Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Secretarial Practice Solutions
Chapter 2 Sources of Corporate Finance Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1A. Select the correct answer from the options given below and rewrite the statements.
Question 1.
___________ is the smallest unit in the total share capital of the company.
(a) Debenture
(b) Bonds
(c) Share
Answer:
(c) Share
Question 2.
The benefit of Depository Receipt is ability to raise capital in ___________ market.
(a) national
(b) local
(c) international
Answer:
(c) international

Question 3.
___________ are residual claimants against the income or assets of the company.
(a) Bondholders
(b) Equity shareholders
(c) Debenture holders
Answer:
(b) Equity shareholders
Question 4.
___________ participate in the management of their company.
(a) Preference shareholders
(b) Depositors
(c) Equity shareholders.
Answer:
(c) Equity shareholders
Question 5.
___________ shares are issued free of cost to existing equity shareholders.
(a) Bonus
(b) Right
(c) Equity
Answer:
(a) Bonus
Question 6.
The holder of preference share has the right to receive ___________ rate of dividend.
(a) fixed
(b) fluctuating
(c) lower
Answer:
(a) Fixed
Question 7.
Accumulated dividend is paid to ___________ preference shares.
(a) redeemable
(b) cumulative
(c) convertible
Answer:
(b) Cumulative

Question 8.
The holder of ___________ preference shares has the right to convert their shares into equity shares.
(a) cumulative
(b) convertible
(c) redeemable
Answer:
(b) Convertible
Question 9.
Debenture holders are ___________ of the company.
(a) creditors
(b) owners
(c) suppliers
Answer:
(a) creditors
Question 10.
___________ is paid on borrowed capital.
(a) Interest
(b) Discount
(c) Dividend
Answer:
(a) Interest
Question 11.
Debenture holders get fixed rate of ___________ return on their investment.
(a) interest
(b) dividend
(c) discount
Answer:
(a) interest
Question 12.
Convertible debentures are converted into ___________ after a specific period.
(a) equity shares
(b) deposits
(c) bonds
Answer:
(a) equity shares

Question 13.
Retained earnings are ___________ source of financing.
(a) internal
(b) external
(c) additional
Answer:
(a) internal
Question 14.
The holder of bond is ___________ of the company.
(a) secretary
(b) owner
(c) creditor
Answer:
(c) creditor
Question 15.
Company can accept deposits from public, minimum for ___________ months.
(a) six
(b) nine
(c) twelve
Answer:
(a) six
Question 16.
Company can accept deposits from public maximum for ___________ months.
(a) 12
(b) 24
(c) 36
Answer:
(c) 36

Question 17.
A depository receipt traded in ___________ is called American Depository Receipt.
(a) London
(b) Japan
(c) USA
Answer:
(c) the USA
1B. Match the pairs.
Question 1.
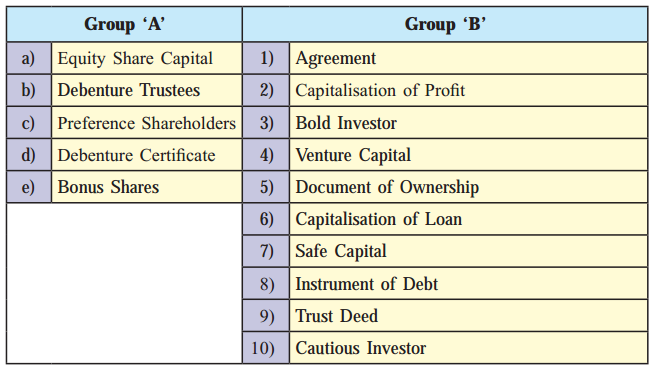
Answer:
1C. Write a word or a term or a phrase that can substitute each of the following statements.
Question 1.
The real masters of the company.
Answer:
Equity shareholders
Question 2.
A document of ownership of shares.
Answer:
Share certificate
Question 3.
The holders of these shares are entitled to participate in surplus profits.
Answer:
Participating preference shares
Question 4.
A party through whom the company deals with debenture holders.
Answer:
Debenture trustees

Question 5.
Name the shareholder who participates in the management.
Answer:
Equity shareholders
Question 6.
The value of a share is written on the share certificate.
Answer:
Face value
Question 7.
The value of a share is determined by demand and supply forces in the share market.
Answer:
Market value
Question 8.
The policy of using undistributed profit for the business.
Answer:
Retained earnings/ploughing back of profit
Question 9.
It is an acknowledgment of a loan issued by the company to the depositor.
Answer:
Deposit receipt

Question 10.
A dollar-denominated instrument trader in the USA.
Answer:
American Depository Receipt
Question 11.
The Depository Receipt is traded in a country other than the USA.
Answer:
Global depository receipt
Question 12.
Money raised by the company from the public for a minimum of 6 months to a maximum of 39 months.
Answer:
Public Deposits
Question 13.
Credit extended by the suppliers with an intention to increase their sales.
Answer:
Trade Credit
Question 14.
The credit facility is provided to a company having a current account with the bank.
Answer:
Overdraft
1D. State Whether the following statements are True or False.
Question 1.
Equity share capital is known as venture capital.
Answer:
True

Question 2.
Equity shareholders enjoy a fixed rate of dividends.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Debenture holders have the right to vote at a general meeting of the company.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Equity shareholders are described as ‘shock absorbers’ when a company has a financial crisis.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Bondholders are owners of the company.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Cash credit is given against hypothecation of goods and security.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
Trade credit is a major source of long-term finance.
Answer:
False

Question 8.
Depository bank stores the shares on behalf of the GDR holder.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
Financial institutions underwrite the issue of securities.
Answer:
True
1E. Find the odd one.
Question 1.
Debenture, Public Deposit, Retained Earnings
Answer:
Retained earnings
Question 2.
Face value, Market value, Redemption value
Answer:
Redemption value
Question 3.
Share certificate, Debenture certificate, ADR
Answer:
ADR
Question 4.
Trade credit, Overdraft, Cash credit
Answer:
Trade credit
1F. Complete the sentences.
Question 1.
The finance needed by business organisation is termed as ___________
Answer:
Capital

Question 2.
The convertible preference shareholders have a right to convert their shares into ___________
Answer:
Equity shares
Question 3.
Equity shareholders elect their representative Called ___________
Answer:
Directors
Question 4.
Bonus shares are issued as gift to ___________
Answer:
Equity share holders
Question 5.
The bondholders are ___________of the company.
Answer:
Creditors
Question 6.
Depository receipt traded in a country other than USA is called ___________
Answer:
Global Depository Receipt

Question 7.
First Industrial policy was declared in the year ___________
Answer:
1948
Question 8.
When goods are delivered by the supplier to the customer on the basis of deferred payment is called as ___________
Answer:
Trade credit
1G. Select the correct option from the bracket.
Question 1.
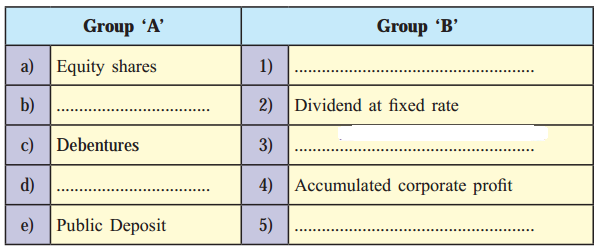
(Fluctuating rate of dividend, Preference shares, Interest at fixed rate, Retained earnings, short term loan)
Answer:
1H. Answer in one sentence.
Question 1.
What is a share?
Answer:
A share is the smallest unit of the share capital of a company.
Question 2.
What are equity shares?
Answer:
Equity shares are shares that do not preference shares and do not carry priority in receiving dividends nor repayment of capital.
Question 3.
What are preference shares?
Answer:
Preference shares are shares that have preferential rights with regard to receiving dividends and repayment of capital.

Question 4.
What are retained earnings?
Answer:
A part of the net profit which is not distributed to shareholders as dividend but retained by the company as reserve fund is retained earnings.
Question 5.
What is a debenture?
Answer:
It is a document/instrument issued in the form of a debenture certificate under the common seal of the company acknowledging/evidencing the debt.
Question 6.
What is a bond?
Answer:
A bond is a debt security and a formal contract to repay borrowed money with interest.
Question 7.
In which country can ADR be issued?
Answer:
ADR (American Depository Receipt) is a depository Receipt that is issued in the USA.

Question 8.
In which country can GDR be issued?
Answer:
GDR (Global depository receipt) can be issued in countries other than the USA.
Question 9.
What are convertible debentures?
Answer:
Convertible debentures are debentures that are converted into equity shares after a specific period as specified at the time of issue.
Question 10.
What are cumulative preference shares?
Answer:
Cumulative preference shares are shares where dividend, if not paid in a year accumulates till it is paid.
1I. Correct the underlined words and rewrite the following sentences.
Question 1.
Owned capital is temporary capital.
Answer:
Owned capital is permanent capital.
Question 2.
Equity shares get dividends at a fixed rate.
Answer:
Equity shares get dividends at fluctuating rates.

Question 3.
Preference shares get dividends at fluctuating rates.
Answer:
Preference shares get dividends at a fixed rate.
Question 4.
Retained earnings are an external source of finance.
Answer:
Retained earnings are an internal source of finance.
Question 5.
The debenture holder is the owner of the company.
Answer:
The debenture holder is a creditor of the company.
Question 6.
Bond is a source of short-term finance.
Answer:
Bond is a source of long-term finance.
Question 7.
Depository receipt traded in the USA is called Global Depository Receipt.
Answer:
Depository receipt traded in the USA is called American Depository Receipt.
2. Explain the following terms/Concepts.
Question 1.
Borrowed capital
Answer:
Question 2.
Owned capital
Answer:
Question 3.
Ploughing back of profit
Answer:

Question 4.
Overdraft
Answer:
Question 5.
Trade Credit
Answer:
3. Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
1. The Balance sheet of a Donald Company for the year 2018-19 reveals equity share capital of Rs. 25,00,000 and retained earnings of Rs. 50,00,000.
Question (a).
Is the company financially sound?
Answer:
The company is financially sound as it has double the amount as reserves or retained earnings or kept aside profits.
Question (b).
Can the retained earnings be converted into capital?
Answer:
Yes, the retained earnings can be converted into capital by means of capitalisation of reserves.
Question (c).
What type of source retained earning is?
Answer:
Retained earning is self-financing or an internal source of finance.
2. Mr. Satish is a speculator. He desires to take advantage of the growing market for the company’s products and earn handsomely.
Question (a).
According to you, which type of share Mr. Satish will choose to invest in.
Answer:
As Mr. Satish is a speculator, he will choose equity shares to invest in because if there are good earnings/profits, so will be the rate of dividend.

Question (b).
What does he receive as a return on investment?
Answer:
He receives a fluctuating rate of dividends.
Question (C).
State anyone, right he will enjoy as a shareholder.
Answer:
The right to attend the meeting and vote on resolutions can be the right Mr. Satish can exercise as a member.
3. Mr. Rohit, an individual investor, invests his own funds in the securities. He depends on investment income and does not want to take any risk. He is interested in the definite rate of income and safety of the principal.
Question (a).
Name the type of security that Mr. Rohit will opt for.
Answer:
As Mr. Rohit does not want to take risks, he will opt for preference shares which will assure him of steady income and safety of his investment.
Question (b).
What does he receive as a return on his investment?
Answer:
Mr. Rohit will receive dividends in return.
Question (c).
The return on investment which he receives is fixed or fluctuating.
Answer:
The return on his investment will be fixed and not fluctuating.
4. Distinguish between the following.
Question 1.
Equity Shares and Preference Shares
Answer:
Question 2.
Shares and Debentures
Answer:

Question 3.
Owned Capital and Borrowed Capital
Answer:
5. Answer in brief:
Question 1.
What is a public deposit?
Answer:
Advantages of deposits to the company
Question 2.
What are Global Depository Receipt and American Depository Receipt?
Answer:

Question 3.
What is Trade Credit?
Answer:
Advantages of Trade Credit:
Question 4.
What are the schemes for disbursement of credit by banks?
Answer:
Meaning: Banks play an important role in terms of providing finance to the companies.
They provide short-term finance for working capital, in the form of bank and trade credits.
The innovative schemes by banks for disbursement of credit are as follows:
(i) Overdraft:
(ii) Cash Credit:
(iii) Cash Loans:
(iv) Discounting bills of exchange:

Question 5.
State the features of bonds.
Answer:
Definition:
According to Webster Dictionary, “a bond is an interest bearing certificate issued by a Government or business firm promising to pay the holder a specific sum at a specified date”.
A bond is thus-
Features:
(i) Nature of finance:
(ii) Status of investor:
(iii) Return on bonds:
(iv) Repayment:
6. Justify the following statements:
Question 1.
Equity shareholders are real owners and controllers of the company.
Answer:
Question 2.
Preference Shares do not carry normal voting rights.
Answer:

Question 3.
The debenture is secured by a charge on assets of the company.
Answer:
Question 4.
Retained earnings are the simple and cheapest method of raising finance.
Answer:
Question 5.
Public deposit is a good source of short-term financing.
Answer:
Question 6.
The bondholder is a creditor of the company.
Answer:
Question 7.
Trade credit is not a cash loan.
Answer:

Question 8.
Different investors have different preferences.
Answer:
Question 9.
Equity Capital is risk capital.
Answer:
7. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What are a share and state its features?
Answer:
Features of shares:
(i) Meaning:
(ii) Ownership:
(iii) Distinctive number:

(iv) Evidence of title:
(v) Value of a share:
(vi) Rights:
(vii) Income:
(viii) Transferability:
(ix) Property of shareholder:
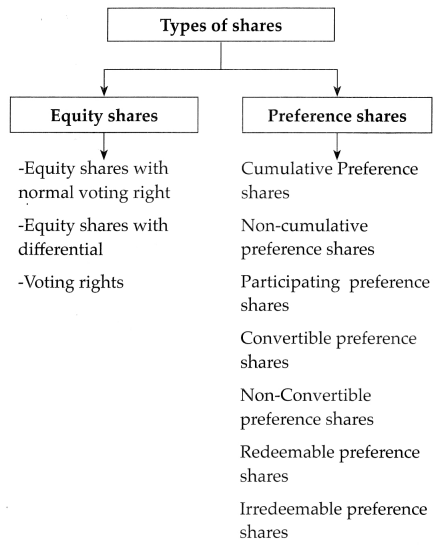
(x) Kinds of shares:
Question 2.
What is an equity share? Explain its features.
Answer:
Features of equity shares:
(i) Permanent Capital:
(ii) Fluctuating dividend:

(iii) Rights:
(iv) No preferential right:
(v) Controlling power:
(vi) Risk:
(vii) Residual claimants:
(viii) No charge on assets:
(ix) Bonus issue:

(x) Rights issue:
(xi) Face value:
(xii) Market value:
(xiii) Capital Appreciation:
Question 3.
Define preference shares/What are preference shares? What are the different types of preference shares?
Answer:
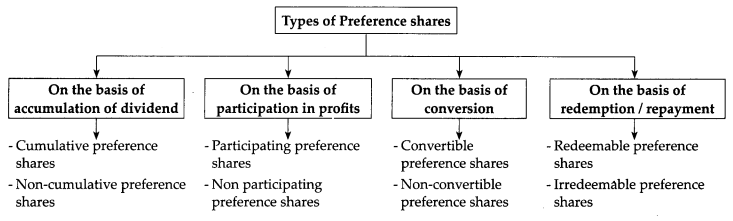
(i) Cumulative Preference Shares:
(ii) Non-Cumulative Preference Shares:
(iii) Participating Preference Shares:
(iv) Non-Participating Preference Shares:
(v) Convertible Preference Shares:
(vi) Non-Convertible Preference Shares:

(vii) Redeemable Preference Shares:
(viii) Irredeemable Preference Shares:
Question 4.
What are preference shares? State its features.
Answer:
Features of preference shares:
(i) Preference for dividend:
(ii) Prior repayment of capital:
(iii) Fixed return:
(iv) Nature of capital:
(v) Market value:
(vi) Voting right:
(vii) Risk:

(viii) Face value:
(ix) Right or Bonus issue:
(x) Nature of investor:
Question 5.
What is Debenture/Define Debenture. Discuss the different types of Debentures.
Answer:
Definitions:
Topham defines: “A debenture is a document given by a company as evidence of debt to the holder, usually arising out of the loan and most commonly secured by the charge.”
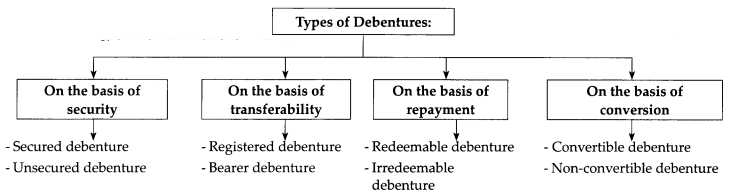
They are as follows:
(i) Secured Debentures:
(ii) Unsecured Debentures:
(iii) Registered Debentures:
(iv) Bearer Debentures:

(v) Redeemable Debentures:
(vi) Irredeemable Debentures:
(vii) Convertible Debentures:
(viii) Non-Convertible Debentures:
Question 6.
Define Debenture/What is a debenture? Explain the features of debenture?
Answer:
Definitions:
Topham defines: “A debenture is a document given by a company as evidence of debt to the holder, usually arising out of the loan and most commonly secured by the charge.”
A debenture is evidence of indebtedness.
Features of Debenture:
(i) Written Promise:
(ii) Face Value:
(iii) Time of payment:
(iv) Priority of Payment:
(v) Assurance of repayment:

(vi) Terms of issue and redemption of Debenture:
(vii) Authority to issue:
Board of Directors has the authority/power to issue debenture as per Companies Act 2013 Section 179(3).
(viii) Interest:
(ix) Parties to Debenture:
(x) Status of debenture holder:
(xi) No Voting Right:
(xii) Security:
(xiii) Issuers:

(xiv) Listing:
(xv) Transferability:
Chapter 2 Sources of Corporate Finance Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
1A. Select the correct answer from the options given below and rewrite the statements.
Question 1.
___________ is the smallest unit in the total share capital of the company.
(a) Debenture
(b) Bonds
(c) Share
Answer:
(c) Share
Question 2.
The benefit of Depository Receipt is ability to raise capital in ___________ market.
(a) national
(b) local
(c) international
Answer:
(c) international

Question 3.
___________ are residual claimants against the income or assets of the company.
(a) Bondholders
(b) Equity shareholders
(c) Debenture holders
Answer:
(b) Equity shareholders
Question 4.
___________ participate in the management of their company.
(a) Preference shareholders
(b) Depositors
(c) Equity shareholders.
Answer:
(c) Equity shareholders
Question 5.
___________ shares are issued free of cost to existing equity shareholders.
(a) Bonus
(b) Right
(c) Equity
Answer:
(a) Bonus
Question 6.
The holder of preference share has the right to receive ___________ rate of dividend.
(a) fixed
(b) fluctuating
(c) lower
Answer:
(a) Fixed
Question 7.
Accumulated dividend is paid to ___________ preference shares.
(a) redeemable
(b) cumulative
(c) convertible
Answer:
(b) Cumulative

Question 8.
The holder of ___________ preference shares has the right to convert their shares into equity shares.
(a) cumulative
(b) convertible
(c) redeemable
Answer:
(b) Convertible
Question 9.
Debenture holders are ___________ of the company.
(a) creditors
(b) owners
(c) suppliers
Answer:
(a) creditors
Question 10.
___________ is paid on borrowed capital.
(a) Interest
(b) Discount
(c) Dividend
Answer:
(a) Interest
Question 11.
Debenture holders get fixed rate of ___________ return on their investment.
(a) interest
(b) dividend
(c) discount
Answer:
(a) interest
Question 12.
Convertible debentures are converted into ___________ after a specific period.
(a) equity shares
(b) deposits
(c) bonds
Answer:
(a) equity shares

Question 13.
Retained earnings are ___________ source of financing.
(a) internal
(b) external
(c) additional
Answer:
(a) internal
Question 14.
The holder of bond is ___________ of the company.
(a) secretary
(b) owner
(c) creditor
Answer:
(c) creditor
Question 15.
Company can accept deposits from public, minimum for ___________ months.
(a) six
(b) nine
(c) twelve
Answer:
(a) six
Question 16.
Company can accept deposits from public maximum for ___________ months.
(a) 12
(b) 24
(c) 36
Answer:
(c) 36

Question 17.
A depository receipt traded in ___________ is called American Depository Receipt.
(a) London
(b) Japan
(c) USA
Answer:
(c) the USA
1B. Match the pairs.
Question 1.

Answer:
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (a) Equity share capital | (1) Venture capital |
| (b) Debenture Trustees | (2) Trust Deed |
| (c) Preference shareholders | (3) Cautious investor |
| (d) Debenture Certificate | (4) Instrument of Debt |
| (e) Bonus shares | (5) Capitalisation of profit |
Question 1.
The real masters of the company.
Answer:
Equity shareholders
Question 2.
A document of ownership of shares.
Answer:
Share certificate
Question 3.
The holders of these shares are entitled to participate in surplus profits.
Answer:
Participating preference shares
Question 4.
A party through whom the company deals with debenture holders.
Answer:
Debenture trustees

Question 5.
Name the shareholder who participates in the management.
Answer:
Equity shareholders
Question 6.
The value of a share is written on the share certificate.
Answer:
Face value
Question 7.
The value of a share is determined by demand and supply forces in the share market.
Answer:
Market value
Question 8.
The policy of using undistributed profit for the business.
Answer:
Retained earnings/ploughing back of profit
Question 9.
It is an acknowledgment of a loan issued by the company to the depositor.
Answer:
Deposit receipt

Question 10.
A dollar-denominated instrument trader in the USA.
Answer:
American Depository Receipt
Question 11.
The Depository Receipt is traded in a country other than the USA.
Answer:
Global depository receipt
Question 12.
Money raised by the company from the public for a minimum of 6 months to a maximum of 39 months.
Answer:
Public Deposits
Question 13.
Credit extended by the suppliers with an intention to increase their sales.
Answer:
Trade Credit
Question 14.
The credit facility is provided to a company having a current account with the bank.
Answer:
Overdraft
1D. State Whether the following statements are True or False.
Question 1.
Equity share capital is known as venture capital.
Answer:
True

Question 2.
Equity shareholders enjoy a fixed rate of dividends.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Debenture holders have the right to vote at a general meeting of the company.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Equity shareholders are described as ‘shock absorbers’ when a company has a financial crisis.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Bondholders are owners of the company.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Cash credit is given against hypothecation of goods and security.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
Trade credit is a major source of long-term finance.
Answer:
False

Question 8.
Depository bank stores the shares on behalf of the GDR holder.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
Financial institutions underwrite the issue of securities.
Answer:
True
1E. Find the odd one.
Question 1.
Debenture, Public Deposit, Retained Earnings
Answer:
Retained earnings
Question 2.
Face value, Market value, Redemption value
Answer:
Redemption value
Question 3.
Share certificate, Debenture certificate, ADR
Answer:
ADR
Question 4.
Trade credit, Overdraft, Cash credit
Answer:
Trade credit
1F. Complete the sentences.
Question 1.
The finance needed by business organisation is termed as ___________
Answer:
Capital

Question 2.
The convertible preference shareholders have a right to convert their shares into ___________
Answer:
Equity shares
Question 3.
Equity shareholders elect their representative Called ___________
Answer:
Directors
Question 4.
Bonus shares are issued as gift to ___________
Answer:
Equity share holders
Question 5.
The bondholders are ___________of the company.
Answer:
Creditors
Question 6.
Depository receipt traded in a country other than USA is called ___________
Answer:
Global Depository Receipt

Question 7.
First Industrial policy was declared in the year ___________
Answer:
1948
Question 8.
When goods are delivered by the supplier to the customer on the basis of deferred payment is called as ___________
Answer:
Trade credit
1G. Select the correct option from the bracket.
Question 1.

(Fluctuating rate of dividend, Preference shares, Interest at fixed rate, Retained earnings, short term loan)
Answer:
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (a) Equity shares | (1) Fluctuating rate of dividend |
| (b) Preference shares | (2) Dividend at a fixed rate |
| (c) Debentures | (3) Interest at a fixed rate |
| (d) Retained earnings | (4) Accumulated corporate profit |
| (e) Public Deposit | (5) short term loan |
Question 1.
What is a share?
Answer:
A share is the smallest unit of the share capital of a company.
Question 2.
What are equity shares?
Answer:
Equity shares are shares that do not preference shares and do not carry priority in receiving dividends nor repayment of capital.
Question 3.
What are preference shares?
Answer:
Preference shares are shares that have preferential rights with regard to receiving dividends and repayment of capital.

Question 4.
What are retained earnings?
Answer:
A part of the net profit which is not distributed to shareholders as dividend but retained by the company as reserve fund is retained earnings.
Question 5.
What is a debenture?
Answer:
It is a document/instrument issued in the form of a debenture certificate under the common seal of the company acknowledging/evidencing the debt.
Question 6.
What is a bond?
Answer:
A bond is a debt security and a formal contract to repay borrowed money with interest.
Question 7.
In which country can ADR be issued?
Answer:
ADR (American Depository Receipt) is a depository Receipt that is issued in the USA.

Question 8.
In which country can GDR be issued?
Answer:
GDR (Global depository receipt) can be issued in countries other than the USA.
Question 9.
What are convertible debentures?
Answer:
Convertible debentures are debentures that are converted into equity shares after a specific period as specified at the time of issue.
Question 10.
What are cumulative preference shares?
Answer:
Cumulative preference shares are shares where dividend, if not paid in a year accumulates till it is paid.
1I. Correct the underlined words and rewrite the following sentences.
Question 1.
Owned capital is temporary capital.
Answer:
Owned capital is permanent capital.
Question 2.
Equity shares get dividends at a fixed rate.
Answer:
Equity shares get dividends at fluctuating rates.

Question 3.
Preference shares get dividends at fluctuating rates.
Answer:
Preference shares get dividends at a fixed rate.
Question 4.
Retained earnings are an external source of finance.
Answer:
Retained earnings are an internal source of finance.
Question 5.
The debenture holder is the owner of the company.
Answer:
The debenture holder is a creditor of the company.
Question 6.
Bond is a source of short-term finance.
Answer:
Bond is a source of long-term finance.
Question 7.
Depository receipt traded in the USA is called Global Depository Receipt.
Answer:
Depository receipt traded in the USA is called American Depository Receipt.
2. Explain the following terms/Concepts.
Question 1.
Borrowed capital
Answer:
Question 2.
Owned capital
Answer:
Question 3.
Ploughing back of profit
Answer:

Question 4.
Overdraft
Answer:
Question 5.
Trade Credit
Answer:
3. Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
1. The Balance sheet of a Donald Company for the year 2018-19 reveals equity share capital of Rs. 25,00,000 and retained earnings of Rs. 50,00,000.
Question (a).
Is the company financially sound?
Answer:
The company is financially sound as it has double the amount as reserves or retained earnings or kept aside profits.
Question (b).
Can the retained earnings be converted into capital?
Answer:
Yes, the retained earnings can be converted into capital by means of capitalisation of reserves.
Question (c).
What type of source retained earning is?
Answer:
Retained earning is self-financing or an internal source of finance.
2. Mr. Satish is a speculator. He desires to take advantage of the growing market for the company’s products and earn handsomely.
Question (a).
According to you, which type of share Mr. Satish will choose to invest in.
Answer:
As Mr. Satish is a speculator, he will choose equity shares to invest in because if there are good earnings/profits, so will be the rate of dividend.

Question (b).
What does he receive as a return on investment?
Answer:
He receives a fluctuating rate of dividends.
Question (C).
State anyone, right he will enjoy as a shareholder.
Answer:
The right to attend the meeting and vote on resolutions can be the right Mr. Satish can exercise as a member.
3. Mr. Rohit, an individual investor, invests his own funds in the securities. He depends on investment income and does not want to take any risk. He is interested in the definite rate of income and safety of the principal.
Question (a).
Name the type of security that Mr. Rohit will opt for.
Answer:
As Mr. Rohit does not want to take risks, he will opt for preference shares which will assure him of steady income and safety of his investment.
Question (b).
What does he receive as a return on his investment?
Answer:
Mr. Rohit will receive dividends in return.
Question (c).
The return on investment which he receives is fixed or fluctuating.
Answer:
The return on his investment will be fixed and not fluctuating.
4. Distinguish between the following.
Question 1.
Equity Shares and Preference Shares
Answer:
| Points | Equity Shares | Preference Shares |
| 1. Meaning | Shares that are not preference shares are called equity shares i.e. these shares do not have the preferential rights for payment of dividends and repayment of capital. | Preferences shares are shares that carry preferential rights as to payment of:
|
| 2. Rate of Dividend | Equity shares are given dividends at a fluctuating rate depending upon the profits of the company. | Preference shareholders get dividends at a fixed rate. |
| 3. Voting Right | Equity shareholders enjoy normal voting rights. They participate in the management of their company. | Preference shareholders do not enjoy normal voting right. They can vote only on matters affecting their interest. |
| 4. Return of Capital | Equity capital can not be returned during the lifetime of the company, (except in case of buyback). | A company can issue redeemable preference shares, which can be repaid during the lifetime of the company. |
| 5. Nature of capital | Equity capital is known as ‘Risk Capital’. | Preference capital is ‘Safe Capital’ with a stable return. |
| 6. Nature of investor | The investors who are ready to take risks to invest in equity shares. | Investors who are cautious about the safety of their investment invest in preference shares. |
| 7. Face Value | The face value of equity shares is generally ₹ 1/- or ₹ 10/- it is relatively low. | The face value of preference shares is relatively higher i.e. ₹ 100/- and so on. |
| 8. Right and bonus issue | Equity shareholder is entitled to get bonus and right issue. | Preference shareholders are not eligible for bonuses and right issues. |
| 9. Capital appreciation | The market value of equity shares increases with the prosperity of the company. It leads to an increase in the value of shares. | The market value of preference shares does not fluctuate, so there is no possibility/cheques of capital appreciation. |
| 10. Risk | Equity shares are subject to higher risk. | Preference shares are subject to less risk. |
| 11. Types | Equity shares are classified into:
|
Preference shares are classified as:
|
Shares and Debentures
Answer:
| Points | Shares | Debentures |
| 1. Meaning | Share is the smallest unit in the total share capital of the company. It is known as ownership securities. | A debenture is an instrument evidencing debt under the seal of the Company. They are also known as creditor ship securities. |
| 2. Status | A holder of shares is the owner of the company. Hence, share capital is owned capital. | A holder of debenture is the creditor of the company. Hence, Debenture capital is loan capital or borrowed capital. |
| 3. Nature | It is permanent capital. It is not repaid during the lifetime of the company. | It is temporary capital. Generally, it is repaid after a specific period. |
| 4. Voting/Right | Shareholders being owners enjoy normal voting rights in general meetings and can participate in the management of the company. | Debenture holders being creditors, do not have any voting right and can not participate in the management of the company. |
| 5. Return on Investment | Return on shares is called a dividend. Equity shareholders receive dividends at a fluctuating rate whereas preference shareholders receive dividends at a fixed rate. | Return on debenture is called interest. It is fixed at the time of issue. Interest is paid even when a company has no profit. |
| 6. Security | Share capital is unsecured capital. No security is offered to the shareholder. | Debenture capital being loan capital is secured by creating a charge on Company’s property. |
| 7. Time of Issue | Shares are issued in the initial stages of the company formation. | Debentures are issued at a later stage when the company has properties to offer as security. |
| 8. Suitability | Shares are suitable for long-term finance. | Debentures are suitable for medium-term finance. |
| 9. Types | Shares are classified into:
|
A debenture is classified as:
|
| 10. Position on liquidation | On liquidation of a company, shareholders rank last in the list of claimants. | Debenture holders being creditors, rank prior to shareholders for repayment on liquidation of the company. |

Question 3.
Owned Capital and Borrowed Capital
Answer:
| Points | Owned Capital | Borrowed Capital |
| 1. Meaning | It is that capital that is contributed by shareholders. | It is that capital that is borrowed from creditors. It is also known as debt capital. |
| 2. Sources | This capital is collected by the issue of equity shares and preference shares, ploughing back of profits (ownership securities). | It is collected by way of the issue of debentures, fixed deposits, loans from banks/financial institutions, etc. (loan, borrowings). |
| 3. Return on Investment | The shareholders get dividends as income on their investment. The rate of dividend is fluctuating, in the case of equity shares but is fixed in the case of preference shares. | The debt capital holders get interested as income on their investment. Interest is paid at a fixed rate. |
| 4. Status | The shareholders are owners of the company. | The debt holders are creditors of the company. |
| 5. Voting right | The equity shareholders enjoy normal voting right at the general meetings. | The creditors do not enjoy voting rights at the general meeting. |
| 6. Repayment of Capital Redemption | The shareholders do not enjoy priority over creditors. They are eligible for repayment of Capital only after making payment to creditors at the time of windings up of the company. | The creditors get priority over the shareholders in case of return of principal amount at the time of winding up of the company. |
| 7. Charge on assets | The shareholders do not have any charge on the assets of the company. | The secured debenture holders have a change on the assets of the company. |
Question 1.
What is a public deposit?
Answer:
Advantages of deposits to the company
Question 2.
What are Global Depository Receipt and American Depository Receipt?
Answer:

Question 3.
What is Trade Credit?
Answer:
Advantages of Trade Credit:
Question 4.
What are the schemes for disbursement of credit by banks?
Answer:
Meaning: Banks play an important role in terms of providing finance to the companies.
They provide short-term finance for working capital, in the form of bank and trade credits.
The innovative schemes by banks for disbursement of credit are as follows:
(i) Overdraft:
(ii) Cash Credit:
(iii) Cash Loans:
(iv) Discounting bills of exchange:

Question 5.
State the features of bonds.
Answer:
Definition:
According to Webster Dictionary, “a bond is an interest bearing certificate issued by a Government or business firm promising to pay the holder a specific sum at a specified date”.
A bond is thus-
Features:
(i) Nature of finance:
(ii) Status of investor:
(iii) Return on bonds:
(iv) Repayment:
6. Justify the following statements:
Question 1.
Equity shareholders are real owners and controllers of the company.
Answer:
Question 2.
Preference Shares do not carry normal voting rights.
Answer:

Question 3.
The debenture is secured by a charge on assets of the company.
Answer:
Question 4.
Retained earnings are the simple and cheapest method of raising finance.
Answer:
Question 5.
Public deposit is a good source of short-term financing.
Answer:
Question 6.
The bondholder is a creditor of the company.
Answer:
Question 7.
Trade credit is not a cash loan.
Answer:

Question 8.
Different investors have different preferences.
Answer:
Question 9.
Equity Capital is risk capital.
Answer:
7. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What are a share and state its features?
Answer:
Features of shares:
(i) Meaning:
(ii) Ownership:
(iii) Distinctive number:

(iv) Evidence of title:
(v) Value of a share:
(vi) Rights:
(vii) Income:
(viii) Transferability:
(ix) Property of shareholder:
(x) Kinds of shares:

Question 2.
What is an equity share? Explain its features.
Answer:
Features of equity shares:
(i) Permanent Capital:
(ii) Fluctuating dividend:

(iii) Rights:
(iv) No preferential right:
(v) Controlling power:
(vi) Risk:
(vii) Residual claimants:
(viii) No charge on assets:
(ix) Bonus issue:

(x) Rights issue:
(xi) Face value:
(xii) Market value:
(xiii) Capital Appreciation:
Question 3.
Define preference shares/What are preference shares? What are the different types of preference shares?
Answer:

(i) Cumulative Preference Shares:
(ii) Non-Cumulative Preference Shares:
(iii) Participating Preference Shares:
(iv) Non-Participating Preference Shares:
(v) Convertible Preference Shares:
(vi) Non-Convertible Preference Shares:

(vii) Redeemable Preference Shares:
(viii) Irredeemable Preference Shares:
Question 4.
What are preference shares? State its features.
Answer:
Features of preference shares:
(i) Preference for dividend:
(ii) Prior repayment of capital:
(iii) Fixed return:
(iv) Nature of capital:
(v) Market value:
(vi) Voting right:
(vii) Risk:

(viii) Face value:
(ix) Right or Bonus issue:
(x) Nature of investor:
Question 5.
What is Debenture/Define Debenture. Discuss the different types of Debentures.
Answer:
Definitions:
Topham defines: “A debenture is a document given by a company as evidence of debt to the holder, usually arising out of the loan and most commonly secured by the charge.”

They are as follows:
(i) Secured Debentures:
(ii) Unsecured Debentures:
(iii) Registered Debentures:
(iv) Bearer Debentures:

(v) Redeemable Debentures:
(vi) Irredeemable Debentures:
(vii) Convertible Debentures:
(viii) Non-Convertible Debentures:
Question 6.
Define Debenture/What is a debenture? Explain the features of debenture?
Answer:
Definitions:
Topham defines: “A debenture is a document given by a company as evidence of debt to the holder, usually arising out of the loan and most commonly secured by the charge.”
A debenture is evidence of indebtedness.
Features of Debenture:
(i) Written Promise:
(ii) Face Value:
(iii) Time of payment:
(iv) Priority of Payment:
(v) Assurance of repayment:

(vi) Terms of issue and redemption of Debenture:
(vii) Authority to issue:
Board of Directors has the authority/power to issue debenture as per Companies Act 2013 Section 179(3).
(viii) Interest:
(ix) Parties to Debenture:
(x) Status of debenture holder:
(xi) No Voting Right:
(xii) Security:
(xiii) Issuers:

(xiv) Listing:
(xv) Transferability: