Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Science Solutions
Chapter 1 Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blanks and rewrite the completed statements.
Question a.
The layer of ozone gas absorbs ……………. rays that come from the sun to the earth.
Answer:
Ultraviolet (U.V) rays
Question b.
Of the total water available on the earth, fresh water forms ……….. percent.
Answer:
0.3 %

Question c.
Both …………. and ………… constituents are present in the soil.
Answer:
biotic, abiotic
2. why is it said that?
Question a.
The ozone layer is a protective shell of earth.
Answer:
Question 2.
Water is life.
Answer:

Question c.
Sea water is useful even though it is not potable.
OR
In what way is sea water useful even though it is salty?
Answer:
3. What will happen if
Question a.
Question a.
Microbes in soil get destroyed.
Answer:
Question b.
The number of vehicles and factories in your surroundings increases.
Answer:

Question c.
The total supply of potable water is finished.
Answer:
4. Match the following.
Question a.
Answer:

5. Name the following.
Question a.
Constituents of biosphere.
Answer:
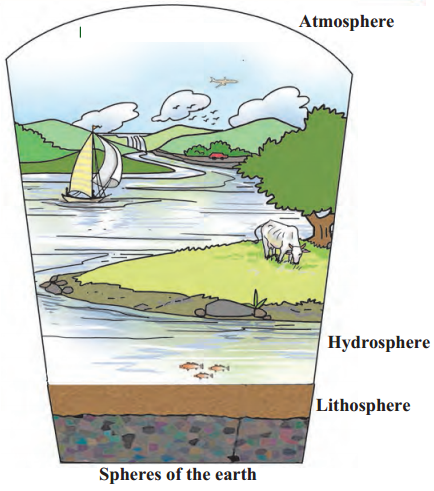
Atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere and all living things on earth.
Question b.
Biotic constituents of soil.
Answer:
Microbes, worms, insects, burrowing rhodents like rats, mice, roots of trees and plants.
Question c.
Fossil fuel.
Answer:
Crude oil from which we get kerosene, petrol, diesel, paraffin wax and tar.
Question d.
Inert gases in air.
Answer:
Neon, argon, helium, krypton, xenon.

Question e.
Gases that are harmful to ozone layer.
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbon and carbon tetrachloride.
6. True or False?
Question a.
Land and soil is the same thing.
Answer:
False – Land consists of stones, soil and big rocks.
Question b.
The water in a lake is called ground water.
Answer:
False – Water trapped below the ground over the bedrocks is called ground water.
Question c.
It takes about thousand years to form a 25 cm thick layer of soil.
Answer:
False – It almost takes around thousand years to form a 2.5 cm thick layer of soil.
Question d.
Radon is used in decorative lights.
Answer:
False – Neon is used in decorative lights.
7. Answer in your own words.
Question a.
Explain with the help of a diagram how soil is formed.
Answer:

Question b.
Why is there a shortage of water even though it occupies about 71% of the earth’s surface?
Answer:
Question c.
What are the various constituents of air? Write their uses.
Answer:
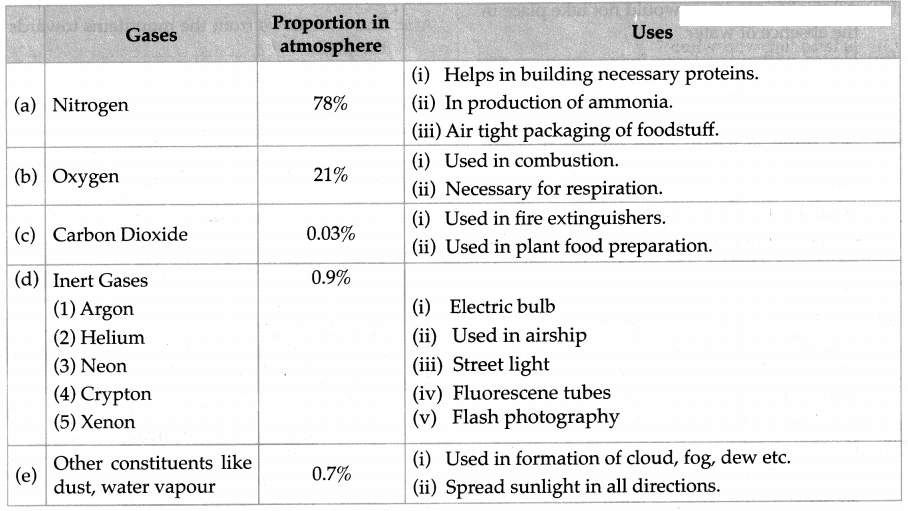
Air contains gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, inert gases, water vapour and dust particles. The uses of constituents of air are as follows.

Question d.
Why are air, water and land considered to be valuable natural resources?
Answer:
Activity:
Natural Resources Air, Water And Land Class 6 Questions And Answers Question 1.
Obtain detailed information about the work of the India Meteorological Department.
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Questions And Answers Question 2.
Find a remedy for water scarcity.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks and rewrite the completed statements.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Natural Resources Air, Water And Land Exercise Question 1.
……………. gas, used for refrigeration and air conditioning, destroys the ozone layer.
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbon or carbon tetrachloride

Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Exercise Question 2.
Air becomes ……………. at higher altitudes.
Answer:
rarer
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Question 3.
………….. of land is reduced if green trees and bushes are grown in it.
Answer:
Erosion
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Question 4.
16th September is celebrated as ………. Day all over the world.
Answer:
Ozone Protection
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Question Answer Question 5.
………….. is the layer of air that surrounds the earth.
Answer:
Atmosphere

Natural Resources Air, Water And Land Question 6.
……………. occupies the largest part of the earth’s surface.
Answer:
Hydrosphere
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Question 7.
Gases are not found in the …………… and beyond.
Answer:
exosphere
Choose the correct alternative:
Question 1.
………….. percentage of the land is covered by water.
(a) 70%
(b) 81%
(c) 71%
(d)80%.
Answer:
71%
Question 2.
The gas used in fluorescent tubes is ………………… .
(a) Argon
(b) Helium
(c) Neon
(d) Krypton.
Answer:
Krypton

Question 3.
The ozone layer is found in the lower part of …………… .
(a) atmosphere
(b) stratosphere
(c) mesosphere
(d) trophosphere.
Answer:
stratosphere
Question 4.
Gas released in air on combustion of fuel is …………….. .
(a) Hydrogen sulphide
(b) Carbon tetrachloride
(c) Nitrogen dioxide
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
Nitrogen dioxide
Question 5.
The proportion of humus in the upper layer of good fertile soil is about ……………… .
(a) 23% to 45%
(b) 33% to 50%
(c) 30% to 53%
(d) 13% to 33%
Answer:
33% to 50%
Match the following:
Question 1.
Answer:

Name the following:
Question 1.
Substances formed when fuel burns.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and smoke.
Question 2.
Layers of the atmosphere.
Answer:
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, ionosphere and exosphere.
Question 3.
Layers of land.
Answer:
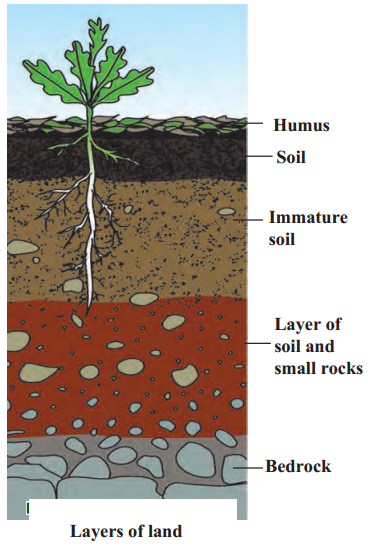
Humus, mature soil, immature soil, small rocks and stones and bedrock.

Question 4.
Gas necessary for building proteins.
Answer:
Nitrogen.
State whether True or False. Correct if False.
Question 1.
The amount of gases in the air is greatest near the surface and becomes rarer at higher altitudes.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Fogs, clouds, snow, and rain are produced in the exosphere.
Answer:
False – Fogs, clouds, snow and rain are formed in the troposphere and lower stratosphere of the atmosphere.
Question 3.
Fossil fuels are formed from the dead remains of animals and plants buried underground for a long period.
Answer:
True.
Explain what will happen if:
Question 1.
Forests are destroyed.
Answer:

Question 2.
What would have happened if there was no air on the earth?
Answer:
Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is humus?
Answer:
Humus is the topmost layer of the soil formed d by decomposition of remains of plants and animals and it makes the soil fertile.
Question 2.
What is land made up of?
Answer:
Land is made up of stones, soil, sand and big rocks.

Question 3.
Is land flat everywhere?
Answer:
No, land is not flat everywhere. It is flat in some regions and hilly in some regions.
Question 4.
Does man produce soil/ land?
Answer:
No, man does not produce soil/land, it is produced naturally.
Question 5.
What do you see on land?
Answer:
We see mountains, rivers, valleys, ocean, also terrestrial animals and plants. We also see roads, bridges, buildings etc.
Question 6.
What has man created on land?
Answer:
Man has dug wells, borewells to lift ground water. He has also constructed bunds and dams. He has also built many industries, buildings, roads for transport.

Question 7.
If a deep pit is dug in the ground, what do you see there?
Answer:
We see different layers of land.
Answer in your own words.
Question 1.
Explain with the help of diagram various layers of land.
Answer:
Observe the picture and answer the questions.
Question 1.
Where do you see the birds?
Answer:
The birds are flying in the sky.

Question 2.
Where is the cow grazing?
Answer:
The cow is grazing in the pasture (field).
Question 3.
Locate the trees.
Answer:
The trees are seen along the river bank.
Question 4.
Where does the river come from?
Answer:
The river flows from the mountains towards the plains.
Question 5.
Where is the aeroplane?
Answer:
The aeroplane is in the sky above the clouds.

Question 6.
Where are fishes seen?
Answer:
Fishes are seen swimming in the river water.
Question 7.
On what is the sail boat floating?
Answer:
Sail boat is floating on the water.
Observe and discuss:

Question 1.
What is the similarity in the three pictures given above?
Answer:
All the pictures given above show large scale emission of smoke through different agencies. This smoke directly mixes with the atmosphere, disturbing the balance between the constituents of air and causing air pollution.
Observe and discuss:
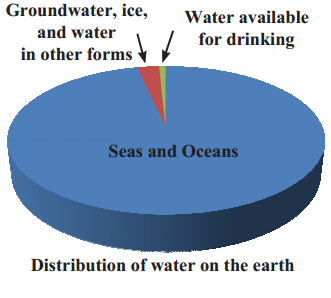
Observe the distribution of water on the earth surface and complete the table.
Question 1.
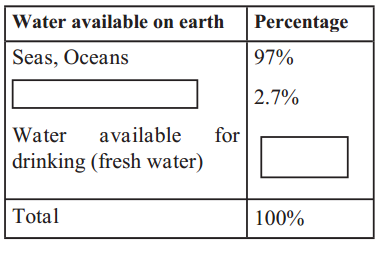
Answer:
Observe given figure carefully and answer the following.
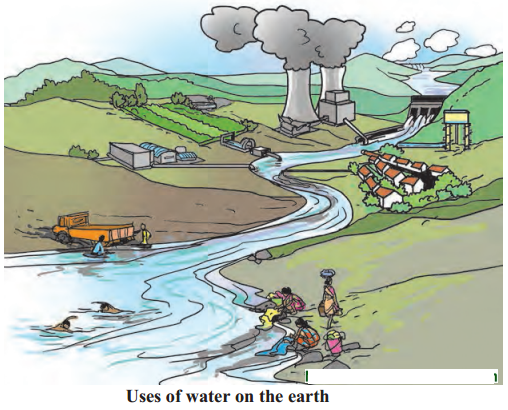
Question 1.
For which purpose is water being used?
Answer:
Water is being used for washing clothes, for bathing, farming, drinking, and industries.

Question 2.
Do other living things use water like we do?
Answer:
Animals do not use water like us. They use water only for drinking. Some animals like buffaloes, rhinoceros, elephants use water for cooling themselves during summers.
Question 3.
What are the constituents of soil? Classify them as biotic and abiotic constituents.
Answer:
The constituents of soil are humus, soil, sand, gravel, stones, bedrock, insects, worms, microbes, roots of trees and dead leaves, burrowing rodents like mice and rats.
Answer the following:
Question 1.
How would you save water? Give some measures you will adopt.
Answer:
Water can be saved in the following ways:

Question 2.
What measures would you take to prevent soil erosion?
Answer:
Let’s try this
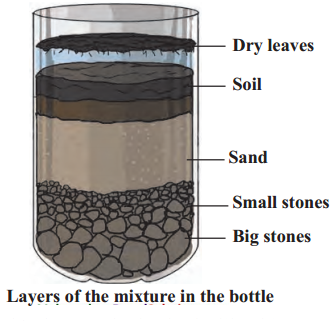
Observe it the next day and answer.
Question 1.
How does the mixture in the bottle look now?
Answer:
The mixture gets segregated into various layers. Heaviest substances settle down and lighter forms topmost layer.
Question 2.
Do you see the layers in it?
Answer:
Yes, we see the layers of soil.

Question 3.
What is seen in the different layers from top to bottom?
Answer:
The dry leaves are floating above the water at the top. Then the layer of the soil, which forms a layer above the sand. Below the sand we see a layer of small stones, and the big ones have settled down at the bottom of the bottle.
Question 4.
Obtain specimens of soil from various places and note the differences in the specimen with respect to colour, feel, texture and size of the particles.
Answer:

Question 5.
Observe how much water is used and for what purposes it is used in your house for a whole day. Record it in a chart. Discuss this data and find out how much water each person needs in your house.
Answer:
Total number of persons = 3
Total water used per person = \(\frac{50}{3}\) = 50 litres.
Approximately 50 litres of water is required for 1 person.

Chapter 1 Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the blanks and rewrite the completed statements.
Question a.
The layer of ozone gas absorbs ……………. rays that come from the sun to the earth.
Answer:
Ultraviolet (U.V) rays
Question b.
Of the total water available on the earth, fresh water forms ……….. percent.
Answer:
0.3 %

Question c.
Both …………. and ………… constituents are present in the soil.
Answer:
biotic, abiotic
2. why is it said that?
Question a.
The ozone layer is a protective shell of earth.
Answer:
Question 2.
Water is life.
Answer:

Question c.
Sea water is useful even though it is not potable.
OR
In what way is sea water useful even though it is salty?
Answer:
3. What will happen if
Question a.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Carbon dioxide | a. Generation of soil |
| 2. Oxygen | b. Rain |
| 3. Water vapour | c. Plants and food production |
| 4. Microbes | d. Combustion |
Microbes in soil get destroyed.
Answer:
Question b.
The number of vehicles and factories in your surroundings increases.
Answer:

Question c.
The total supply of potable water is finished.
Answer:
4. Match the following.
Question a.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Carbon dioxide | a. Generation of soil |
| 2. Oxygen | b. Rain |
| 3. Water vapour | c. Plants and food production |
| 4. Microbes | d. Combustion |
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Carbon dioxide | c. Plants and food production |
| 2. Oxygen | d. Combustion |
| 3. Water vapour | b. Rain |
| 4. Microbes | a. Generation of soil |

5. Name the following.
Question a.
Constituents of biosphere.
Answer:
Atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere and all living things on earth.
Question b.
Biotic constituents of soil.
Answer:
Microbes, worms, insects, burrowing rhodents like rats, mice, roots of trees and plants.
Question c.
Fossil fuel.
Answer:
Crude oil from which we get kerosene, petrol, diesel, paraffin wax and tar.
Question d.
Inert gases in air.
Answer:
Neon, argon, helium, krypton, xenon.

Question e.
Gases that are harmful to ozone layer.
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbon and carbon tetrachloride.
6. True or False?
Question a.
Land and soil is the same thing.
Answer:
False – Land consists of stones, soil and big rocks.
Question b.
The water in a lake is called ground water.
Answer:
False – Water trapped below the ground over the bedrocks is called ground water.
Question c.
It takes about thousand years to form a 25 cm thick layer of soil.
Answer:
False – It almost takes around thousand years to form a 2.5 cm thick layer of soil.
Question d.
Radon is used in decorative lights.
Answer:
False – Neon is used in decorative lights.
7. Answer in your own words.
Question a.
Explain with the help of a diagram how soil is formed.
Answer:

Question b.
Why is there a shortage of water even though it occupies about 71% of the earth’s surface?
Answer:
Question c.
What are the various constituents of air? Write their uses.
Answer:
Air contains gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, inert gases, water vapour and dust particles. The uses of constituents of air are as follows.


Question d.
Why are air, water and land considered to be valuable natural resources?
Answer:
Activity:
Natural Resources Air, Water And Land Class 6 Questions And Answers Question 1.
Obtain detailed information about the work of the India Meteorological Department.
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Questions And Answers Question 2.
Find a remedy for water scarcity.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks and rewrite the completed statements.
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Natural Resources Air, Water And Land Exercise Question 1.
……………. gas, used for refrigeration and air conditioning, destroys the ozone layer.
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbon or carbon tetrachloride

Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Exercise Question 2.
Air becomes ……………. at higher altitudes.
Answer:
rarer
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Question 3.
………….. of land is reduced if green trees and bushes are grown in it.
Answer:
Erosion
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Question 4.
16th September is celebrated as ………. Day all over the world.
Answer:
Ozone Protection
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Question Answer Question 5.
………….. is the layer of air that surrounds the earth.
Answer:
Atmosphere

Natural Resources Air, Water And Land Question 6.
……………. occupies the largest part of the earth’s surface.
Answer:
Hydrosphere
Natural Resources Air Water And Land Class 6 Question 7.
Gases are not found in the …………… and beyond.
Answer:
exosphere
Choose the correct alternative:
Question 1.
………….. percentage of the land is covered by water.
(a) 70%
(b) 81%
(c) 71%
(d)80%.
Answer:
71%
Question 2.
The gas used in fluorescent tubes is ………………… .
(a) Argon
(b) Helium
(c) Neon
(d) Krypton.
Answer:
Krypton

Question 3.
The ozone layer is found in the lower part of …………… .
(a) atmosphere
(b) stratosphere
(c) mesosphere
(d) trophosphere.
Answer:
stratosphere
Question 4.
Gas released in air on combustion of fuel is …………….. .
(a) Hydrogen sulphide
(b) Carbon tetrachloride
(c) Nitrogen dioxide
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
Nitrogen dioxide
Question 5.
The proportion of humus in the upper layer of good fertile soil is about ……………… .
(a) 23% to 45%
(b) 33% to 50%
(c) 30% to 53%
(d) 13% to 33%
Answer:
33% to 50%
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Group ‘A’ | Group’B’ |
| 1. Argon | a. temperature for obtaining low |
| 2. Neon | b. Used in electric bulb |
| 3. Xenon | c. Decorative lights |
| 4. Chlorofluoro – carbon | d. Flash photography |
| 5. Helium | e. Ozone depletion |
| Group ‘A’ | Group’B’ |
| 1. Argon | b. Used in electric bulb |
| 2. Neon | c. Decorative lights |
| 3. Xenon | d. Flash photography |
| 4. Chlorofluoro – carbon | e. Ozone depletion |
| 5. Helium | a. temperature for obtaining low |

Name the following:
Question 1.
Substances formed when fuel burns.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide and smoke.
Question 2.
Layers of the atmosphere.
Answer:
Troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, ionosphere and exosphere.
Question 3.
Layers of land.
Answer:
Humus, mature soil, immature soil, small rocks and stones and bedrock.

Question 4.
Gas necessary for building proteins.
Answer:
Nitrogen.
State whether True or False. Correct if False.
Question 1.
The amount of gases in the air is greatest near the surface and becomes rarer at higher altitudes.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Fogs, clouds, snow, and rain are produced in the exosphere.
Answer:
False – Fogs, clouds, snow and rain are formed in the troposphere and lower stratosphere of the atmosphere.
Question 3.
Fossil fuels are formed from the dead remains of animals and plants buried underground for a long period.
Answer:
True.
Explain what will happen if:
Question 1.
Forests are destroyed.
Answer:

Question 2.
What would have happened if there was no air on the earth?
Answer:
Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is humus?
Answer:
Humus is the topmost layer of the soil formed d by decomposition of remains of plants and animals and it makes the soil fertile.
Question 2.
What is land made up of?
Answer:
Land is made up of stones, soil, sand and big rocks.

Question 3.
Is land flat everywhere?
Answer:
No, land is not flat everywhere. It is flat in some regions and hilly in some regions.
Question 4.
Does man produce soil/ land?
Answer:
No, man does not produce soil/land, it is produced naturally.
Question 5.
What do you see on land?
Answer:
We see mountains, rivers, valleys, ocean, also terrestrial animals and plants. We also see roads, bridges, buildings etc.
Question 6.
What has man created on land?
Answer:
Man has dug wells, borewells to lift ground water. He has also constructed bunds and dams. He has also built many industries, buildings, roads for transport.

Question 7.
If a deep pit is dug in the ground, what do you see there?
Answer:
We see different layers of land.
Answer in your own words.
Question 1.
Explain with the help of diagram various layers of land.
Answer:

Observe the picture and answer the questions.

Question 1.
Where do you see the birds?
Answer:
The birds are flying in the sky.

Question 2.
Where is the cow grazing?
Answer:
The cow is grazing in the pasture (field).
Question 3.
Locate the trees.
Answer:
The trees are seen along the river bank.
Question 4.
Where does the river come from?
Answer:
The river flows from the mountains towards the plains.
Question 5.
Where is the aeroplane?
Answer:
The aeroplane is in the sky above the clouds.

Question 6.
Where are fishes seen?
Answer:
Fishes are seen swimming in the river water.
Question 7.
On what is the sail boat floating?
Answer:
Sail boat is floating on the water.
Observe and discuss:

Question 1.
What is the similarity in the three pictures given above?
Answer:
All the pictures given above show large scale emission of smoke through different agencies. This smoke directly mixes with the atmosphere, disturbing the balance between the constituents of air and causing air pollution.
Observe and discuss:

Observe the distribution of water on the earth surface and complete the table.
Question 1.

Answer:
| Water available on earth | percentage |
| Seas, oceans | 97% |
| Groundwater and water in other forms | 2.7% |
| Water available for drinking | 0.3% |
| Total | 100% |

Question 1.
For which purpose is water being used?
Answer:
Water is being used for washing clothes, for bathing, farming, drinking, and industries.

Question 2.
Do other living things use water like we do?
Answer:
Animals do not use water like us. They use water only for drinking. Some animals like buffaloes, rhinoceros, elephants use water for cooling themselves during summers.
Question 3.
What are the constituents of soil? Classify them as biotic and abiotic constituents.
Answer:
The constituents of soil are humus, soil, sand, gravel, stones, bedrock, insects, worms, microbes, roots of trees and dead leaves, burrowing rodents like mice and rats.
| Biotic | Abiotic |
| Microbes, rodents like mice and rats, humus containing microbes and dead leaves. | Soil, sand, gravel, stones, bedrock. |
Question 1.
How would you save water? Give some measures you will adopt.
Answer:
Water can be saved in the following ways:

Question 2.
What measures would you take to prevent soil erosion?
Answer:
Let’s try this

Observe it the next day and answer.
Question 1.
How does the mixture in the bottle look now?
Answer:
The mixture gets segregated into various layers. Heaviest substances settle down and lighter forms topmost layer.
Question 2.
Do you see the layers in it?
Answer:
Yes, we see the layers of soil.

Question 3.
What is seen in the different layers from top to bottom?
Answer:
The dry leaves are floating above the water at the top. Then the layer of the soil, which forms a layer above the sand. Below the sand we see a layer of small stones, and the big ones have settled down at the bottom of the bottle.
Question 4.
Obtain specimens of soil from various places and note the differences in the specimen with respect to colour, feel, texture and size of the particles.
Answer:
| Area from where soil sample is taken | Colour | Texture |
| 1. Own yard | Red colour | Smooth soil which is dry. |
| 2. Garden | Black colour | Sticky soil, rich in humus and insects. |
| 3. Hills | Red colour | Rough soil with small stones and pebbles. |
| 4. River banks | White colour | Sandy and moist in nature. |
| 5. Fields | Black soil | Sticky soil with fine particles, rich in humus and worms. |
| 6. Rocky ground | Black | Coarse with stones and pebbles, hardly any fine soil is seen. |

Question 5.
Observe how much water is used and for what purposes it is used in your house for a whole day. Record it in a chart. Discuss this data and find out how much water each person needs in your house.
Answer:
| Purpose for which water is used | Amount of water (approx in litres) |
| 1. Bath | 50 litres |
| 2. Brushing teeth | 1 litre |
| 3. Washing clothes and utensils | 75 litres |
| 4. Mopping the floor | 10 litres |
| 5. Drinking | 8 litres |
| 6. Cooking | 6 litres |
| Total use of water | 150 litres |
Total water used per person = \(\frac{50}{3}\) = 50 litres.
Approximately 50 litres of water is required for 1 person.
