Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions
Chapter 3 Tides Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Tides Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Prepare a chain by matching the following:
Question 1.
Answer:
1 – e – iii
2 – c – i
3 – d – v
4 – b – ii
5 – a – iv

2. Give geographical reasons:
Question 1.
Tides are influenced more by the moon than the sun.
Answer:
Question 2.
At some places along the coast, the low lying areas turn into lagoons or marshy lands.
Answer:
(i) Generally the areas along the sea coast are low lying and get flooded easily by the sea water during high tide.
(ii) This leads to accumulation of sea water over a long period of time leading to formation of swamps & marshes.
(iii) The tides help in maintaining the mangroves and the coastal biodiversity here.
(iv) Certain areas near the sea coast being low lying & waters being shallow also lead to sediment deposition by sea waves leading to formation of lagoons.
(v) In this way, at some places along the coast, the low lying areas turn into lagoons or marshy lands.
Question 3.
Place located on the opposite meridian experiencing high or low tide will also experience high or low tide respectively.
Answer:
(i) The gravitational force of moon, the sun & the earth and the centrifugal force generated due to the rotation of the earth are two major factors responsible for the occurrence of tides.
(ii) When a place (meridian) faces the moon the gravitational force of the moon exceeds the centrifugal force of the earth leading to high tide here as the water is pulled towards the moon.
(iii) At the same time the place on the earth located at the opposite meridian to the place experiencing high tide, the centrifugal force of the earth exceeds the gravitational force of the moon. Thus, the water is pulled in the direction away from the moon leading to high tide.
(iv) The water required for the high tide moves in from places that are at right angles to those having high tides causing a low tide at those places.
(v) Thus, place located on the opposite meridian to the place experiencing high or low tide will also experience high or low tide respectively.
3. Answer in brief:
Question 1.
If there is high tide at 7 am, find the timings of the next high and low tides on the same day at a given place.
Answer:

Question 2.
If at Mumbai (73° E meridian), there is high tide at 1.00 pm on Thursday, then on which other meridian will there be a high tide too? State with reasons.
Answer:
The other meridian which will experience high tide will be 107°W (180°-73°) because it is exactly 180° opposite from 73°E.
Question 3.
Explain the reasons for the generation of waves.
Answer:
4. In what way will the following depend on the tides:
Question 1.
Swimming:
Answer:
A lack of an understanding of the timings of high and low tides may cause accidents to swimmers entering the sea.
Question 2.
Steering a ship:
Answer:
Ships can move up to the ports during high tide.
Question 3.
Fishing:
Answer:
With the high tide, fish moves into the creeks and this helps the fishing activity.
Question 4.
Salt Pans:
Answer:
During high tide, seawater can be stored in salt pans from which salt can be obtained.
Question 5.
Going to coastal areas for trips:
Answer:
Plan for going to trips after full moon or new moon day. Also one must have details about the timings of the tides for better enjoyment.
5. Observe figure of neap tide and answer the following questions:
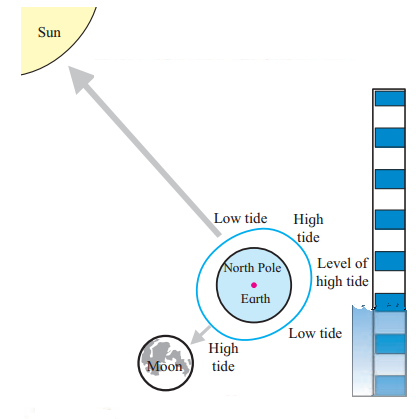
Question 1.
Which phase of the moon does it show?
Answer:
The diagram shows the phase of the quarter moon.

Question 2.
What are the relative positions of the moon, the sun and the earth?
Answer:
The moon, the earth and the sun make an angle of 90° (right angle)
Question 3.
What effect will it have on the tides?
Answer:
It will lead to neap tide. Due to such conditions during high tide the water level will rise less than usual while during low tide water level will fall less than usual.
6. Differentiate between:
Question 1.
High tide and low tide:
Answer:
Question 2.
Spring tide and neap tide.
Answer:
7. Describe the positive and negative effects of tides:
Answer:
The positive effects of tides are as follows:
The negative effects of tides are as follows:
Activities:
Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Tides InText Questions and Answers
Differentiate between:
Question 1.
Centrifugal force and Gravitational
Answer:
Write short notes:
Question 1.
Spring tide
Answer:
(i) On new moon & full moon days, the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon act in the same direction due to which the total pull increases.
(ii) Hence, the tide on these days is much higher than the average high tide.
(iii) This is known as spring tide.

Question 2.
Neap tide
Answer:
(i) While revolving around the earth, the moon makes a right angle with respect to the earth and the sun, twice a month.
(ii) This position occurs on the first and third quarter of each month. On both these days the forces of both the sun & the moon operate at right angles on the earth.
(iii) At the places where the sun causes high tide, the gravitational pull of the moon which is at right angles also acts on the water.
(iv) Due to such conditions the water level rise is less than usual at the time of high tide. Similarly, fall in water level is less than usual at the time of low tide.
(v) Such tides are called neap tides.
Question 3.
Waves
Answer:
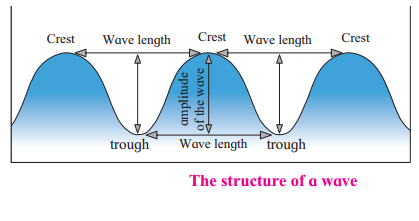
Question 4.
Struture of the waves
Answer:
(i) The sea water gets pushed up & down because of the wind. The raised up portion of the wave is called crest & the depressed one is called trough.
(ii) The vertical distance between a crest and the following trough is called the amplitude of the wave whereas the distance between two successive crests or troughs is called wave length.
(iii) The wave length, its amplitude & its velocity depend on the velocity of the wind.
Formative Assessment:
Observe the activity on pages 9, 10 of the textbook & discuss the result of the activities and answer the question given below:



Question 1.
In which direction will the piece of chalk fall? (fig. 1)
Answer:
The chalk will fall to the right.
Question 2.
Where did the water in the glass show a bulge? (fig. 2)
Answer:
At the sides of the glass.
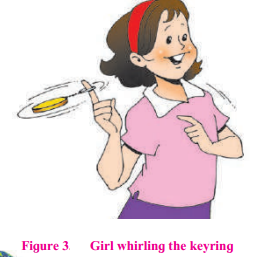
Question 3.
What effect did the movement have on the things attached to the keyring? (fig. 3)
Answer:
The things attached to the keyring will move round.
Question 4.
What happened to the water in the container and the mixer? (fig. 1)
Answer:
The water will swirl round forming a bulge at the sides and a depression in the centre.
Question 5.
Which forces could be operating in activities listed above?
Answer:
In the first activity (fig. 1) gravitational force acted and in the fig. 2, fig. 3 centrifugal force.
Question 6.
In the following activities, which force is greater, centrifugal or gravitational?
Answer:
The centrifugal force was greater than the gravitational force.
Can you tell?
Answer the following of questions with the help of figure
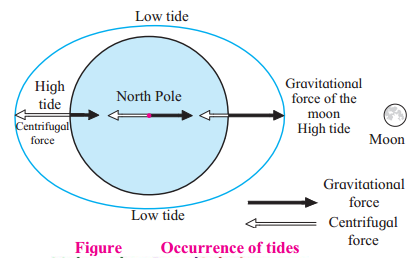
Question 1.
How do the tides occur?
Answer:
Tides occur due to the relative positions of the moon, the sun, and the earth.
Question 2.
Which force is applied when the moon is closer to the earth?
Answer:
Gravitational force becomes more effective than that of the sun when the moon is closer to the earth.
Question 3.
If it is high tide those having high tide at 0° and 180° meridian then at which meridians will low tide occur?
Answer:
The meridians that are at right angle to those having high tide will experience low tide at the same time ie. at 90°E & 90°W.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Tides Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct options from the brackets:

Question 1.
Due to rotation, the force that works away from the centre of the earth is the ______force. (gravitational, rotational, centrifugal)
Answer:
centrifugal
Question 2.
Neap tide occurs on the days of the ______ and _______ quarter of each month. (first, second, third)
Answer:
first, third
Question 3.
The tidal range in open seas is ______ cms. (20, 30, 40)
Answer:
30
Question 4.
The highest tidal range in the world is observed at _______.(Bay of Fundy, Bay of Biscay, Bay of Bengal)
Answer:
Bay of Fundy
Question 5.
The main reason for wave generation is ______ (wind, gravitational force, centrifugal force)
Answer:
wind
Question 6.
The raised up portion of a wave is called a _______ .(trough, wave length, crest)
Answer:
crest
Question 7.
The depressed portion of a wave is called a ______. (trough, wave length, crest)
Answer:
trough
Question 8.
The vertical distance between a crest and a trough is called the _____.(wave length, amplitude, tide)
Answer:
amplitude
Question 9.
The distance between a crest or trough is called _____ (amplitude, wave length, tide)
Answer:
wave length
Question 10.
Tall sea waves caused by earthquakes below the floor of the sea are called _____.(cyclones, tsunamis, eruption)
Answer:
tsunamis
Match the following:
Question 1.
Answer:
1 – c
2- a
3 – d
4 – b
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
High and low tides are _______ phenomena.
Answer:
Natural
Question 2.
_________ are movements of sea water occurring daily and regularly.
Answer:
Tides

Question 3.
Any object on the surface of the earth remains at the place due to the ______ force.
Answer:
Gravitational
Question 4.
The meridians that are at right angles to those having high, tide will experience tide _______.
Answer:
Low
Question 5.
On the days of the first and the third quarter, the high tide is at its _____.
Answer:
Minimum
Question 6.
On new moon and full moon days, the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon acting the ______ direction.
Answer:
Same
Question 7.
At every ______ a cycle of high tide and low tide gets completed.
Answer:
12 hrs & 25 min
Name the following:
Question 1.
Movement of sea water.
Answer:
Tides.
Question 2.
Two forces directly related with tides.
Answer:
Gravitational and Centrifugal forces.
Question 3.
Two types of tide.
Answer:
Spring tide and Neap tide.
Question 4.
The difference in the water level of the high tide and low tide.
Answer:
Tidal range.
Question 5.
The region with highest tidal range in India.
Answer:
The Gulf of Khambhat.
Question 6.
Tall waves caused by earthquakes in the shallow waters near the coast, which are very destructive.
Answer:
Tsunami.
Question 7.
Place where tsunami waves were generated in 2004.
Answer:
Sumatra islands of Indonesia.

Question 8.
Type of tide occuring on full moon day.
Answer:
Spring tide.
Question 9.
Type of tide occuring when sun and the moon are at right angles to each other.
Answer:
Neap tide.
Question 10.
Distance between two successive crests or troughs.
Answer:
Wavelength.
Define the following:
Question 1.
Tide:
Answer:
The alternate rising and falling of the sea water after a specific period is called tide.
Question 2.
Centrifugal force:
Answer:
Due to the earth’s rotation, the earth gets a type of power or force. This force works away from the centre. It is called the centrifugal force.
Question 3.
Tidal range:
Answer:
The difference in the water level of the high tide and low tide is called tidal range.
Question 4.
Waves:
Answer:
The sea water gets pushed by the wind and so ripples are generated on the water surface. These are called waves.
Question 5.
Amplitude of the wave:
Answer:
The vertical distance between a crest and the following trough is called the amplitude of the wave.
Question 6.
Wave length:
Answer:
The wave length is the distance between two successive crests or troughs.
Write whether the following statements are true or false:
Question 1.
The gravitational force is many times greater than the centrifugal force.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Spring tides are lower than average high tides.
Answer:
False

Question 3.
Centrifugal force is generated due to the revolution of the earth.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
When there is high tide at 0° meridian, the 180° meridian also experiences high tide.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Tides occur due to the relative positions of the moon, the sun and the earth.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
The tides clean the waste and hence the coastal areas become clean.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
The tides worsen the maintaining of mangroves and the coastal biodiversity.
Answer:
False
Question 8.
Generation of waves is a natural and regularly occurring phenomenon.
Answer:
True
Give geographical reasons:
Question 1
Any object on the surface of the earth remains at the place where it exists.
Answer:
Question 2.
On new moon and full moon days the tides are higher than average.
Answer:

Question 3.
Neap tides are a little lower than average high tides.
Answer:
Answer in brief:
Question 1.
Which factors are responsible for the occurrence of tides?
Answer:
The following factors are responsible for the occurrence of tides.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of:
Question 1.
The structure of a wave:
Answer:
Question 2.
Springtide:
Answer:
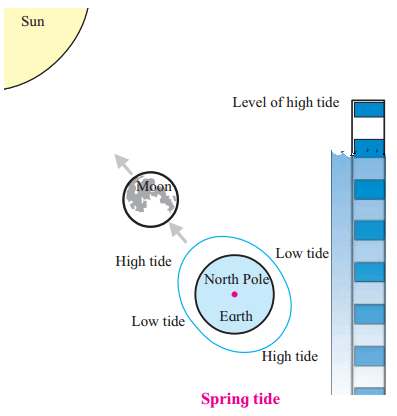

Question 3.
Neap tide:
Answer:
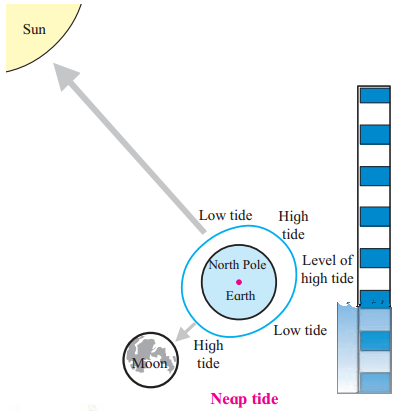
Question 4.
Occurrence of tides:
Answer:

Observe the following pictures and answer the following questions given below and discuss:


Question 1.
Do the above photographs show the same place or different places?
Answer:
Both the photographs show the same place.
Question 2.
Observe and note the spread of water seen in both the photographs.
Answer:
The level of water is higher in the first picture and lower in the second.
Question 3.
What is this natural event called?
Answer:
This natural event is called tide.

Try this:
Take a wide open large dish.
Keep the dish on a table or a flat surface.
Fill water in the dish up to the rim,(we have to generate waves in the dish).
Question 1.
Is it possible to generate waves without touching or shoving the dish? Try doing so.
Answer:
By blowing air with your mouth on the water surface of the dish.
Question 2.
In what different ways can you generate waves in the dish?
Answer:
Chapter 3 Tides Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Tides Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Prepare a chain by matching the following:
Question 1.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ | Group ‘C’ |
| (1) Waves | (a) 8th phase of the moon (Quarter) | (i) Objects get thrown towards the outer side. |
| (2) Centrifugal force | (b) Newmoon day | (ii) Highest high tide occurs on this day. |
| (3) Gravitational force | (c) Rotation of the earth | (iii) These are also generated due to earthquakes and volcanoes. |
| (4) Spring Tide | (d) The moon, the sun and the earth | (iv) The forces of the sun and the moon operate in different directions. |
| (5) Neap tide | (e) Wind | (v) Operates in the direction towards the centre of the earth. |
1 – e – iii
2 – c – i
3 – d – v
4 – b – ii
5 – a – iv

2. Give geographical reasons:
Question 1.
Tides are influenced more by the moon than the sun.
Answer:
Question 2.
At some places along the coast, the low lying areas turn into lagoons or marshy lands.
Answer:
(i) Generally the areas along the sea coast are low lying and get flooded easily by the sea water during high tide.
(ii) This leads to accumulation of sea water over a long period of time leading to formation of swamps & marshes.
(iii) The tides help in maintaining the mangroves and the coastal biodiversity here.
(iv) Certain areas near the sea coast being low lying & waters being shallow also lead to sediment deposition by sea waves leading to formation of lagoons.
(v) In this way, at some places along the coast, the low lying areas turn into lagoons or marshy lands.
Question 3.
Place located on the opposite meridian experiencing high or low tide will also experience high or low tide respectively.
Answer:
(i) The gravitational force of moon, the sun & the earth and the centrifugal force generated due to the rotation of the earth are two major factors responsible for the occurrence of tides.
(ii) When a place (meridian) faces the moon the gravitational force of the moon exceeds the centrifugal force of the earth leading to high tide here as the water is pulled towards the moon.
(iii) At the same time the place on the earth located at the opposite meridian to the place experiencing high tide, the centrifugal force of the earth exceeds the gravitational force of the moon. Thus, the water is pulled in the direction away from the moon leading to high tide.
(iv) The water required for the high tide moves in from places that are at right angles to those having high tides causing a low tide at those places.
(v) Thus, place located on the opposite meridian to the place experiencing high or low tide will also experience high or low tide respectively.
3. Answer in brief:
Question 1.
If there is high tide at 7 am, find the timings of the next high and low tides on the same day at a given place.
Answer:

Question 2.
If at Mumbai (73° E meridian), there is high tide at 1.00 pm on Thursday, then on which other meridian will there be a high tide too? State with reasons.
Answer:
The other meridian which will experience high tide will be 107°W (180°-73°) because it is exactly 180° opposite from 73°E.
Question 3.
Explain the reasons for the generation of waves.
Answer:
4. In what way will the following depend on the tides:
Question 1.
Swimming:
Answer:
A lack of an understanding of the timings of high and low tides may cause accidents to swimmers entering the sea.
Question 2.
Steering a ship:
Answer:
Ships can move up to the ports during high tide.
Question 3.
Fishing:
Answer:
With the high tide, fish moves into the creeks and this helps the fishing activity.
Question 4.
Salt Pans:
Answer:
During high tide, seawater can be stored in salt pans from which salt can be obtained.
Question 5.
Going to coastal areas for trips:
Answer:
Plan for going to trips after full moon or new moon day. Also one must have details about the timings of the tides for better enjoyment.
5. Observe figure of neap tide and answer the following questions:

Question 1.
Which phase of the moon does it show?
Answer:
The diagram shows the phase of the quarter moon.

Question 2.
What are the relative positions of the moon, the sun and the earth?
Answer:
The moon, the earth and the sun make an angle of 90° (right angle)
Question 3.
What effect will it have on the tides?
Answer:
It will lead to neap tide. Due to such conditions during high tide the water level will rise less than usual while during low tide water level will fall less than usual.
6. Differentiate between:
Question 1.
High tide and low tide:
Answer:
| High tide | Low Tide |
| (i) The rise in the level of sea water is caused by the combined effect of centrifugal and gravitational force of the moon and the sun. | (i) The fall in the level of sea water is caused by the combined effect of centrifugal and gravitational force of the moon and the sun. |
| (ii) At the time of high tide, sea water is very close to the coast. | (ii) At the time of low tide, sea water is far away from the coast. |
Spring tide and neap tide.
Answer:
| Spring tide | Neap Tide |
| (i) It occurs on the new moon day and the full moon day. | (i) It occurs on the the first and the third quarter days. |
| (ii) The gravitational pull of the moon and the sun as well as that of the earth are in a straight line and act in the same direction. | (i) The gravitational pull of the moon and the sun are at right angle. |
| (iii) Spring tides are a little higher than the average high tides and a little lower than the average low tides. | (iii) Neap tides are a little lower than the average high tides and little higher than the average low tides. |
Answer:
The positive effects of tides are as follows:
The negative effects of tides are as follows:
Activities:
Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Tides InText Questions and Answers
Differentiate between:
Question 1.
Centrifugal force and Gravitational
Answer:
| Centrifugal force | Gravitational force |
| (i) Due to rotation, the earth gets a type of power of force. This force works away from the centre. It is called centrifugal force. (ii) Centrifugal force works away from the centre. (iii) Due to centrifugal force an object on the earth would be thrown into the space. |
(i) Gravitational force is working towards the centre of the earth. This force is many times greater than the centrifugal force. (ii) Gravitational force works towards the centre. (iii) Due to gravitational force an object on the surface of the earth remains at the place where it exists. |
Question 1.
Spring tide
Answer:
(i) On new moon & full moon days, the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon act in the same direction due to which the total pull increases.
(ii) Hence, the tide on these days is much higher than the average high tide.
(iii) This is known as spring tide.

Question 2.
Neap tide
Answer:
(i) While revolving around the earth, the moon makes a right angle with respect to the earth and the sun, twice a month.
(ii) This position occurs on the first and third quarter of each month. On both these days the forces of both the sun & the moon operate at right angles on the earth.
(iii) At the places where the sun causes high tide, the gravitational pull of the moon which is at right angles also acts on the water.
(iv) Due to such conditions the water level rise is less than usual at the time of high tide. Similarly, fall in water level is less than usual at the time of low tide.
(v) Such tides are called neap tides.
Question 3.
Waves
Answer:
Question 4.
Struture of the waves
Answer:
(i) The sea water gets pushed up & down because of the wind. The raised up portion of the wave is called crest & the depressed one is called trough.
(ii) The vertical distance between a crest and the following trough is called the amplitude of the wave whereas the distance between two successive crests or troughs is called wave length.
(iii) The wave length, its amplitude & its velocity depend on the velocity of the wind.
Formative Assessment:
Observe the activity on pages 9, 10 of the textbook & discuss the result of the activities and answer the question given below:




Question 1.
In which direction will the piece of chalk fall? (fig. 1)
Answer:
The chalk will fall to the right.
Question 2.
Where did the water in the glass show a bulge? (fig. 2)
Answer:
At the sides of the glass.
Question 3.
What effect did the movement have on the things attached to the keyring? (fig. 3)
Answer:
The things attached to the keyring will move round.
Question 4.
What happened to the water in the container and the mixer? (fig. 1)
Answer:
The water will swirl round forming a bulge at the sides and a depression in the centre.
Question 5.
Which forces could be operating in activities listed above?
Answer:
In the first activity (fig. 1) gravitational force acted and in the fig. 2, fig. 3 centrifugal force.
Question 6.
In the following activities, which force is greater, centrifugal or gravitational?
Answer:
The centrifugal force was greater than the gravitational force.
Can you tell?
Answer the following of questions with the help of figure

Question 1.
How do the tides occur?
Answer:
Tides occur due to the relative positions of the moon, the sun, and the earth.
Question 2.
Which force is applied when the moon is closer to the earth?
Answer:
Gravitational force becomes more effective than that of the sun when the moon is closer to the earth.
Question 3.
If it is high tide those having high tide at 0° and 180° meridian then at which meridians will low tide occur?
Answer:
The meridians that are at right angle to those having high tide will experience low tide at the same time ie. at 90°E & 90°W.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Tides Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct options from the brackets:

Question 1.
Due to rotation, the force that works away from the centre of the earth is the ______force. (gravitational, rotational, centrifugal)
Answer:
centrifugal
Question 2.
Neap tide occurs on the days of the ______ and _______ quarter of each month. (first, second, third)
Answer:
first, third
Question 3.
The tidal range in open seas is ______ cms. (20, 30, 40)
Answer:
30
Question 4.
The highest tidal range in the world is observed at _______.(Bay of Fundy, Bay of Biscay, Bay of Bengal)
Answer:
Bay of Fundy
Question 5.
The main reason for wave generation is ______ (wind, gravitational force, centrifugal force)
Answer:
wind
Question 6.
The raised up portion of a wave is called a _______ .(trough, wave length, crest)
Answer:
crest
Question 7.
The depressed portion of a wave is called a ______. (trough, wave length, crest)
Answer:
trough
Question 8.
The vertical distance between a crest and a trough is called the _____.(wave length, amplitude, tide)
Answer:
amplitude
Question 9.
The distance between a crest or trough is called _____ (amplitude, wave length, tide)
Answer:
wave length
Question 10.
Tall sea waves caused by earthquakes below the floor of the sea are called _____.(cyclones, tsunamis, eruption)
Answer:
tsunamis
Match the following:
Question 1.
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ |
| (1) Bay of Fundy (2) Gulf of Khambhat (3) Open Seas (4) Peninsular India |
(a) 1100 cm (b) 100 -150 cm (c) 1600 cm (d) 30 cm |
1 – c
2- a
3 – d
4 – b
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
High and low tides are _______ phenomena.
Answer:
Natural
Question 2.
_________ are movements of sea water occurring daily and regularly.
Answer:
Tides

Question 3.
Any object on the surface of the earth remains at the place due to the ______ force.
Answer:
Gravitational
Question 4.
The meridians that are at right angles to those having high, tide will experience tide _______.
Answer:
Low
Question 5.
On the days of the first and the third quarter, the high tide is at its _____.
Answer:
Minimum
Question 6.
On new moon and full moon days, the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon acting the ______ direction.
Answer:
Same
Question 7.
At every ______ a cycle of high tide and low tide gets completed.
Answer:
12 hrs & 25 min
Name the following:
Question 1.
Movement of sea water.
Answer:
Tides.
Question 2.
Two forces directly related with tides.
Answer:
Gravitational and Centrifugal forces.
Question 3.
Two types of tide.
Answer:
Spring tide and Neap tide.
Question 4.
The difference in the water level of the high tide and low tide.
Answer:
Tidal range.
Question 5.
The region with highest tidal range in India.
Answer:
The Gulf of Khambhat.
Question 6.
Tall waves caused by earthquakes in the shallow waters near the coast, which are very destructive.
Answer:
Tsunami.
Question 7.
Place where tsunami waves were generated in 2004.
Answer:
Sumatra islands of Indonesia.

Question 8.
Type of tide occuring on full moon day.
Answer:
Spring tide.
Question 9.
Type of tide occuring when sun and the moon are at right angles to each other.
Answer:
Neap tide.
Question 10.
Distance between two successive crests or troughs.
Answer:
Wavelength.
Define the following:
Question 1.
Tide:
Answer:
The alternate rising and falling of the sea water after a specific period is called tide.
Question 2.
Centrifugal force:
Answer:
Due to the earth’s rotation, the earth gets a type of power or force. This force works away from the centre. It is called the centrifugal force.
Question 3.
Tidal range:
Answer:
The difference in the water level of the high tide and low tide is called tidal range.
Question 4.
Waves:
Answer:
The sea water gets pushed by the wind and so ripples are generated on the water surface. These are called waves.
Question 5.
Amplitude of the wave:
Answer:
The vertical distance between a crest and the following trough is called the amplitude of the wave.
Question 6.
Wave length:
Answer:
The wave length is the distance between two successive crests or troughs.
Write whether the following statements are true or false:
Question 1.
The gravitational force is many times greater than the centrifugal force.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Spring tides are lower than average high tides.
Answer:
False

Question 3.
Centrifugal force is generated due to the revolution of the earth.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
When there is high tide at 0° meridian, the 180° meridian also experiences high tide.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Tides occur due to the relative positions of the moon, the sun and the earth.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
The tides clean the waste and hence the coastal areas become clean.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
The tides worsen the maintaining of mangroves and the coastal biodiversity.
Answer:
False
Question 8.
Generation of waves is a natural and regularly occurring phenomenon.
Answer:
True
Give geographical reasons:
Question 1
Any object on the surface of the earth remains at the place where it exists.
Answer:
Question 2.
On new moon and full moon days the tides are higher than average.
Answer:

Question 3.
Neap tides are a little lower than average high tides.
Answer:
Answer in brief:
Question 1.
Which factors are responsible for the occurrence of tides?
Answer:
The following factors are responsible for the occurrence of tides.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of:
Question 1.
The structure of a wave:
Answer:

Question 2.
Springtide:
Answer:


Question 3.
Neap tide:
Answer:

Question 4.
Occurrence of tides:
Answer:

Observe the following pictures and answer the following questions given below and discuss:


Question 1.
Do the above photographs show the same place or different places?
Answer:
Both the photographs show the same place.
Question 2.
Observe and note the spread of water seen in both the photographs.
Answer:
The level of water is higher in the first picture and lower in the second.
Question 3.
What is this natural event called?
Answer:
This natural event is called tide.

Try this:
Take a wide open large dish.
Keep the dish on a table or a flat surface.
Fill water in the dish up to the rim,(we have to generate waves in the dish).
Question 1.
Is it possible to generate waves without touching or shoving the dish? Try doing so.
Answer:
By blowing air with your mouth on the water surface of the dish.
Question 2.
In what different ways can you generate waves in the dish?
Answer: