Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 History Solutions
Chapter 4 Colonialism and the Marathas Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1A. Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the statement.
Question 1.
Marathas defeated the Portuguese during the siege of __________
(a) Vengurla
(b) Phonda
(c) Surat
(d) Rajapur
Answer:
(b) Phonda
Question 2.
The political relations between Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj and the British began due to the __________ episode.
(a) Kudal campaign
(b) Afzal Khan
(c) Fazal Khan
(d) coronation
Answer:
(b) Afzal Khan

Question 3.
The younger brother of Bajirao Peshwa I defeated the __________ at Vasai.
(a) British
(b) French
(c) Dutch
(d) Portuguese
Answer:
(d) Portuguese
Question 4.
The ‘Third Battle of Panipat’ was fought between Marathas and the __________
(a) British
(b) Abdali
(c) Ahmed Khan Bangash
(d) Najib Khan
Answer:
(b) Abdali
1B. Find the incorrect pair from group ‘B’ and write the corrected one.
Question 1.
Answer:
(c) Francois Martin – Governor General of Pondicherry
2A. Write the names of historical places/persons/events.
Question 1.
The first Europeans to arrive in India-
Answer:
Portuguese
Question 2.
The place where the Portuguese stored their ammunition-
Answer:
Panvel

Question 3.
They honoured Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj with tributes for ensuring the safety of their factories and issuing trade permits-
Answer:
The Dutch
Question 4.
The British agent at Jaitapur-
Answer:
Velaji
2B. Choose the correct reason from those given below and complete the sentence.
Question 1.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj levied octroi on the salt trade to __________
(a) oppose the Portuguese
(b) stop the British trade of salt
(c) raise funds for Swarajya
(d) oppose the colonialists
Answer:
(b) stop the British trade of salt
3. State your opinion.
Question 1.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj built a naval force.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj had foreseen the ulterior motives of the foreigners and their ways of infiltration. He built strategies to arrest their advances in India. He took immediate measures by creating a strong naval force. He levied octroi on British trade salt as a measure to protect the local salt trade. Thus, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj adopted a strong policy against the European colonizers.
Question 2.
Maratha’s policies were anti-colonial.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj had foreseen the ulterior motives of the Europeans and their ways of infiltration. So, he built strategies to arrest their advances in India. Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj adopted a very strong policy against the European colonisers by levying octroi on the British salt trade etc. The Marathas were the only Indian rulers to adopt a policy of resistance against the European colonisers.
4. Answer the following questions in detail.
Question 1.
Write about Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s policies regarding the European traders as seen in his Adnyapatra.
Answer:
The strategy of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj against the Europeans is clearly seen in Adnyapatra.
The following were his policies:

Question 2.
Explain Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s resolute policy of safeguarding Maratha sovereignty.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj took several steps to safeguard the Maratha empire.
Question 3.
Why did the strongest Maratha rule come to an end?
Answer:
There were several reasons for the downfall of the Maratha empire:
(i) Internal weakness of the Maratha Empire: The empire of the Marathas was not well knit. It was a confederacy of the Maratha chiefs who were in conflict with one another. The nominal unity of the Marathas remained only up to the period of the rule of Madhav Rao I.
(ii) Lack of Political Foresight: The Marathas lacked wisdom and farsightedness. They failed to achieve the political unity of India and therefore failed to utilise the resources of the country either for the benefit of the people or for meeting the challenge of a foreign foe.
(iii) Incapable Leadership: All capable Maratha chiefs died by the end of the eighteenth century. After that the leadership of the Marathas was taken over by Bajirao II, Daulatrao Scindia, Yashwant Rao Holkar, and Nana Phadnavis. The Marathas thus lacked leadership.
(iv) Military weakness of the Marathas: The Marathas were militarily weak compared to the English as they had left their traditional method of guerrilla warfare and adopted European methods which they failed to perfect.
(v) Diplomacy of the English: The English were more diplomatic than the Marathas. The quarrels among the Marathas provided a good opportunity for the English to take advantage. Besides, the English had their eyes on the politics of the entire India.
5. Observe the map on textbook page 29 and answer the questions based on it.
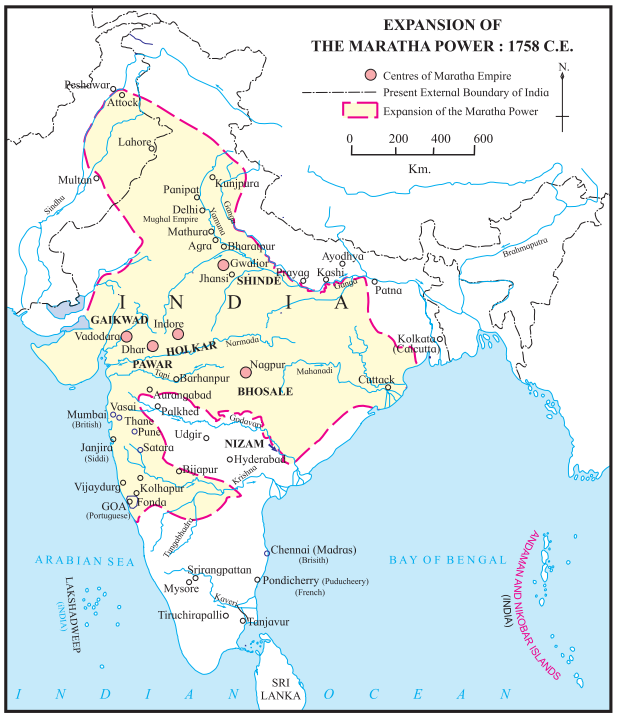
Question 1.
Where were the Dutch colonies on the west coast of India?
Answer:
On the west coast of India, there were warehouses at Vengurla in Konkan and at Photo Novo (Parangi Pettai) and Tegna Pattam (Devanapattinam) in Karnataka.

Question 2.
Where did the French establish their colonies on the east coast of India?
Answer:
The French had their colony in Pondicherry (Puducherry) on the east coast.
Question 3.
Whose warehouses were at Agra and Allahabad?
Answer:
This warehouse is not mentioned on the map. This area was ruled by the Mughals.
Project (Textbook Page No. 33)
Question 1.
Collect information about the colonies established by the European colonialists in various countries with the help of internet.
Answer:
The European colonialists had their colonies in the following countries.
(A) Africa:
(B) Asia:
(C) North America:

(D) South America:
Chapter 4 Colonialism and the Marathas Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1A. Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the statement.
Question 1.
Marathas defeated the Portuguese during the siege of __________
(a) Vengurla
(b) Phonda
(c) Surat
(d) Rajapur
Answer:
(b) Phonda
Question 2.
The political relations between Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj and the British began due to the __________ episode.
(a) Kudal campaign
(b) Afzal Khan
(c) Fazal Khan
(d) coronation
Answer:
(b) Afzal Khan

Question 3.
The younger brother of Bajirao Peshwa I defeated the __________ at Vasai.
(a) British
(b) French
(c) Dutch
(d) Portuguese
Answer:
(d) Portuguese
Question 4.
The ‘Third Battle of Panipat’ was fought between Marathas and the __________
(a) British
(b) Abdali
(c) Ahmed Khan Bangash
(d) Najib Khan
Answer:
(b) Abdali
1B. Find the incorrect pair from group ‘B’ and write the corrected one.
Question 1.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (a) Cosme da Guarda | Portuguese historian |
| (b) Gonsalo Martez | Portuguese emissary |
| (c) Francois Martin | Chief of the Dutch factory |
| (d) Henry Revington | British Officer |
(c) Francois Martin – Governor General of Pondicherry
2A. Write the names of historical places/persons/events.
Question 1.
The first Europeans to arrive in India-
Answer:
Portuguese
Question 2.
The place where the Portuguese stored their ammunition-
Answer:
Panvel

Question 3.
They honoured Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj with tributes for ensuring the safety of their factories and issuing trade permits-
Answer:
The Dutch
Question 4.
The British agent at Jaitapur-
Answer:
Velaji
2B. Choose the correct reason from those given below and complete the sentence.
Question 1.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj levied octroi on the salt trade to __________
(a) oppose the Portuguese
(b) stop the British trade of salt
(c) raise funds for Swarajya
(d) oppose the colonialists
Answer:
(b) stop the British trade of salt
3. State your opinion.
Question 1.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj built a naval force.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj had foreseen the ulterior motives of the foreigners and their ways of infiltration. He built strategies to arrest their advances in India. He took immediate measures by creating a strong naval force. He levied octroi on British trade salt as a measure to protect the local salt trade. Thus, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj adopted a strong policy against the European colonizers.
Question 2.
Maratha’s policies were anti-colonial.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj had foreseen the ulterior motives of the Europeans and their ways of infiltration. So, he built strategies to arrest their advances in India. Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj adopted a very strong policy against the European colonisers by levying octroi on the British salt trade etc. The Marathas were the only Indian rulers to adopt a policy of resistance against the European colonisers.
4. Answer the following questions in detail.
Question 1.
Write about Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s policies regarding the European traders as seen in his Adnyapatra.
Answer:
The strategy of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj against the Europeans is clearly seen in Adnyapatra.
The following were his policies:

Question 2.
Explain Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’s resolute policy of safeguarding Maratha sovereignty.
Answer:
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj took several steps to safeguard the Maratha empire.
Question 3.
Why did the strongest Maratha rule come to an end?
Answer:
There were several reasons for the downfall of the Maratha empire:
(i) Internal weakness of the Maratha Empire: The empire of the Marathas was not well knit. It was a confederacy of the Maratha chiefs who were in conflict with one another. The nominal unity of the Marathas remained only up to the period of the rule of Madhav Rao I.
(ii) Lack of Political Foresight: The Marathas lacked wisdom and farsightedness. They failed to achieve the political unity of India and therefore failed to utilise the resources of the country either for the benefit of the people or for meeting the challenge of a foreign foe.
(iii) Incapable Leadership: All capable Maratha chiefs died by the end of the eighteenth century. After that the leadership of the Marathas was taken over by Bajirao II, Daulatrao Scindia, Yashwant Rao Holkar, and Nana Phadnavis. The Marathas thus lacked leadership.
(iv) Military weakness of the Marathas: The Marathas were militarily weak compared to the English as they had left their traditional method of guerrilla warfare and adopted European methods which they failed to perfect.
(v) Diplomacy of the English: The English were more diplomatic than the Marathas. The quarrels among the Marathas provided a good opportunity for the English to take advantage. Besides, the English had their eyes on the politics of the entire India.
5. Observe the map on textbook page 29 and answer the questions based on it.

Question 1.
Where were the Dutch colonies on the west coast of India?
Answer:
On the west coast of India, there were warehouses at Vengurla in Konkan and at Photo Novo (Parangi Pettai) and Tegna Pattam (Devanapattinam) in Karnataka.

Question 2.
Where did the French establish their colonies on the east coast of India?
Answer:
The French had their colony in Pondicherry (Puducherry) on the east coast.
Question 3.
Whose warehouses were at Agra and Allahabad?
Answer:
This warehouse is not mentioned on the map. This area was ruled by the Mughals.
Project (Textbook Page No. 33)
Question 1.
Collect information about the colonies established by the European colonialists in various countries with the help of internet.
Answer:
The European colonialists had their colonies in the following countries.
(A) Africa:
(B) Asia:
(C) North America:

(D) South America: