Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Geography Solutions
Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Textbook Questions and Answers
A. Who am I?
Question 1.
I keep on changing.
Answer:
Weather.
Question 2.
I am not the same in all places.
Answer:
Climate.
Question 3.
I am the solid state of water droplets.
Answer:
Snow.

Question 4.
I am present in the atmosphere in the form of vapour.
Answer:
Moisture.
B. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Why is the climate of Mahabaleshwar cool ?
Answer:
The climate of Mahabaleshwar is cool because it is situated at a high elevation. So, as we move upward from sea-level, the temperature of air decreases.
Question 2.
Why is the climate near the sea humid?
Answer:
The climate near the sea is humid because it contains greater amount of vapour mixed in the air.

Question 3.
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Answer:
Question 4.
What are the elements of weather?
Answer:
The elements of weather are:
Question 5.
What effects do nearness to the sea and height above mean sea level have on the climate?
Answer:
Nearness to the sea leads to a humid climate whereas height above mean sea level will lead to a cool climate.
C. For the climatic conditions mentioned in the table, name the representative places known to you. (Use an atlas.)
Answer:

D. Complete the following table
Answer:
Activity:
Understand the climate of your place with the help of your teacher.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Weather and Climate InText Questions and Answers
Can you tell?
A. The weather conditions of a few places in India are as follows on 10th June. Use the table to answer the questions.
Question 1.
In which place will the clothes on a clothesline dry quickly? Why?
Answer:
In Bhopal the clothes on the clothesline will dry quickly. Due to the hot sun the water in the wet clothes get converted into vapour quickly.
Question 2.
In which place will they dry slowly? Why?
Answer:
Clothes will take longer time to dry in Mussoorie because of the medium heat and cold air.
Question 3.
Will the atmospheric conditions at these places always remain the same or will they change?
Answer:
The atmospheric conditions of these places will change from time to time.

B. Which of the following statements are applicable to the conditions that you have experienced today or yesterday at the place where you live?
Answer:
Students have to give answer to this question depending on the weather condition of one particular day where they live.
C. Since childhood you have experienced summers, rainy seasons and winters. On the basis of your experience answer the following questions.
Question 1.
In which months do summer, monsoon season and winter occur in a year from January to December? Show it in a chart.
Answer:
Question 2.
Which special clothes do we use if it is raining?
Answer:
If it is raining, we wear a raincoat or carry an umbrella.
Question 3.
When do we use woollen clothes?
Answer:
We wear woollen clothes in winter.
Question 4.
In which season do we mainly use thin cotton clothes?
Answer:
We wear cotton clothes in summer.
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Which occupation will you practice in cold regions?
Answer:
Occupations practiced in cold region are lumbering and agriculture.
Question 2.
Which occupations will you practice in hot region?
Answer:
Occupations practiced in hot regions are animal husbandry and agriculture.

Observe the following map and write the answer to the question given below it.
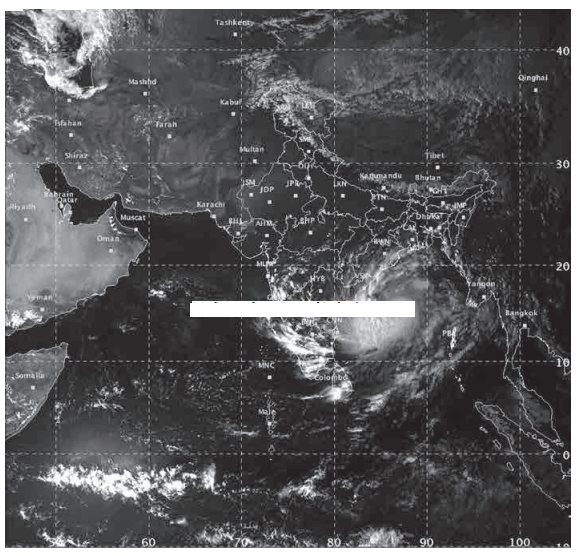
Question 1.
An Indian Meteorological Department image of the storm that visited in November 2014 was shown. Tell in which sea the storm was located.
Answer:
Bay of Bengal.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks with the right option in the brackets:
Question 1.
Atmospheric conditions prevailing at a place and at a given time is called ______. (wind, weather, climate)
Answer:
weather
Question 2.
The temperature goes on ______ from the equator towards both the poles. (decreasing, increasing, being constant)
Answer:
decreasing
Question 3.
The horizontal movement of air is called ______. (pressure, humidity, wind)
Answer:
wind
Question 4.
_____ is defined by elements such as temperature, wind and humidity. (precipitation, weather, climate)
Answer:
weather

Question 5.
The air that has greater amount of vapour is called _____ air. (dry, hot, humid)
Answer:
humid
Question 6.
The humidity in the atmosphere is called _______. (moisture, oxygen, heat)
Answer:
moisture
Question 7.
The proportion of moisture in the atmosphere depends on ________.(winds, temperature, air pressure)
Answer:
temperature
Question 8.
Vapour in the atmosphere condenses into water droplets or snow and their showering on the earth is called ________.(precipitation, wind, climate)
Answer:
precipitation
Match the pairs correctly:
Question 1.
Answer:
1 – c
2 – d
3 – a
4 – b
5 – e

Name the following statements:
Question 1.
Elements of weather:
Answer:
Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity and precipitation.
Question 2.
Forms of precipitation:
Answer:
Rainfall, snowfall and hailstorm.
Question 3.
Climate is generally expressed as:
Answer:
‘Cool and dry ‘or ‘hot and humid’ or ‘hot and dry’, etc.
Question 4.
Factors influencing climate:
Answer:
Latitudinal position, height above sea level, nearness to ocean and oceanic currents.
Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
What is precipitation?
Answer:
Vapour in the atmosphere condenses into water droplets or snow particles, which shower on the earth. This is called as precipitation.
Question 2.
What is called air pressure?
Answer:
Air has weight and as a result it creates pressure. This is called air pressure.
Question 3.
What is wind?
Answer:
Air moving from high pressure towards low pressure areas in a horizontal direction is called wind.
Question 4.
What is called humid air?
Answer:
The atmosphere contains vapour. The air that has greater amount of vapour is called humid air.

Give geographical reasons for the following statements:
Question 1.
As we move upward from the sea-level, temperature of the air decreases.
Answer:
Question 2.
Air pressure decreases with increasing height.
Answer:
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is known as precipitation?
Answer:
Vapour in the atmosphere condenses into water droplets or snow particles. Their showering on the earth is called precipitation.

Question 2.
What is called moisture?
Answer:
The humidity in the atmosphere is called moisture. The proportion of moisture in the atmosphere depends on the temperature. Air with higher temperature holds a greater amount of moisture.
Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Textbook Questions and Answers
A. Who am I?
Question 1.
I keep on changing.
Answer:
Weather.
Question 2.
I am not the same in all places.
Answer:
Climate.
Question 3.
I am the solid state of water droplets.
Answer:
Snow.

Question 4.
I am present in the atmosphere in the form of vapour.
Answer:
Moisture.
B. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Why is the climate of Mahabaleshwar cool ?
Answer:
The climate of Mahabaleshwar is cool because it is situated at a high elevation. So, as we move upward from sea-level, the temperature of air decreases.
Question 2.
Why is the climate near the sea humid?
Answer:
The climate near the sea is humid because it contains greater amount of vapour mixed in the air.

Question 3.
What is the difference between weather and climate?
Answer:
| Weather | Climate |
| (i) Weather is described on the basis of the conditions prevailing at the given time. | (i) Climate is described on the basis of conditions prevailing over a longer period of time. |
| (ii) Weather keeps changing frequently and we can experience the change easily. | (ii) Change in the climate takes place over a long ! period of time. These are not percieved easily. |
What are the elements of weather?
Answer:
The elements of weather are:
Question 5.
What effects do nearness to the sea and height above mean sea level have on the climate?
Answer:
Nearness to the sea leads to a humid climate whereas height above mean sea level will lead to a cool climate.
C. For the climatic conditions mentioned in the table, name the representative places known to you. (Use an atlas.)
| Hot | Death valley |
| Hot and humid | |
| Cold | |
| Hot and dry | |
| Cold and dry |
| Hot | Death valley |
| Hot and humid | Amazon |
| Cold | Greenland |
| Hot and dry | Sahara desert |
| Cold and dry | Atacama desert |

D. Complete the following table
| Weather | Climate |
| Short-lived condition of the atmosphere | |
| Does not change quickly | |
| Expressed with respect to a specific place | |
| Elements of climate: Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity and precipitation |
| Weather | Climate |
| Short-lived condition of the atmosphere | Long-lived condition of the atmosphere |
| Keeps changing | Does not change quickly |
| Expressed with respect to a specific place | Expressed with respect to a specific region |
| Elements of weather: Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity and precipitation | Elements of climate: Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity and precipitation |
Understand the climate of your place with the help of your teacher.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Weather and Climate InText Questions and Answers
Can you tell?
A. The weather conditions of a few places in India are as follows on 10th June. Use the table to answer the questions.
| S. No. | Place | State | Time | Weather |
| (1) | Kochi | Kerala | 12.30 pm | Cloudy |
| (2) | Bhopal | M.P. | 12.30 pm | Hot and sunny |
| (3) | Mussoorie | Uttarakhand | 12.30 pm | Cold weather mild sun |
In which place will the clothes on a clothesline dry quickly? Why?
Answer:
In Bhopal the clothes on the clothesline will dry quickly. Due to the hot sun the water in the wet clothes get converted into vapour quickly.
Question 2.
In which place will they dry slowly? Why?
Answer:
Clothes will take longer time to dry in Mussoorie because of the medium heat and cold air.
Question 3.
Will the atmospheric conditions at these places always remain the same or will they change?
Answer:
The atmospheric conditions of these places will change from time to time.

B. Which of the following statements are applicable to the conditions that you have experienced today or yesterday at the place where you live?
Answer:
Students have to give answer to this question depending on the weather condition of one particular day where they live.
C. Since childhood you have experienced summers, rainy seasons and winters. On the basis of your experience answer the following questions.
Question 1.
In which months do summer, monsoon season and winter occur in a year from January to December? Show it in a chart.
Answer:
| Summer | Rainy season | Winter |
| February to May | June to September | October to January |
Which special clothes do we use if it is raining?
Answer:
If it is raining, we wear a raincoat or carry an umbrella.
Question 3.
When do we use woollen clothes?
Answer:
We wear woollen clothes in winter.
Question 4.
In which season do we mainly use thin cotton clothes?
Answer:
We wear cotton clothes in summer.
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Which occupation will you practice in cold regions?
Answer:
Occupations practiced in cold region are lumbering and agriculture.
Question 2.
Which occupations will you practice in hot region?
Answer:
Occupations practiced in hot regions are animal husbandry and agriculture.

Observe the following map and write the answer to the question given below it.

Question 1.
An Indian Meteorological Department image of the storm that visited in November 2014 was shown. Tell in which sea the storm was located.
Answer:
Bay of Bengal.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 4 Weather and Climate Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks with the right option in the brackets:
Question 1.
Atmospheric conditions prevailing at a place and at a given time is called ______. (wind, weather, climate)
Answer:
weather
Question 2.
The temperature goes on ______ from the equator towards both the poles. (decreasing, increasing, being constant)
Answer:
decreasing
Question 3.
The horizontal movement of air is called ______. (pressure, humidity, wind)
Answer:
wind
Question 4.
_____ is defined by elements such as temperature, wind and humidity. (precipitation, weather, climate)
Answer:
weather

Question 5.
The air that has greater amount of vapour is called _____ air. (dry, hot, humid)
Answer:
humid
Question 6.
The humidity in the atmosphere is called _______. (moisture, oxygen, heat)
Answer:
moisture
Question 7.
The proportion of moisture in the atmosphere depends on ________.(winds, temperature, air pressure)
Answer:
temperature
Question 8.
Vapour in the atmosphere condenses into water droplets or snow and their showering on the earth is called ________.(precipitation, wind, climate)
Answer:
precipitation
Match the pairs correctly:
Question 1.
| A | B |
| (1) Winds | (a) hailstorm |
| (2) Moisture | (b) solar energy |
| (3) Precipitation | (c) the difference in air pressure |
| (4) Temperature | (d) vapor |
| (5) Weather | (e) hot, cool, dry, sultry |
| (f) humidity |
1 – c
2 – d
3 – a
4 – b
5 – e

Name the following statements:
Question 1.
Elements of weather:
Answer:
Temperature, pressure, winds, humidity and precipitation.
Question 2.
Forms of precipitation:
Answer:
Rainfall, snowfall and hailstorm.
Question 3.
Climate is generally expressed as:
Answer:
‘Cool and dry ‘or ‘hot and humid’ or ‘hot and dry’, etc.
Question 4.
Factors influencing climate:
Answer:
Latitudinal position, height above sea level, nearness to ocean and oceanic currents.
Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
What is precipitation?
Answer:
Vapour in the atmosphere condenses into water droplets or snow particles, which shower on the earth. This is called as precipitation.
Question 2.
What is called air pressure?
Answer:
Air has weight and as a result it creates pressure. This is called air pressure.
Question 3.
What is wind?
Answer:
Air moving from high pressure towards low pressure areas in a horizontal direction is called wind.
Question 4.
What is called humid air?
Answer:
The atmosphere contains vapour. The air that has greater amount of vapour is called humid air.

Give geographical reasons for the following statements:
Question 1.
As we move upward from the sea-level, temperature of the air decreases.
Answer:
Question 2.
Air pressure decreases with increasing height.
Answer:
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is known as precipitation?
Answer:
Vapour in the atmosphere condenses into water droplets or snow particles. Their showering on the earth is called precipitation.

Question 2.
What is called moisture?
Answer:
The humidity in the atmosphere is called moisture. The proportion of moisture in the atmosphere depends on the temperature. Air with higher temperature holds a greater amount of moisture.