:
b. lindane
Question iii.
The prefix ‘nano’ comes from
a. French word meaning billion
b. Greek word meaning dwarf
c. Spanish word meaning particle
d. Latin word meaning invisible
Answer:
(b) Greek word meaning dwarf
Question iv.
Which of the following information is given by FTIR technique?
a. Absorption of functional groups
b. Particle size
c. Confirmation of formation of nanoparticles
d. Crystal structure
Answer:
(a) Absorption of functional groups
Question v.
The concept of green chemistry was coined by
a. Born Haber
b. Nario Taniguchi
c. Richard Feynman
d. Paul T. Anastas
Answer:
(d) Paul T. Anastas
2. Answer the following
Question i.
Write the formula to calculate % atom economy.
Answer:

Question ii.
Name the ϒ-isomer of BHC.
Answer:
Lindane
Question iii.
Ridhima wants to detect structure of surface of materials. Name the technique she has to use.
Answer:
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Question iv.
Which nanomaterial is used for tyres of car to increase the life of tyres?
Answer:
Carbon black
Question v.
Name the scientist who discovered scanning tunneling microscope (STM) in 1980.
Answer:
Gerd Binning and Heinrich Rohrer. (Nobel prize 1986)
Question vi.
1 nm = …..m?
Answer:
1 nm = 109 m

3. Answer the following
Question i.
Define
(i) Green chemistry
(ii) sustainable development.
Answer:
(i) Green chemistry : Green chemistry is the use of chemistry for pollution prevention and it designs the use of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use or generation of hazardous substances.
(ii) Sustainable development : Sustainable development is the development that meets the needs of the present, without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Question ii.
Explain the role of green chemistry.
Answer:
When the waste and pollution that society generates exceeds the Earth’s natural capacity for dealing with it, the green chemistry approach plays an important role.
Question iii.
Give the full form (long form) of the names for the following instruments.
a. XRD
b. TEM.
c. STM
d. FTIR
e. SEM
Answer:
a. XRD-X-ray diffraction
b. TEM-Tunneling Electron Microscope
c. STM – Scanning Tunneling Microscope
d. FTIR-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscope
e. SEM-Scanning Electron Microscope
Question iv.
Define the following terms :
a. Nanoscience
b. Nanotechnology
c. Nanomaterial
d. Nanochemistry
Answer:
a. Nanoscience : The study of phenomena and manipulation of materials at atomic, molecular and macromolecular scales where properties differ significantly from those at a larger scale is called nanoscience.
b. Nanotechnology : The design, characterization, production and application of structures, device and system by controlling shape and size at nanometer scale is called nanotechnology.
c. Nanomaterial : A material having structural components with at least one dimension in the nanometer scale that is 1 -100 nm is called the nanomaterial. Nanomaterials are larger than single atoms but smaller than bacteria and cells.
d. Nanochemistry : It is the combination of chemistry and nanoscience. It deals with designing and synthesis of materials of nanoscale with different size and shape, structure and composition and their organization into functional architectures.

Question v.
How nanotechnology plays an important role in water purification techniques?
Answer:
Question vi.
Which nanomaterial is used in sunscreen lotion? Write its use.
Answer:
Zinc oxide (ZnO) and Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles are used sunscreen lotions. The chemicals protect the skin against harmful u.v (ultraviolet) rays by absorbing or reflecting the light and prevent the skin from damage.
Question vii.
How will you illustrate the use of safer solvent and auxiliaries?
Answer:
Question viii.
Define catalyst. Give two examples.
Answer:
A substance which speeds up the rate of a reaction without itself being changed chemically in the reaction is called a catalyst. It helps to increase selectivity, minimise waste and reduce reaction time and energy demands. For example : Hydrogenation of oil the catalyst used are platinum or palladium, Raney nickel.
4. Answer the following
Question i.
Explain any three principles of green chemistry.
Answer:
Question ii.
Explain atom economy with suitable example.
Answer:
(1) Atom economy is a measure of the amount of atoms from the starting material that are present in the final product at the end of a chemical process. Good atom economy means most of the atoms of the reactants are incorporated in the desired products. Only small amount of waste is produced, hence lesser problem of waste disposal.

(2) The atom economy of a process can be calculated using the following formula.
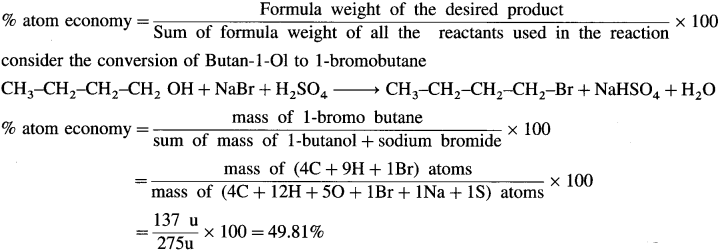
The atom economy of the above reacijon is less than 50% and waste produced is higher.
Question iii.
How will you illustrate the principle, minimization of steps?
Answer:
(1) The technique of protecting or blocking group is commonly used in organic synthesis. Finally on completion of reaction deprotection of the group is required. This leads to unnecessary increase in the number of steps and decreased atom economy.
(2) The green chemistry principle aims to develop processes to avoid necessary steps i.e. (minimization of steps). When biocatalyst is used very often there is no need for protection of selective group. For example, conversion of m-hydroxyl benzaldehyde to m-hydroxybenzoic acid.
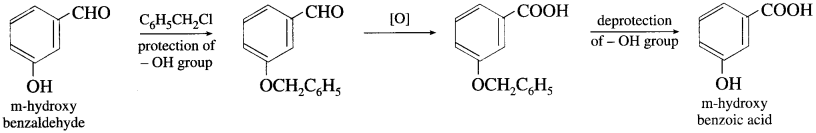
Question iv.
What do you mean by sol and gel? Describe the sol-gel method of preparation for nanoparticles.
Answer:
(1) Sol : Sols are dispersions of colloidal particles in a liquid. Colloids are solid particles with diameter of 1-100 nm.
(2) Gel : A gel is interconnected rigid network with pores of submicrometer dimensions and polymeric chains whose average length is greater than a micrometer.
(3) Sol-gel Process : A sol-gel process is an inorganic polymerisation reaction. It is generally carried out at room temperature, it includes four steps : Hydrolysis, polycondensation, drying and thermal decomposition. This method is widely used to prepare oxide materials.
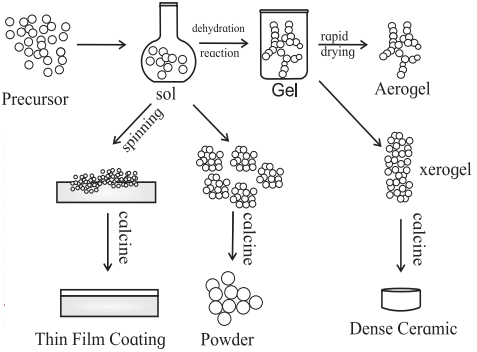
The reactions involved in the sol-gel process are as follows :
MOR + H2O → MOH + ROH (hydrolysis)
metal alkoxide
MOH + ROM → M-O-M + ROH (condensation)

Question v.
Which flower is an example of self-cleaning?
Answer:
Activity :
Collect information about the application of nanochemistry in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
12th Chemistry Digest Chapter 16 Green Chemistry and Nanochemistry Intext Questions and Answers
Do you know? (Textbook page 343)
Question 1.
Does plastic packaging impact the food they wrap ?
Answer:
Phthalates leach into food through packaging so you should avoid microwaving food or drinks in plastic and not use plastic cling wrap and store your food in glass container whenever possible. Try to avoid prepackaging, processed food so that you will reduce exposure to the harmful effects of plastic.
Used Catalyst (Textbook page 342)
Question 18.
Complete the chart:
Answer:
Chapter 10 Halogen Derivatives Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Choose the most correct option.
Question i.
The development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own need is known as
a. Continuous development
b. Sustainable development
c. True development
d. Irrational development
Answer:
b. Sustainable development

Question ii.
Which of the following is ϒ-isomer of BHC?
a. DDT
b. lindane
c. Chloroform
d. Chlorobenzene
Answer:
b. lindane
Question iii.
The prefix ‘nano’ comes from
a. French word meaning billion
b. Greek word meaning dwarf
c. Spanish word meaning particle
d. Latin word meaning invisible
Answer:
(b) Greek word meaning dwarf
Question iv.
Which of the following information is given by FTIR technique?
a. Absorption of functional groups
b. Particle size
c. Confirmation of formation of nanoparticles
d. Crystal structure
Answer:
(a) Absorption of functional groups
Question v.
The concept of green chemistry was coined by
a. Born Haber
b. Nario Taniguchi
c. Richard Feynman
d. Paul T. Anastas
Answer:
(d) Paul T. Anastas
2. Answer the following
Question i.
Write the formula to calculate % atom economy.
Answer:

Question ii.
Name the ϒ-isomer of BHC.
Answer:
Lindane
Question iii.
Ridhima wants to detect structure of surface of materials. Name the technique she has to use.
Answer:
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Question iv.
Which nanomaterial is used for tyres of car to increase the life of tyres?
Answer:
Carbon black
Question v.
Name the scientist who discovered scanning tunneling microscope (STM) in 1980.
Answer:
Gerd Binning and Heinrich Rohrer. (Nobel prize 1986)
Question vi.
1 nm = …..m?
Answer:
1 nm = 109 m

3. Answer the following
Question i.
Define
(i) Green chemistry
(ii) sustainable development.
Answer:
(i) Green chemistry : Green chemistry is the use of chemistry for pollution prevention and it designs the use of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use or generation of hazardous substances.
(ii) Sustainable development : Sustainable development is the development that meets the needs of the present, without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Question ii.
Explain the role of green chemistry.
Answer:
When the waste and pollution that society generates exceeds the Earth’s natural capacity for dealing with it, the green chemistry approach plays an important role.
Question iii.
Give the full form (long form) of the names for the following instruments.
a. XRD
b. TEM.
c. STM
d. FTIR
e. SEM
Answer:
a. XRD-X-ray diffraction
b. TEM-Tunneling Electron Microscope
c. STM – Scanning Tunneling Microscope
d. FTIR-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscope
e. SEM-Scanning Electron Microscope
Question iv.
Define the following terms :
a. Nanoscience
b. Nanotechnology
c. Nanomaterial
d. Nanochemistry
Answer:
a. Nanoscience : The study of phenomena and manipulation of materials at atomic, molecular and macromolecular scales where properties differ significantly from those at a larger scale is called nanoscience.
b. Nanotechnology : The design, characterization, production and application of structures, device and system by controlling shape and size at nanometer scale is called nanotechnology.
c. Nanomaterial : A material having structural components with at least one dimension in the nanometer scale that is 1 -100 nm is called the nanomaterial. Nanomaterials are larger than single atoms but smaller than bacteria and cells.
d. Nanochemistry : It is the combination of chemistry and nanoscience. It deals with designing and synthesis of materials of nanoscale with different size and shape, structure and composition and their organization into functional architectures.

Question v.
How nanotechnology plays an important role in water purification techniques?
Answer:
Question vi.
Which nanomaterial is used in sunscreen lotion? Write its use.
Answer:
Zinc oxide (ZnO) and Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles are used sunscreen lotions. The chemicals protect the skin against harmful u.v (ultraviolet) rays by absorbing or reflecting the light and prevent the skin from damage.
Question vii.
How will you illustrate the use of safer solvent and auxiliaries?
Answer:
Question viii.
Define catalyst. Give two examples.
Answer:
A substance which speeds up the rate of a reaction without itself being changed chemically in the reaction is called a catalyst. It helps to increase selectivity, minimise waste and reduce reaction time and energy demands. For example : Hydrogenation of oil the catalyst used are platinum or palladium, Raney nickel.
4. Answer the following
Question i.
Explain any three principles of green chemistry.
Answer:
Question ii.
Explain atom economy with suitable example.
Answer:
(1) Atom economy is a measure of the amount of atoms from the starting material that are present in the final product at the end of a chemical process. Good atom economy means most of the atoms of the reactants are incorporated in the desired products. Only small amount of waste is produced, hence lesser problem of waste disposal.

(2) The atom economy of a process can be calculated using the following formula.

The atom economy of the above reacijon is less than 50% and waste produced is higher.
Question iii.
How will you illustrate the principle, minimization of steps?
Answer:
(1) The technique of protecting or blocking group is commonly used in organic synthesis. Finally on completion of reaction deprotection of the group is required. This leads to unnecessary increase in the number of steps and decreased atom economy.
(2) The green chemistry principle aims to develop processes to avoid necessary steps i.e. (minimization of steps). When biocatalyst is used very often there is no need for protection of selective group. For example, conversion of m-hydroxyl benzaldehyde to m-hydroxybenzoic acid.

Question iv.
What do you mean by sol and gel? Describe the sol-gel method of preparation for nanoparticles.
Answer:
(1) Sol : Sols are dispersions of colloidal particles in a liquid. Colloids are solid particles with diameter of 1-100 nm.
(2) Gel : A gel is interconnected rigid network with pores of submicrometer dimensions and polymeric chains whose average length is greater than a micrometer.
(3) Sol-gel Process : A sol-gel process is an inorganic polymerisation reaction. It is generally carried out at room temperature, it includes four steps : Hydrolysis, polycondensation, drying and thermal decomposition. This method is widely used to prepare oxide materials.

The reactions involved in the sol-gel process are as follows :
MOR + H2O → MOH + ROH (hydrolysis)
metal alkoxide
MOH + ROM → M-O-M + ROH (condensation)

Question v.
Which flower is an example of self-cleaning?
Answer:
Activity :
Collect information about the application of nanochemistry in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
12th Chemistry Digest Chapter 16 Green Chemistry and Nanochemistry Intext Questions and Answers
Do you know? (Textbook page 343)
Question 1.
Does plastic packaging impact the food they wrap ?
Answer:
Phthalates leach into food through packaging so you should avoid microwaving food or drinks in plastic and not use plastic cling wrap and store your food in glass container whenever possible. Try to avoid prepackaging, processed food so that you will reduce exposure to the harmful effects of plastic.
Used Catalyst (Textbook page 342)
Question 18.
Complete the chart:
| Reaction | Name of Catalyst used |
| 1. Hydrogenation of oil (Hardening) | ………………………………… |
| 2. Haber’s process of manufacture of ammonia | ………………………………… |
| 3. Manufacture of HDPE polymer | ………………………………… |
| 4. Manufacture of H2S04 by contact process | ………………………………… |
| 5. Fischer-Tropsch process (synthesis of gasoline) | ………………………………… |
| Reaction | Name of Catalyst used |
| 1. Hydrogenation of oil (Hardening) | Nickel (Ni) |
| 2. Haber’s process of manufacture of ammonia | Iron |
| 3. Manufacture of HDPE polymer | Zeigler-Natta catalyst |
| 4. Manufacture of H2S04 by contact process | Vanadium oxide (V205) |
| 5. Fischer-Tropsch process (synthesis of gasoline) | Cobalt-based or Iron based |