Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 History Solutions
Chapter 11 India Transformed Part 1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1A. Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the statement.
Question 1.
A legal agreement was signed in Geneva which is known as ____________
(a) SEATO
(b) NATO
(c) GATT
(d) SAARC
Answer:
(c) GATT
Question 2.
An act similar to ‘Right to Information’ was first applied in ____________ in 1776.
(a) Sweden
(b) France
(c) England
(d) India
Answer:
(a) Sweden

Question 3.
The birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda is observed as ____________
(a) National Education Day
(b) National Youth Day
(c) National Integration Day
(d) National Science Day
Answer:
(b) National Youth Day
2A. Write the names of historical places/persons/events.
Question 1.
In 2004, this became the biggest firm in Asia providing software services –
Answer:
Tata Consultancy Services
Question 2.
In 2002, the Metro railway was flagged off –
Answer:
The Delhi Metro Railway
2B. Choose the correct reason from those given below and complete the sentence.
Question 1.
India became member of World Trade Organisation, because ____________
(a) India want to compete with other nations
(b) India cannot stay aloof from the global economy
(c) India adopted the policy of liberalisation
(d) India wanted to be in the leading position at the global level
Answer:
(c) India adopted the policy of liberalisation
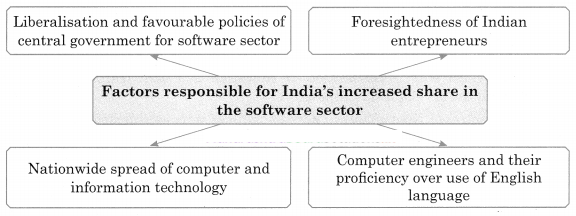
3. Complete the following concept map.
Question 1.
Answer:
4. Write short notes.
Question 1.
The Youth Policy of Government of India.
Answer:

Question 2.
‘Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana’.
Answer:
5. State your opinion.
Question 1.
India is a leading country in the field of space research.
Answer:
6. Answer the following questions in detail.
Question 1.
Which programmes were launched in India for making the opportunities of wage-earning?
Answer:
Creating employment opportunities for an ever-increasing population is a major challenge for the government. There are several programmes launched by the government of India for wage earners.
These programs are as follows:
7. Answer the following question with the help of the given points.
Question 1.
Give information about the ‘Right to Information Act.
(a) Background of the act and the beginning of this movement in India.
(b) Definition of ‘Information’.
(c) The rights of citizens under this act.
Answer:
(a) Background of the act and the beginning of this movement in India:

(b) Definition of ‘Information’:
The definition of term ‘Information’ includes official records, documents, memoranda, emails, comments, consultations, press notes, circulars, orders, logbooks, tenders, reports, correspondence, formats, models, electronic data, the information of a private institution or an individual that is available in the records of any public establishment.
(c) The rights of citizens under this act:
Class 12 History Chapter 11 India Transformed Part 1 Intext Questions and Answers
Collect information of following schemes: (Textbook Page No. 92)
National Pension Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Vima Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Vima Yojana, Atal Pension Yojana, Indian Post Payments Bank.
Answer:
(A) National Pension Scheme:
(B) Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Vima Yojana:
(C) Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Vima Yojana:
(D) Atal Pension Yojana:
(E) Indian Postal Payments Bank :

Let us know: (Textbook Page No. 92)
Collect information with the help of the internet about the ‘Rafi Ahmad Kidwai National Postal Academy (Gaziabad).

Answer:
Let us collect information (Textbook Page No. 92)
Collect information about various services like ‘Sarvabhaum Suvarn Rokhe’ (Gold Bonds issued by the Government), ‘Electronic Indian Postal Order’, ‘E-Dakghar’, ‘E-Payment Portal’, ‘Mobile App’ etc. by interviewing the Postmaster of any branch.
Answer:
(A) Sarvabhaum Suvarn Rokhe:
(B) Electronic Indian Postal Order:
(C) e-Payment portal:

(D) e-Dak Ghar:
The e-Post Office of India post offers a variety of online Postal services to the users. One can avail services-philately (purchase of stamps), PLI/RPLI (payment of the premium), and IPO (purchase order for RTI).
(E) Mobile app:
Project (Textbook Page No. 98)
Collect information about the States of India and Union Territories, as well as the names of their capital cities, with the help of the internet.
Answer:
The states of India and its capitals are as follows:
Union Territories and its Capitals:
Chapter 11 India Transformed Part 1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1A. Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the statement.
Question 1.
A legal agreement was signed in Geneva which is known as ____________
(a) SEATO
(b) NATO
(c) GATT
(d) SAARC
Answer:
(c) GATT
Question 2.
An act similar to ‘Right to Information’ was first applied in ____________ in 1776.
(a) Sweden
(b) France
(c) England
(d) India
Answer:
(a) Sweden

Question 3.
The birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda is observed as ____________
(a) National Education Day
(b) National Youth Day
(c) National Integration Day
(d) National Science Day
Answer:
(b) National Youth Day
2A. Write the names of historical places/persons/events.
Question 1.
In 2004, this became the biggest firm in Asia providing software services –
Answer:
Tata Consultancy Services
Question 2.
In 2002, the Metro railway was flagged off –
Answer:
The Delhi Metro Railway
2B. Choose the correct reason from those given below and complete the sentence.
Question 1.
India became member of World Trade Organisation, because ____________
(a) India want to compete with other nations
(b) India cannot stay aloof from the global economy
(c) India adopted the policy of liberalisation
(d) India wanted to be in the leading position at the global level
Answer:
(c) India adopted the policy of liberalisation
3. Complete the following concept map.
Question 1.

Answer:

4. Write short notes.
Question 1.
The Youth Policy of Government of India.
Answer:

Question 2.
‘Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana’.
Answer:
5. State your opinion.
Question 1.
India is a leading country in the field of space research.
Answer:
6. Answer the following questions in detail.
Question 1.
Which programmes were launched in India for making the opportunities of wage-earning?
Answer:
Creating employment opportunities for an ever-increasing population is a major challenge for the government. There are several programmes launched by the government of India for wage earners.
These programs are as follows:
7. Answer the following question with the help of the given points.
Question 1.
Give information about the ‘Right to Information Act.
(a) Background of the act and the beginning of this movement in India.
(b) Definition of ‘Information’.
(c) The rights of citizens under this act.
Answer:
(a) Background of the act and the beginning of this movement in India:

(b) Definition of ‘Information’:
The definition of term ‘Information’ includes official records, documents, memoranda, emails, comments, consultations, press notes, circulars, orders, logbooks, tenders, reports, correspondence, formats, models, electronic data, the information of a private institution or an individual that is available in the records of any public establishment.
(c) The rights of citizens under this act:
Class 12 History Chapter 11 India Transformed Part 1 Intext Questions and Answers
Collect information of following schemes: (Textbook Page No. 92)
National Pension Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Vima Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Vima Yojana, Atal Pension Yojana, Indian Post Payments Bank.
Answer:
(A) National Pension Scheme:
(B) Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Vima Yojana:
(C) Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Vima Yojana:
(D) Atal Pension Yojana:
(E) Indian Postal Payments Bank :

Let us know: (Textbook Page No. 92)
Collect information with the help of the internet about the ‘Rafi Ahmad Kidwai National Postal Academy (Gaziabad).

Answer:
Let us collect information (Textbook Page No. 92)
Collect information about various services like ‘Sarvabhaum Suvarn Rokhe’ (Gold Bonds issued by the Government), ‘Electronic Indian Postal Order’, ‘E-Dakghar’, ‘E-Payment Portal’, ‘Mobile App’ etc. by interviewing the Postmaster of any branch.
Answer:
(A) Sarvabhaum Suvarn Rokhe:
(B) Electronic Indian Postal Order:
(C) e-Payment portal:

(D) e-Dak Ghar:
The e-Post Office of India post offers a variety of online Postal services to the users. One can avail services-philately (purchase of stamps), PLI/RPLI (payment of the premium), and IPO (purchase order for RTI).
(E) Mobile app:
Project (Textbook Page No. 98)
Collect information about the States of India and Union Territories, as well as the names of their capital cities, with the help of the internet.
Answer:
The states of India and its capitals are as follows:
| States | Capital |
| 1. Andhra Pradesh | Hyderabad |
| 2. Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar |
| 3. Assam | Dispur |
| 4. Bihar | Patna |
| 5. Chhattisgarh | Raipur |
| 6. Goa | Panaji |
| 7. Gujrat | Gandhinagar |
| 8. Haryana | Chandigarh |
| 9. Himachal Pradesh | Shimla |
| 10. Jharkhand | Ranchi |
| 11. Karnataka | Bengaluru |
| 12. Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram |
| 13. Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal |
| 14. Maharashtra | Mumbai |
| 15. Manipur | Imphal |
| 16. Meghalaya | Shillong |
| 17. Mizoram | Aizawl |
| 18. Nagaland | Kohima |
| 19. Odisha | Bhubaneswar |
| 20. Punjab | Chandigarh |
| 21. Rajasthan | Jaipur |
| 22. Sikkim | Gangtok |
| 23. Telangana | Hyderabad |
| 24. Tamil Nadu | Chennai |
| 25. Tripura | Agartala |
| 26. Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow |
| 27. West Bengal | Kolkata |
| 28. Uttarakhand | Dehradun |
| Union Territories | Capitals |
| 1. Anadaman and Nicobar Island | Port Blair |
| 2. Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| 3. Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | Daman |
| 4. Delhi | New Delhi |
| 5. Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| 6. Puducherry | Pondicherry |
| 7. Ladakh | Leh (summer), Kargil (winter) |
| 8. Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (summer) Jammu (winter) |