Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Solutions
Chapter 4 Supply Analysis Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Complete the following statements:
Question 1.
Price elasticity of demand on a linear demand curve at the X-axis is ……………
a) zero
b) one
c) infinity
d) less than one
Answer:
a) zero

Question 2.
Price elasticity of demand on a linear demand curve at the Y-axis is equal to
a) zero
b) one
c) infinity
d) greater than one
Answer:
c) infinity
Question 3.
Demand curve is parallel to X axis, in case of …………..
a) perfectly elastic demand
b) perfectly inelastic demand
c) relatively elastic demand
d) relatively inelastic demand
Answer:
a) perfectly elastic demand
Question 4.
When percentage change in quantity demanded is more than the percentage change in price, the demand curve is ………………..
a) flatter
b) steeper
c) rectangular
d) horizontal
Answer:
a) flatter
Question 5.
Ed = 0 in case of ………………
a) luxuries
b) normal goods
c) necessities
d) comforts
Answer:
c) necessities
2. Give et onomic terms:
Question 1.
Degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded o change in income only.
Answer:
Income elasticity
Question 2.
Degree of responsiveness of a change in quantity demanded of one commodity due to change in the price of another commodity.
Answer:
Cross elasticity

Question 3.
Degree of responsiveness of a change of quantity demanded of a good to a change in its price.
Answer:
Elasticity of demand
Question 4.
Elasticity resulting from infinite change in quantity demanded.
Answer:
Perfectly elastic demand
Question 5.
Elasticity resulting from a proportionate change in quantity demanded due to a proportionate change in price.
Answer:
Price elasticity
3. Complete the correlation:
1) Perfectly elastic demand: Ed = ∞ :: ……………. : Ed = 0
2) Rectangular hyperbola : ………………. : Steeper demand curve : Relatively inelastic demand.
3) Straight line demand curve : Linear demand curve:: …………….. non linear demand curve.
4) Pen and ink : …………….. :: Tea or Coffee: Substitutes.
5) Ratio method : Ed = \(\frac{\% \Delta \mathbf{Q}}{\% \Delta \mathrm{P}}\) :: …………… : Ed = \(\frac{\text { Lower segment }}{\text { Upper segment }}\)
Answer:
4. Assertion and Reasoning type questions:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Elasticity of demand explains that one variable is influenced by another variable.
Reasoning (R) : The concept of elasticity of demand indicates the effect of price and changes in other factors on demand.
Options: 1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)

Question 2.
Assertion (A) : A change in quantity demanded of one commodity due to a change in the price of other commodity is cross elasticity.
Reasoning (R) : Changes in consumers income leads to a change in the quantity demanded.
Options:
1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Degree of price elasticity is less than one in case of relatively inelastic demand.
Reasoning (R): Change in demand is less then the change in price.
Options: 1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
5. Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Relatively elastic demand and Relatively inelastic demand.
Answer:
Relatively Elastic Demand
Relatively inelastic demand.

Question 2.
Perfectly elastic demand and Perfectly inelastic demand.
Answer:
Perfectly elastic demand :
Perfectly inelastic demand.
6. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
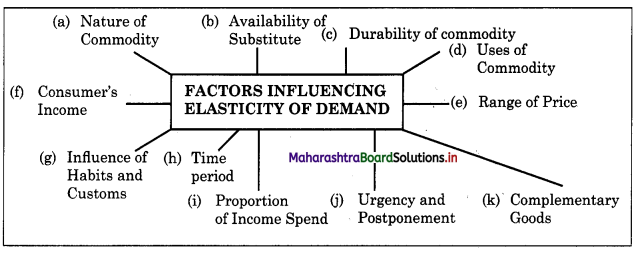
Explain the factors influencing elasticity of demand.
Answer:
The concept of Price Elasticity was developed i by great neo-classical economist Dr. Alfred \ Marshall in the year 1890.
According to Dr. Alfred Marshall, “The elasticity or responsiveness of demand in a market is great or small, according to the amount demanded which increases much or little for a given fall in price, and diminishes much or little for a given rise in price. ”
Elasticity of demand in fact refers to the £ degree of responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a commodity to change in the variable on which demand depends.
Question 2.
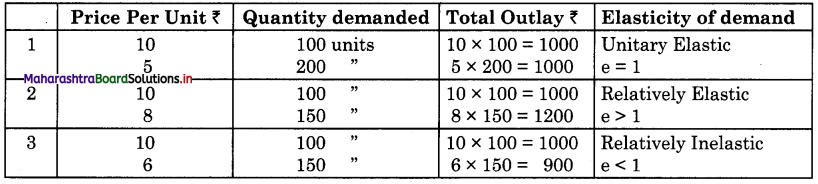
Explain the total outlay method of measuring elasticity of demand?
Answer:
Total Outlay Method : This method was introduced by Dr. Alfred Marshall. The limitation of this method is that in this method unlike ratio method, the exact numerical value of the elasticity of demand cannot be determined. According, to this method, the elasticity of demand is measured on the basis of expenditure incurred by consumer when the price of a commodity changes.
Total outlay or total expenditure can be calculated by multiplying the price with the quantity demanded (Price x Quantity demand = Total Expenditure). Depending upon the kind of change in total outlay, whether it increases, or decreases, or remain constant with the change in price we will be able to decide the type of elasticity. This can be explained with the following example:-

Question 3.
Explain importance of elasticity of demand.
Answer:
7. Observe the following figure and answer the questions:
Question 1.
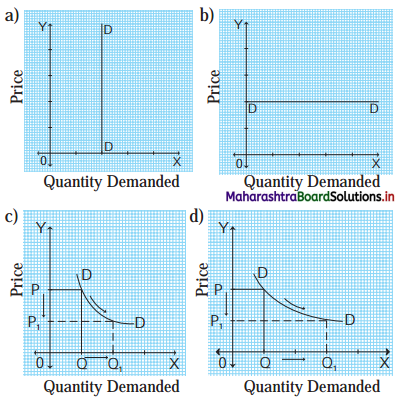
Identify and define the degrees of elasticity of demand from the following demand curves.
Answer:
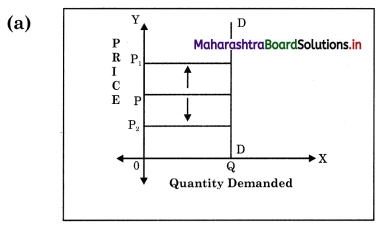
Concept: Perfectly Inelastic demand (Ed = 0) Explanation : When change in price has no effect on the quantity demanded of that commodity, then it is called as perfectly inelastic demand. Demand curve ‘DD’ is a vertical straight line parallel to ‘Y’ – axis.

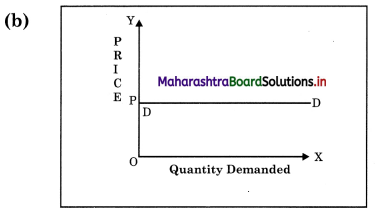
Concept: Perfectly Elastic demand (Ed = ∞) (infinity)
Explanation: When a change in price leads to infinite change in quantity demanded of a commodity then it is called as perfectly) (d) elastic demand.
Demand curve is horizontal straight line ( parallel to ‘X’ – axis.
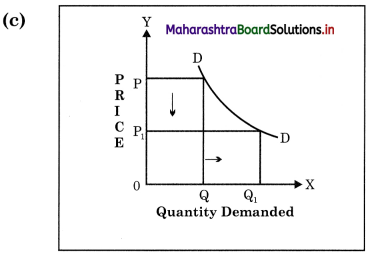
Concept: Ed = 1 Unitary elastic demand Explanation : When proportionate or percentage change in quantity demanded is exactly equal to proportionate or percentage change in price, then it is called as Unitary Elastic demand. Demand curve is called as rectangular hyperbola.
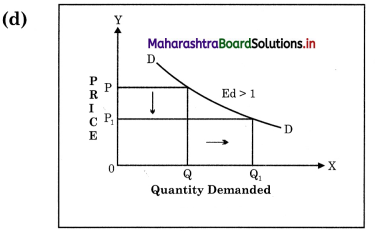
Concept: Relatively Elastic Demand (Ed > 1)
Explanation : When proportionate or percentage change in quantity demanded is more than proportionate change it its price, then it is called as Relatively Elastic Demand. Demand curve is called as flatter curve.
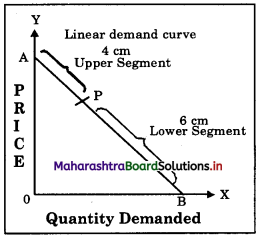
Question 2.
In the following diagram AE is the linear demand curve of a commodity. On the basis of the given diagram state whether the following statements are True or False. Give reasons to your answer.
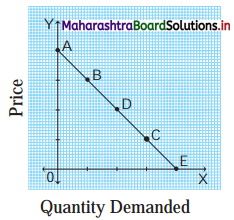
1) Demand at point ‘C’ is relatively elastic demand.
2) Demand at point ‘B’ is unitaiy elastic demand.
3) Demand at point ‘D’ is perfectly inelastic demand.
4) Demand at point ‘A’ is perfectly elastic demand.
Answer:
Chapter 4 Supply Analysis Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1. Complete the following statements:
Question 1.
Price elasticity of demand on a linear demand curve at the X-axis is ……………
a) zero
b) one
c) infinity
d) less than one
Answer:
a) zero

Question 2.
Price elasticity of demand on a linear demand curve at the Y-axis is equal to
a) zero
b) one
c) infinity
d) greater than one
Answer:
c) infinity
Question 3.
Demand curve is parallel to X axis, in case of …………..
a) perfectly elastic demand
b) perfectly inelastic demand
c) relatively elastic demand
d) relatively inelastic demand
Answer:
a) perfectly elastic demand
Question 4.
When percentage change in quantity demanded is more than the percentage change in price, the demand curve is ………………..
a) flatter
b) steeper
c) rectangular
d) horizontal
Answer:
a) flatter
Question 5.
Ed = 0 in case of ………………
a) luxuries
b) normal goods
c) necessities
d) comforts
Answer:
c) necessities
2. Give et onomic terms:
Question 1.
Degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded o change in income only.
Answer:
Income elasticity
Question 2.
Degree of responsiveness of a change in quantity demanded of one commodity due to change in the price of another commodity.
Answer:
Cross elasticity

Question 3.
Degree of responsiveness of a change of quantity demanded of a good to a change in its price.
Answer:
Elasticity of demand
Question 4.
Elasticity resulting from infinite change in quantity demanded.
Answer:
Perfectly elastic demand
Question 5.
Elasticity resulting from a proportionate change in quantity demanded due to a proportionate change in price.
Answer:
Price elasticity
3. Complete the correlation:
1) Perfectly elastic demand: Ed = ∞ :: ……………. : Ed = 0
2) Rectangular hyperbola : ………………. : Steeper demand curve : Relatively inelastic demand.
3) Straight line demand curve : Linear demand curve:: …………….. non linear demand curve.
4) Pen and ink : …………….. :: Tea or Coffee: Substitutes.
5) Ratio method : Ed = \(\frac{\% \Delta \mathbf{Q}}{\% \Delta \mathrm{P}}\) :: …………… : Ed = \(\frac{\text { Lower segment }}{\text { Upper segment }}\)
Answer:
4. Assertion and Reasoning type questions:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Elasticity of demand explains that one variable is influenced by another variable.
Reasoning (R) : The concept of elasticity of demand indicates the effect of price and changes in other factors on demand.
Options: 1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)

Question 2.
Assertion (A) : A change in quantity demanded of one commodity due to a change in the price of other commodity is cross elasticity.
Reasoning (R) : Changes in consumers income leads to a change in the quantity demanded.
Options:
1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Degree of price elasticity is less than one in case of relatively inelastic demand.
Reasoning (R): Change in demand is less then the change in price.
Options: 1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
5. Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Relatively elastic demand and Relatively inelastic demand.
Answer:
Relatively Elastic Demand
Relatively inelastic demand.

Question 2.
Perfectly elastic demand and Perfectly inelastic demand.
Answer:
Perfectly elastic demand :
Perfectly inelastic demand.
6. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Explain the factors influencing elasticity of demand.
Answer:
The concept of Price Elasticity was developed i by great neo-classical economist Dr. Alfred \ Marshall in the year 1890.
According to Dr. Alfred Marshall, “The elasticity or responsiveness of demand in a market is great or small, according to the amount demanded which increases much or little for a given fall in price, and diminishes much or little for a given rise in price. ”
Elasticity of demand in fact refers to the £ degree of responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a commodity to change in the variable on which demand depends.
Question 2.
Explain the total outlay method of measuring elasticity of demand?
Answer:
Total Outlay Method : This method was introduced by Dr. Alfred Marshall. The limitation of this method is that in this method unlike ratio method, the exact numerical value of the elasticity of demand cannot be determined. According, to this method, the elasticity of demand is measured on the basis of expenditure incurred by consumer when the price of a commodity changes.
Total outlay or total expenditure can be calculated by multiplying the price with the quantity demanded (Price x Quantity demand = Total Expenditure). Depending upon the kind of change in total outlay, whether it increases, or decreases, or remain constant with the change in price we will be able to decide the type of elasticity. This can be explained with the following example:-



Question 3.
Explain importance of elasticity of demand.
Answer:

7. Observe the following figure and answer the questions:
Question 1.
Identify and define the degrees of elasticity of demand from the following demand curves.

Answer:

Concept: Perfectly Inelastic demand (Ed = 0) Explanation : When change in price has no effect on the quantity demanded of that commodity, then it is called as perfectly inelastic demand. Demand curve ‘DD’ is a vertical straight line parallel to ‘Y’ – axis.


Concept: Perfectly Elastic demand (Ed = ∞) (infinity)
Explanation: When a change in price leads to infinite change in quantity demanded of a commodity then it is called as perfectly) (d) elastic demand.
Demand curve is horizontal straight line ( parallel to ‘X’ – axis.

Concept: Ed = 1 Unitary elastic demand Explanation : When proportionate or percentage change in quantity demanded is exactly equal to proportionate or percentage change in price, then it is called as Unitary Elastic demand. Demand curve is called as rectangular hyperbola.

Concept: Relatively Elastic Demand (Ed > 1)
Explanation : When proportionate or percentage change in quantity demanded is more than proportionate change it its price, then it is called as Relatively Elastic Demand. Demand curve is called as flatter curve.
Question 2.
In the following diagram AE is the linear demand curve of a commodity. On the basis of the given diagram state whether the following statements are True or False. Give reasons to your answer.

1) Demand at point ‘C’ is relatively elastic demand.
2) Demand at point ‘B’ is unitaiy elastic demand.
3) Demand at point ‘D’ is perfectly inelastic demand.
4) Demand at point ‘A’ is perfectly elastic demand.
Answer: