Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions
Chapter 5 Winds Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Winds Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Rewrite the following statements after choosing the correct option:
Question 1.
When the air expands, it ______.
(a) becomes solid,
(b) becomes thinner,
(c) gets lost.
(d) becomes humid.
Answer:
(b) becomes thinner,

Question 2.
From high air pressure regions, winds ______.
(a) blow to regions of still higher pressure.
(b) blow towards regions of cooler air.
(c) blow towards regions of low air pressure.
(d) remains still.
Answer:
(c) blow towards regions of low air pressure.
Question 3.
In the northern hemisphere, winds blowing towards the equator due to the _____.
rotation of the earth.
(a) turn to the south
(b) turn to the east,
(c) turn to the west
(d) turn to the north.
Answer:
(c) turn to the west
Question 4.
The direction of seasonal winds blowing over the Indian subcontinent during winter is from the _____.
(a) south-east to north-west.
(b) south-west towards north-east.
(c) north-east to south-west.
(d) north-west to south-east.
Answer:
(c) north-east to south-west.
Question 5.
The Roaring Forties in the southern hemisphere ______.
(a) blow towards the equator.
(b) blow in the areas around 40°S parallel.
(c) blow from the subpolar region of low pressure.
Answer:
(b) blow in the areas around 40°S parallel.
2. Identify the type of winds from the description given below:
Question 1.
These winds from the south-west bring rains to Indian subcontinent. During June to September, India gets rains. After this period these winds retreat.
Answer:
South West Monsoon Winds.
Question 2.
These winds blowing from the north pole region towards 60°N parallel cause cold wave conditions in extensive areas covering North America, Europe and Russia
Answer:
Polar Winds.

Question 3.
Hilltops get heated quickly during the day. The air in this part becomes hot, light and starts ascending. Hence, a low pressure area forms in this region. At the same time the air at the foothills become cooler and also experiences high pressure. Air in that area blows towards low pressure.
Answer:
Valley Winds.
3. Given below are the values of air pressure in millibars. Using the same, draw diagrams to show a cyclone and an anticyclone:
Question 1.
990, 994, 996,1000
Answer:
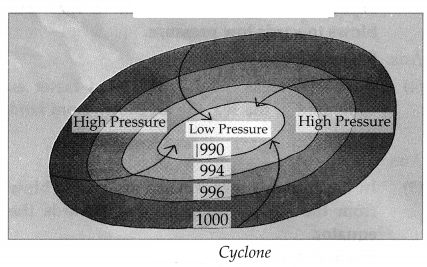
Question 2.
1030,1020,1010,1000
Answer:
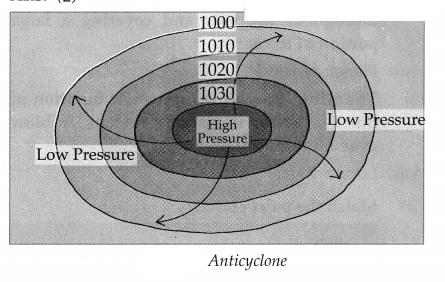
4. State one reason why:
Question 1.
A belt of calm exists near the equator.
Answer:
(i) A belt of calm exists near the equator because there is not much difference in the temperature and air pressure.
(ii) So winds do not blow in this region.
Question 2.
The winds coming from the north-west in the southern hemisphere have greater velocities than the winds coming from the south-west in the northern hemisphere.
Answer:
(i) In the southern hemisphere the obstacle caused by the relief of the land surface is almost absent.
(ii) Therefore the winds coming from the north – west in the southern hemisphere have greater velocity than the winds coming from the south-west in the northern hemisphere.
Question 3.
The monsoon winds in the summer come from the sea but the retreating monsoon winds come from land.
Answer:
(i) Monsoon winds are generated due to the uneven heating of land and water in the different seasons.
(ii) During summers, land heats up quickly as compared to water & an area of low pressure is created on the land whereas an area of high pressure is created on the water.
(iii) But during winters low pressure is created on the water and an area of high pressure is created on land as it cools down quickly as compared to the water.
(iv) As winds blow from high pressure areas to low pressure areas, it blows from sea to land in summers & from land to sea in winters.
Thus the monsoon winds in summer come from sea but the retreating monsoon winds come from land.

5. Complete the flow chart:
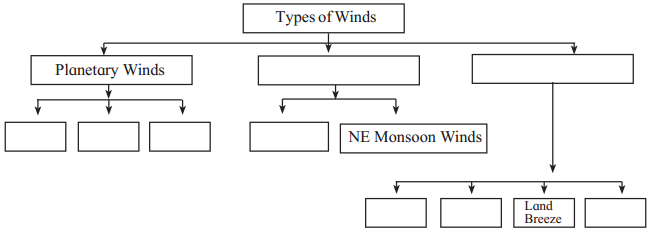
Answer:
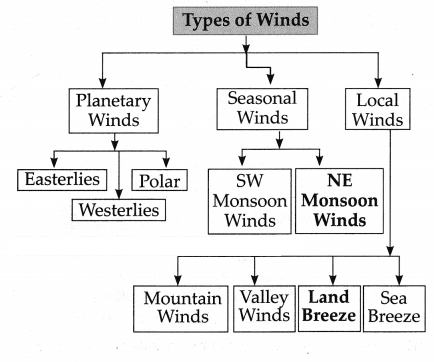
6. Answer in short:
Question 1.
Why is the air pressure high in polar areas in both the hemispheres?
Answer:
Question 2.
What effect does the rotation of the earth have on the wind?
Answer:
Question 3.
Why do the cyclonic winds blow in a circular manner?
Answer:
(i) Cyclones are created when a low pressure area is surrounded by high pressure areas. In these conditions, winds start blowing towards the low pressure area from the surrounding high pressure areas.
(ii) But due to the rotation of the earth in the northern hemisphere the winds deflected towards the right of their original direction whereas in the southern hemisphere they get deflected towards the left of their original direction which causes the cyclone winds to blow in a circular manner.
Question 4.
State the reasons that lead to the formation of cyclones and describe the effects of cyclones.
Answer:
(i) Cyclonic conditions are created when a low pressure area is surrounded by high pressure areas.
(ii) In these conditions, winds start blowing towards the low pressure area from the surrounding high pressure areas.
(iii) The effects of cyclone are as follows.
Activity:
Using the internet, obtain information, photos and maps of the recent cyclone that arrived at India’s eastern coast.
Write the social and economic effects of that cyclone.
ICT Question:
Use the mobile app ‘Windyty’ and try to know the direction of winds and pressure areas in the world.

Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Winds InText Questions and Answers
Formative Assessment
Can you tell?
Observe the diagrams given below. Answer the questions related to sea and land breeze
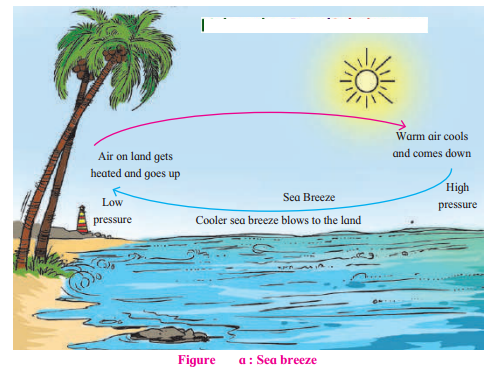
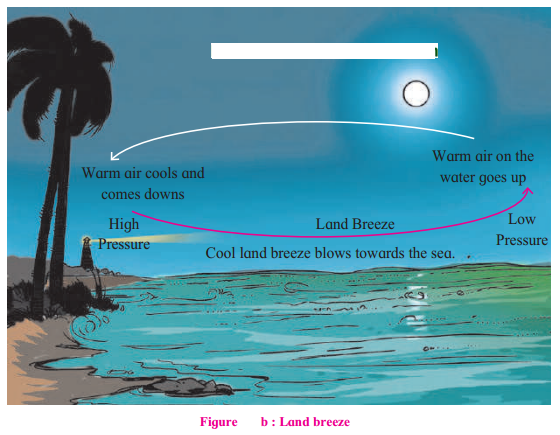
Question 1.
Why do the breezes blow from the sea to the land during the day?
Answer:
During the day as land gets heated up faster than water, an area of low pressure is created on land whereas there is a region of comparatively higher pressure on the sea. As a result the breezes blow from the sea to the land during the day.
Question 2.
When do the winds blow from the d to the sea?
Answer:
The winds blow from land to the sea during the night.
Question 3.
Describe the winds shown in fig. (a).
Answer:
It is sea breeze.
Question 4.
Compare fig.(a) and (b) with reference fo temperature conditions, air pressure and
winds.
Answer:
In figure (a) the temperature is higher on land & the pressure is low so winds blow from sea to land. In figure (b) the temperature is low on the land & the pressure is high. Winds blow from land to sea.
Question 5.
Which winds are called sea breezes and which are called land breezes? Why?
Answer:
Winds in (a) are sea breeze because they blow from the sea and (b) are land breeze because they blow from the land.

Question 6.
In which part of India are land and sea breezes experienced?
Answer:
In India, it is experienced near the coastal areas.
Question 7.
Do you experience sea and land breezes in your area?
Answer:
The answer may vary.
Give it a try.
Write the changed directions of the wind in the table below:
Question 1.
Answer:
Try this:
Question 1.
Observe the pictures given below and describe the valley breeze considering the elevation of land, the heating and cooling properties of land and water, the air pressure, etc.
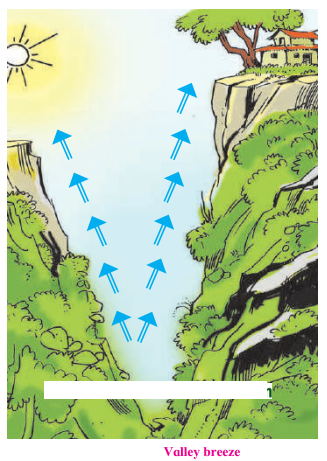
Answer:
Characteristics of Valley Breeze:
Question 2.
Read the following information carefully and draw a diagram for the mountain breeze accordingly.
Characteristics of the Mountain breeze:

Answer:

Try this:
Question 1.
Without touching the roll of the paper on the table, what can be done to move the paper rolls to the other end of the table?
Answer:
To move the paper rolls to the other end of the table without touching a person can
Question 2.
See who moves the paper roll first to the other end of the table:
Answer:
The object which blows the air with maximum force, moves the paper roll first to the other end of the table.
Question 3.
What could be the reason of the delay in making the rolls reach to the other end of the table?
Answer:
There will be a delay in making the rolls reach the other end of the table if the air is blown with lesser force.
Question 4.
What can we do to move the rolls to the other end of the table with a greater speed?
Answer:
We mostly use the technique/object which will blow air with maximum force to move the rolls to the other end of the table with a greater speed.
Question 5.
Can a bottle filled with water be moved to the other end of the table in this manner? Can we use the same method that you tried for moving paper rolls?
Answer:
A bottle filled with water cannot be moved to the other end of the table in this manner. We cannot use the same methods that we tried for moving paper rolls to move a bottle filled with water as it is heavier in weight, (we can if we tilt the table which was an option.)
Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Winds Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct option from the bracket:
Question 1.
Air moves from high pressure to low pressure areas in a ______ manner. (vertical, horizontal, parallel)
Answer:
horizontal.

Question 2.
Winds velocity is measured in the units of ________. (knots, metres, seconds)
Answer:
knots.
Question 3.
Wind which cover a large portion of the earth are called _____ wind. (local, polar, planetary)
Answer:
planetary.
Question 4.
Winds blowing between mid latitudinal high pressure belt and the equator are called ______. (westerlies, easterlies, polar)
Answer:
easterlies.
Question 5.
Winds blowing between mid latitudinal high pressure belt and the sub polar low pressure belt are called _______. (easterlies, westerlies, polar)
Answer:
westerlies.
Question 6.
Winds that blow for a short duration of time, over a limited area are called ______. wind. (polar, local, easterlies)
Answer:
local.
Question 7.
Mountain winds blow during ______ .(morning, night, midday)
Answer:
night.
Question 8.
Winds that blow at night in coastal areas are called ________ breeze, (sea, land, valley)
Answer:
land.
Question 9.
Cyclones occurring in the western part of the Pacific ocean are called ______.(hurricane, typhoons)
Answer:
typhoons.
Question 10.
Hot winds blowing in the Thar Desert are called the _______ (simoons, loo, chinook)
Answer:
loo.
Rewrite the following statements after choosing the correct option:
Question 1.
During an anticyclone the sky ______.
(a) is dark.
(b) is cloudy.
(c) is clear.
(d) is white.
Answer:
(c) is clear.

Question 2.
Winds blowing from the polar high pressure to sub polar low pressure belt
(a) blow from west to east.
(b) blow from east to west.
(c) blow from south to north.
(d) blow from north to south.
Answer:
(b) blow from east to west.
Question 3.
The minimum velocity of cyclonic storms is ________.
(a) 50 km per hour
(b) 60 km per hour
(c) 70 km per hour
(d) 80 km per hour.
Answer:
(b) 60 km per hour
Question 4.
Winds which originate in specific regions and blow over a limited area are called _____.
(a) local winds.
(b) seasonal winds
(c) monsoon winds
(d) planetary winds
Answer:
(a) local winds.
Find out the odd man out and give reason for your answer:
Question 1.
Polar winds, Local winds, Easterlies, Westerlies
Answer:
Local winds – Others are names of planetary winds.
Question 2.
Landbreeze, Valley winds, Westerlies, Mountain winds.
Answer:
Westerlies – Others are names of local winds.
Question 3.
Mistral, Bora, Pampero, Foehn
Answer:
Foehn – Others are cold and dry winds.
Question 4.
Loo, Foehn, Mistral, Simoon
Answer:
Mistral – Others are hot and dry winds.
Question 5.
Mistral, Bora, Chinook, Foehn
Answer:
Chinook – Others originate in the Alps Mountain.
Question 6.
Southeast Asia, West Europe, East Africa, North Australia.
Answer:
West Europe – Others receive monsoon rains.

Question 7.
India, Japan, China, Phillippines.
Answer:
India – Others experience typhoons.
Question 8.
Furious Fifties, Screaming Seventies, Screeching Sixties,, Roaring Forties.
Answer:
Screaming Seventies – Others are names of winds in the southern hemisphere.
Place a tick mark (✓) against the correct option:
Question 1.
Towards which direction do the southern hemisphere winds get deflected? .
(a) Towards the left.
(b) Towards the right.
(c) Towards the centre.
Answer:
(a) Towards the left.
Question 2.
What are the winds blowing between polar high pressure belt and subpolar low pressure belt called?
(a) Monsoon winds
(b) Polar winds
(c) Westerlies winds
Answer:
(a) Monsoon winds
Question 3.
Hot and destructive winds blowing in the Sahara
(a) Chinook
(b) Simoom
(c) Loo
Answer:
(b) Simoom
Question 4.
Cold winds around the Mediterranean.
(a) Foehn
(b) Pampero
(c) Mistral
Answer:
(b) Pampero
Question 5.
How is cyclonic condition created?
(a) Low pressure area is surrounded by high pressure.
(b) A high pressure area is surrounded by low pressure.
(c) A low pressure area is surrounded by mid pressure.
Answer:
(c) A low pressure area is surrounded by mid pressure.
Identify the type of winds from the description given below:
Question 1.
In coastal areas, land cools down faster as compared to the sea, the air blows from land to sea.
Answer:
Land Breeze.
Question 2.
In the Indian subcontinent, dry winds blow from the Indian Subcontinent towards the equator.
Answer:
North-East monsoon winds.

Question 3.
The winds blowing over the earth’s surface throughout the year and covering a large portion of the earth.
Answer:
Planetary winds.
Question 4.
The winds that blow for a short duration of time, originate in specific regions & blow over a limited area.
Answer:
Local winds.
Match the pairs correctly:
Question 1.
Answer:
1 – a
2 – c
3 – d
4 – b
Define the following terms:
Question 1.
Roaring Forties:
Answer:
Beyond 40°S winds blow with tremendous velocity. These winds are called the Roaring Forties.
Question 2.
Furious Fifties:
Answer:
Around 50°S winds are stormy hence they are called the Furious Fifties.
Question 3.
Screeching Sixties:
Answer:
The stormy winds around 60°S make tremendous noise and hence they are called the Screeching Sixties.

Question 4.
Local Winds:
Answer:
The winds that blow for a short duration of time, originate in specific region and blow over a limited area are called Local Winds.
Question 5.
Doldrums:
Answer:
The region up to 5° North and 5° South of the equator remains calm for most of the year and winds do not blow in this region. It is called the equatorial calm zone or Doldrums.
Question 6.
Horse Latitudes:
Answer:
In the area near the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, that is between 25° and 35° north and south, there exist a high pressure belt, which is a calm belt. This belt is called as the Horse latitudes.
Question 7.
Typhoons:
Answer:
Storms arising in the months between June and October in the western part of the Pacific Ocean which blow with high velocity winds and heavy rains causing destruction are called Typhoons.
Question 8.
Hurricanes:
Answer:
The cyclones in the Caribbean sea which are destructive in nature are called Hurricanes.
Observe the pictures given below of Seasonal winds and write its characteristics:
Question 1.
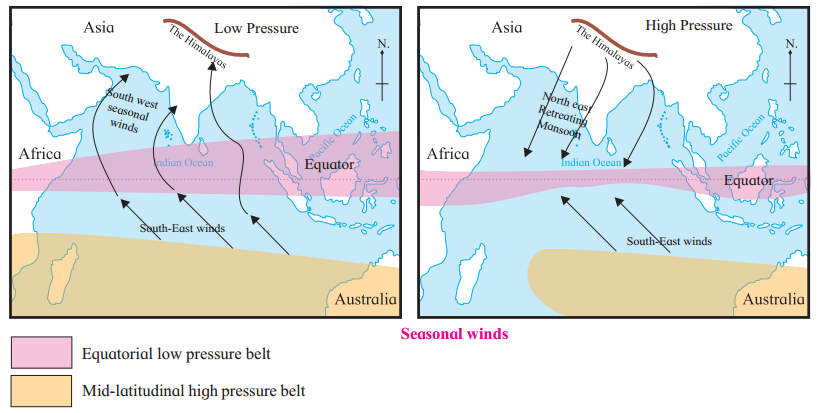
Answer:
Characteristics of the Seasonal winds (Monsoon):

change in direction of wind:
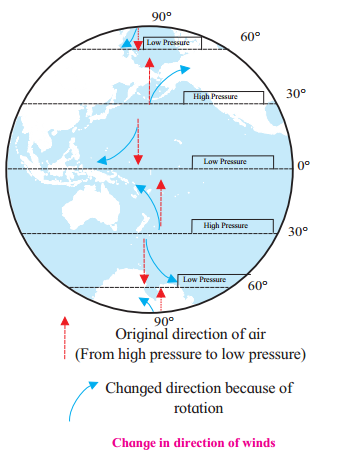
Draw a neat labelled diagram:
Question 1.
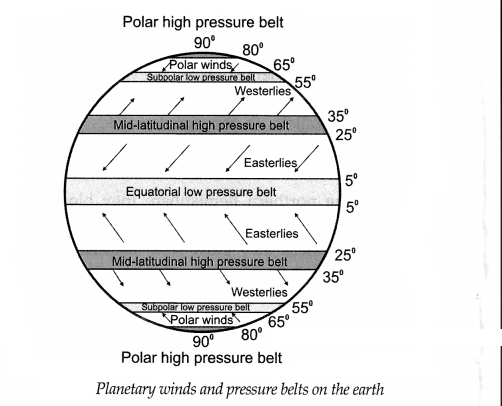
Planetary winds and pressure belts on the earth
Answer:
Distinguish between the following:
Question 1.
Easterlies and Westerlies:
Answer:

Question 2.
Valley breeze and Mountain breeze:
Answer:
Question 3.
Cyclones and Anticyclones:
Answer:
State one reason why:
Question 1.
Planetary winds change their original direction.
Answer:
The rotation from the west to east causes the change in the original direction of the planetary winds.
Question 2.
The air pressure in land and water is different
Answer:
(a) The land is made up of dense matter. Land is stable and opaque. As a result, heat is transferred at a greater speed and in a higher proportion. Hence, land gets heated quickly.
(b) The density of water is comparatively less. Water is transparent and unstable. Hence, water does not get heated quickly.
(c) As a result, the air pressure in land and water areas is different.
Question 3.
The Indian subcontinent experiences monsoon and retreating monsoon seasons.
Answer:
(a) Monsoon winds are generated due to uneven heating of land & water in different seasons. During summers, monsoon winds blow from sea to land & in winter they blow from land to the sea.
(b) The influence of monsoon winds is seen in summer season in the Indian subcontinent due to high temperature & low pressure in Thar desert region & Punjab plains.
(c) As these winds blow from sea to land the Indian subcontinent experiences monsoon (rainy) season.
(d) During winters, due to high pressure & low temperature in the Indian subcontinent & comparatively low pressure & high temperature in the Indian ocean winds blow from land to sea.
(e) This is the retreating monsoon season in the Indian subcontinent.
Thus the Indian subcontinent experiences monsoon & retreating monsoon season.
Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Give detailed information about the types of planetary winds.
Answer:
The following are the types of Planetary winds:
(i) Easterlies:
(ii) Westerlies:
(iii) Polar winds:

Question 2.
Write in detail about cyclonic storms.
Answer:
(i) Cyclones occurring in the western part of the Pacific ocean along the coasts of Japan, China, Philippines, etc. are known as ‘Typhoons’.
(ii) These storms arise in the months between June & October.
(iii) Due to high velocity winds & heavy rains, these prove to be destructive.
(iv) The cyclones in the Caribbean Sea are known as ‘hurricanes’. These are also destructive in nature.
(v) During these storms, the minimum velocity of the wind is 60 km per hour.
(vi) Cyclones also originate in the temperate zone but they are not so powerful & hence are not destructive.
Question 3.
What are anticyclones?
Answer:
(i) Under specific atmospheric conditions, the air pressure in a particular region increases & the pressure in the surrounding areas remain low.
(ii) In this situation, winds blow from the centre towards the surrounding areas in a circular manner.
(iii) In the northern hemisphere, these winds blow in a clockwise direction whereas in the southern hemisphere they blow in an anticlockwise direction.
(iv) During anticyclone, the skies are clear, winds blow with lesser velocities and the weather is pleasant.
Can you tell?
Observe the picture given below and answer the following questions.:

Question 1.
Which are the winds in the northern hemisphere that blow from the mid latitudinal high pressure belt to the equatorial low pressure belt?
Answer:
Easterlies blow from mid latitudinal high pressure belt to equatorial low pressure belt in the northern hemisphere
Question 2.
What is the direction of the Westerlies in the southern hemisphere?
Answer:
Westerlies blow from north west to south east in the southern hemisphere
Question 3.
Which planetary winds blow from the mid-latitudinal high pressure belts to the subpolar low pressure belts in the northern hemisphere?
Answer:
The Westerlies blow from mid latitudinal high pressure belts to subpolar low pressure belts in the northern hemisphere
Question 4.
Why is the direction of polar winds not the same in both the hemispheres?
Answer:
The rotation of the earth causes the change in the direction of winds in both the hemisphere. So polar winds blow from northeast to south west in the northern hemisphere & from south east to north-west in the southern hemisphere.

Question 5.
Name the winds that blow in the southern hemisphere.
Answer:
Easterlies, Westerlies and Polar Winds blow in the southern hemisphere.
Question 6.
In which direction do the Easterlies blow in the Northern and Southern hemisphere?
Answer:
Easterlies blow from northeast to southeast in northern hemisphere & from southeast to northwest in the southern hemisphere.
Chapter 5 Winds Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Winds Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Rewrite the following statements after choosing the correct option:
Question 1.
When the air expands, it ______.
(a) becomes solid,
(b) becomes thinner,
(c) gets lost.
(d) becomes humid.
Answer:
(b) becomes thinner,

Question 2.
From high air pressure regions, winds ______.
(a) blow to regions of still higher pressure.
(b) blow towards regions of cooler air.
(c) blow towards regions of low air pressure.
(d) remains still.
Answer:
(c) blow towards regions of low air pressure.
Question 3.
In the northern hemisphere, winds blowing towards the equator due to the _____.
rotation of the earth.
(a) turn to the south
(b) turn to the east,
(c) turn to the west
(d) turn to the north.
Answer:
(c) turn to the west
Question 4.
The direction of seasonal winds blowing over the Indian subcontinent during winter is from the _____.
(a) south-east to north-west.
(b) south-west towards north-east.
(c) north-east to south-west.
(d) north-west to south-east.
Answer:
(c) north-east to south-west.
Question 5.
The Roaring Forties in the southern hemisphere ______.
(a) blow towards the equator.
(b) blow in the areas around 40°S parallel.
(c) blow from the subpolar region of low pressure.
Answer:
(b) blow in the areas around 40°S parallel.
2. Identify the type of winds from the description given below:
Question 1.
These winds from the south-west bring rains to Indian subcontinent. During June to September, India gets rains. After this period these winds retreat.
Answer:
South West Monsoon Winds.
Question 2.
These winds blowing from the north pole region towards 60°N parallel cause cold wave conditions in extensive areas covering North America, Europe and Russia
Answer:
Polar Winds.

Question 3.
Hilltops get heated quickly during the day. The air in this part becomes hot, light and starts ascending. Hence, a low pressure area forms in this region. At the same time the air at the foothills become cooler and also experiences high pressure. Air in that area blows towards low pressure.
Answer:
Valley Winds.
3. Given below are the values of air pressure in millibars. Using the same, draw diagrams to show a cyclone and an anticyclone:
Question 1.
990, 994, 996,1000
Answer:

Question 2.
1030,1020,1010,1000
Answer:

4. State one reason why:
Question 1.
A belt of calm exists near the equator.
Answer:
(i) A belt of calm exists near the equator because there is not much difference in the temperature and air pressure.
(ii) So winds do not blow in this region.
Question 2.
The winds coming from the north-west in the southern hemisphere have greater velocities than the winds coming from the south-west in the northern hemisphere.
Answer:
(i) In the southern hemisphere the obstacle caused by the relief of the land surface is almost absent.
(ii) Therefore the winds coming from the north – west in the southern hemisphere have greater velocity than the winds coming from the south-west in the northern hemisphere.
Question 3.
The monsoon winds in the summer come from the sea but the retreating monsoon winds come from land.
Answer:
(i) Monsoon winds are generated due to the uneven heating of land and water in the different seasons.
(ii) During summers, land heats up quickly as compared to water & an area of low pressure is created on the land whereas an area of high pressure is created on the water.
(iii) But during winters low pressure is created on the water and an area of high pressure is created on land as it cools down quickly as compared to the water.
(iv) As winds blow from high pressure areas to low pressure areas, it blows from sea to land in summers & from land to sea in winters.
Thus the monsoon winds in summer come from sea but the retreating monsoon winds come from land.

5. Complete the flow chart:

Answer:

6. Answer in short:
Question 1.
Why is the air pressure high in polar areas in both the hemispheres?
Answer:
Question 2.
What effect does the rotation of the earth have on the wind?
Answer:
Question 3.
Why do the cyclonic winds blow in a circular manner?
Answer:
(i) Cyclones are created when a low pressure area is surrounded by high pressure areas. In these conditions, winds start blowing towards the low pressure area from the surrounding high pressure areas.
(ii) But due to the rotation of the earth in the northern hemisphere the winds deflected towards the right of their original direction whereas in the southern hemisphere they get deflected towards the left of their original direction which causes the cyclone winds to blow in a circular manner.
Question 4.
State the reasons that lead to the formation of cyclones and describe the effects of cyclones.
Answer:
(i) Cyclonic conditions are created when a low pressure area is surrounded by high pressure areas.
(ii) In these conditions, winds start blowing towards the low pressure area from the surrounding high pressure areas.
(iii) The effects of cyclone are as follows.
Activity:
Using the internet, obtain information, photos and maps of the recent cyclone that arrived at India’s eastern coast.
Write the social and economic effects of that cyclone.
ICT Question:
Use the mobile app ‘Windyty’ and try to know the direction of winds and pressure areas in the world.

Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Winds InText Questions and Answers
Formative Assessment
Can you tell?
Observe the diagrams given below. Answer the questions related to sea and land breeze


Question 1.
Why do the breezes blow from the sea to the land during the day?
Answer:
During the day as land gets heated up faster than water, an area of low pressure is created on land whereas there is a region of comparatively higher pressure on the sea. As a result the breezes blow from the sea to the land during the day.
Question 2.
When do the winds blow from the d to the sea?
Answer:
The winds blow from land to the sea during the night.
Question 3.
Describe the winds shown in fig. (a).
Answer:
It is sea breeze.
Question 4.
Compare fig.(a) and (b) with reference fo temperature conditions, air pressure and
winds.
Answer:
In figure (a) the temperature is higher on land & the pressure is low so winds blow from sea to land. In figure (b) the temperature is low on the land & the pressure is high. Winds blow from land to sea.
Question 5.
Which winds are called sea breezes and which are called land breezes? Why?
Answer:
Winds in (a) are sea breeze because they blow from the sea and (b) are land breeze because they blow from the land.

Question 6.
In which part of India are land and sea breezes experienced?
Answer:
In India, it is experienced near the coastal areas.
Question 7.
Do you experience sea and land breezes in your area?
Answer:
The answer may vary.
Give it a try.
Write the changed directions of the wind in the table below:
Question 1.
| Pressure Belts | Northern Hemisphere | Southern Hemisphere |
| Mid Latitudes | ……….. | ………….. |
| ………… | ………….. | |
| Poles | ……………….. | ……………. |
| Pressure Belts | Northern Hemisphere | Southern Hemisphere |
| Mid Latitudes | (1) Easterlies blow from northeast to south west | Easterlies blow from south east to northwest |
| (2) Westerlies blow from southwest to northeast | Westerlies blow from northwest to southeast | |
| Poles | Polar winds blow from northeast to south west | Polar winds blow from southeast to northwest |
Question 1.
Observe the pictures given below and describe the valley breeze considering the elevation of land, the heating and cooling properties of land and water, the air pressure, etc.

Answer:
Characteristics of Valley Breeze:
Question 2.
Read the following information carefully and draw a diagram for the mountain breeze accordingly.
Characteristics of the Mountain breeze:

Answer:

Try this:
Question 1.
Without touching the roll of the paper on the table, what can be done to move the paper rolls to the other end of the table?
Answer:
To move the paper rolls to the other end of the table without touching a person can
Question 2.
See who moves the paper roll first to the other end of the table:
Answer:
The object which blows the air with maximum force, moves the paper roll first to the other end of the table.
Question 3.
What could be the reason of the delay in making the rolls reach to the other end of the table?
Answer:
There will be a delay in making the rolls reach the other end of the table if the air is blown with lesser force.
Question 4.
What can we do to move the rolls to the other end of the table with a greater speed?
Answer:
We mostly use the technique/object which will blow air with maximum force to move the rolls to the other end of the table with a greater speed.
Question 5.
Can a bottle filled with water be moved to the other end of the table in this manner? Can we use the same method that you tried for moving paper rolls?
Answer:
A bottle filled with water cannot be moved to the other end of the table in this manner. We cannot use the same methods that we tried for moving paper rolls to move a bottle filled with water as it is heavier in weight, (we can if we tilt the table which was an option.)
Class 7 Geography Chapter 5 Winds Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct option from the bracket:
Question 1.
Air moves from high pressure to low pressure areas in a ______ manner. (vertical, horizontal, parallel)
Answer:
horizontal.

Question 2.
Winds velocity is measured in the units of ________. (knots, metres, seconds)
Answer:
knots.
Question 3.
Wind which cover a large portion of the earth are called _____ wind. (local, polar, planetary)
Answer:
planetary.
Question 4.
Winds blowing between mid latitudinal high pressure belt and the equator are called ______. (westerlies, easterlies, polar)
Answer:
easterlies.
Question 5.
Winds blowing between mid latitudinal high pressure belt and the sub polar low pressure belt are called _______. (easterlies, westerlies, polar)
Answer:
westerlies.
Question 6.
Winds that blow for a short duration of time, over a limited area are called ______. wind. (polar, local, easterlies)
Answer:
local.
Question 7.
Mountain winds blow during ______ .(morning, night, midday)
Answer:
night.
Question 8.
Winds that blow at night in coastal areas are called ________ breeze, (sea, land, valley)
Answer:
land.
Question 9.
Cyclones occurring in the western part of the Pacific ocean are called ______.(hurricane, typhoons)
Answer:
typhoons.
Question 10.
Hot winds blowing in the Thar Desert are called the _______ (simoons, loo, chinook)
Answer:
loo.
Rewrite the following statements after choosing the correct option:
Question 1.
During an anticyclone the sky ______.
(a) is dark.
(b) is cloudy.
(c) is clear.
(d) is white.
Answer:
(c) is clear.

Question 2.
Winds blowing from the polar high pressure to sub polar low pressure belt
(a) blow from west to east.
(b) blow from east to west.
(c) blow from south to north.
(d) blow from north to south.
Answer:
(b) blow from east to west.
Question 3.
The minimum velocity of cyclonic storms is ________.
(a) 50 km per hour
(b) 60 km per hour
(c) 70 km per hour
(d) 80 km per hour.
Answer:
(b) 60 km per hour
Question 4.
Winds which originate in specific regions and blow over a limited area are called _____.
(a) local winds.
(b) seasonal winds
(c) monsoon winds
(d) planetary winds
Answer:
(a) local winds.
Find out the odd man out and give reason for your answer:
Question 1.
Polar winds, Local winds, Easterlies, Westerlies
Answer:
Local winds – Others are names of planetary winds.
Question 2.
Landbreeze, Valley winds, Westerlies, Mountain winds.
Answer:
Westerlies – Others are names of local winds.
Question 3.
Mistral, Bora, Pampero, Foehn
Answer:
Foehn – Others are cold and dry winds.
Question 4.
Loo, Foehn, Mistral, Simoon
Answer:
Mistral – Others are hot and dry winds.
Question 5.
Mistral, Bora, Chinook, Foehn
Answer:
Chinook – Others originate in the Alps Mountain.
Question 6.
Southeast Asia, West Europe, East Africa, North Australia.
Answer:
West Europe – Others receive monsoon rains.

Question 7.
India, Japan, China, Phillippines.
Answer:
India – Others experience typhoons.
Question 8.
Furious Fifties, Screaming Seventies, Screeching Sixties,, Roaring Forties.
Answer:
Screaming Seventies – Others are names of winds in the southern hemisphere.
Place a tick mark (✓) against the correct option:
Question 1.
Towards which direction do the southern hemisphere winds get deflected? .
(a) Towards the left.
(b) Towards the right.
(c) Towards the centre.
Answer:
(a) Towards the left.
Question 2.
What are the winds blowing between polar high pressure belt and subpolar low pressure belt called?
(a) Monsoon winds
(b) Polar winds
(c) Westerlies winds
Answer:
(a) Monsoon winds
Question 3.
Hot and destructive winds blowing in the Sahara
(a) Chinook
(b) Simoom
(c) Loo
Answer:
(b) Simoom
Question 4.
Cold winds around the Mediterranean.
(a) Foehn
(b) Pampero
(c) Mistral
Answer:
(b) Pampero
Question 5.
How is cyclonic condition created?
(a) Low pressure area is surrounded by high pressure.
(b) A high pressure area is surrounded by low pressure.
(c) A low pressure area is surrounded by mid pressure.
Answer:
(c) A low pressure area is surrounded by mid pressure.
Identify the type of winds from the description given below:
Question 1.
In coastal areas, land cools down faster as compared to the sea, the air blows from land to sea.
Answer:
Land Breeze.
Question 2.
In the Indian subcontinent, dry winds blow from the Indian Subcontinent towards the equator.
Answer:
North-East monsoon winds.

Question 3.
The winds blowing over the earth’s surface throughout the year and covering a large portion of the earth.
Answer:
Planetary winds.
Question 4.
The winds that blow for a short duration of time, originate in specific regions & blow over a limited area.
Answer:
Local winds.
Match the pairs correctly:
Question 1.
| Name of the Wind | Nature of the Wind |
| (1) Loo | (a) Hot and dry |
| (2) Simoom | (b) Cold and dry |
| (3) Chinook | (c) Hot, dry and destructive |
| (4) Mistral | (d) Warm and dry |
1 – a
2 – c
3 – d
4 – b
Define the following terms:
Question 1.
Roaring Forties:
Answer:
Beyond 40°S winds blow with tremendous velocity. These winds are called the Roaring Forties.
Question 2.
Furious Fifties:
Answer:
Around 50°S winds are stormy hence they are called the Furious Fifties.
Question 3.
Screeching Sixties:
Answer:
The stormy winds around 60°S make tremendous noise and hence they are called the Screeching Sixties.

Question 4.
Local Winds:
Answer:
The winds that blow for a short duration of time, originate in specific region and blow over a limited area are called Local Winds.
Question 5.
Doldrums:
Answer:
The region up to 5° North and 5° South of the equator remains calm for most of the year and winds do not blow in this region. It is called the equatorial calm zone or Doldrums.
Question 6.
Horse Latitudes:
Answer:
In the area near the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, that is between 25° and 35° north and south, there exist a high pressure belt, which is a calm belt. This belt is called as the Horse latitudes.
Question 7.
Typhoons:
Answer:
Storms arising in the months between June and October in the western part of the Pacific Ocean which blow with high velocity winds and heavy rains causing destruction are called Typhoons.
Question 8.
Hurricanes:
Answer:
The cyclones in the Caribbean sea which are destructive in nature are called Hurricanes.
Observe the pictures given below of Seasonal winds and write its characteristics:
Question 1.

Answer:
Characteristics of the Seasonal winds (Monsoon):

change in direction of wind:

Draw a neat labelled diagram:
Question 1.
Planetary winds and pressure belts on the earth
Answer:

Distinguish between the following:
Question 1.
Easterlies and Westerlies:
Answer:
| Easterlies | Westerlies |
| (i) Easterlies blow from mid latitudinal high pressure belt to equatorial low pressure belt in both the hemispheres | (i) Westerlies blow from mid latitudinal high pressure belt to subpolar low pressure belt in both the hemispheres |
| (ii) In the northern hemisphere, they blow from the northeast to the southwest. | (ii) In the northern hemisphere, they blow from the southwest to the northeast. |
| (iii) In the southern hemisphere, they blow from the southeast to the northwest. | (iii) In the southern hemisphere, they blow from northwest to the southeast. |

Question 2.
Valley breeze and Mountain breeze:
Answer:
| Valley Breeze | Mountain Breeze |
| (i) Valley breeze blow during the day. | (i) Mountain breeze blow during the night. |
| (ii) Winds blow from the valley to the mountain. | (ii) Winds blow from the mountain to the valley. |
| (iii) Valley breeze blows because of the high pressure area created iin the valley. | (iii) Mountain Breeze blows because of the high pressure area created on the mountains. |
Cyclones and Anticyclones:
Answer:
| Cyclones | Anticyclones |
| (i) Cyclonic conditions are created when a low pressure area is surrounded by high pressure areas. | (i) Anticyclonic conditions are created when a high pressure area is surrounded by low pressure areas. |
| (ii) The cyclonic winds move in an anticlockwise direction in the northern hemisphere and clockwise direction in the southern hemisphere. | (ii) The anticyclonic winds move in a clockwise direction in the northern hemisphere and anticlockwise direction in the southern hemisphere. |
| (iii) The sky is cloudy. | (iii) The skies are clear. |
| (iv) The velocity of wind is very high and cause rain. | (iv) The velocity of wind is less and weather is pleasant. |
Question 1.
Planetary winds change their original direction.
Answer:
The rotation from the west to east causes the change in the original direction of the planetary winds.
Question 2.
The air pressure in land and water is different
Answer:
(a) The land is made up of dense matter. Land is stable and opaque. As a result, heat is transferred at a greater speed and in a higher proportion. Hence, land gets heated quickly.
(b) The density of water is comparatively less. Water is transparent and unstable. Hence, water does not get heated quickly.
(c) As a result, the air pressure in land and water areas is different.
Question 3.
The Indian subcontinent experiences monsoon and retreating monsoon seasons.
Answer:
(a) Monsoon winds are generated due to uneven heating of land & water in different seasons. During summers, monsoon winds blow from sea to land & in winter they blow from land to the sea.
(b) The influence of monsoon winds is seen in summer season in the Indian subcontinent due to high temperature & low pressure in Thar desert region & Punjab plains.
(c) As these winds blow from sea to land the Indian subcontinent experiences monsoon (rainy) season.
(d) During winters, due to high pressure & low temperature in the Indian subcontinent & comparatively low pressure & high temperature in the Indian ocean winds blow from land to sea.
(e) This is the retreating monsoon season in the Indian subcontinent.
Thus the Indian subcontinent experiences monsoon & retreating monsoon season.
Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Give detailed information about the types of planetary winds.
Answer:
The following are the types of Planetary winds:
(i) Easterlies:
(ii) Westerlies:
(iii) Polar winds:

Question 2.
Write in detail about cyclonic storms.
Answer:
(i) Cyclones occurring in the western part of the Pacific ocean along the coasts of Japan, China, Philippines, etc. are known as ‘Typhoons’.
(ii) These storms arise in the months between June & October.
(iii) Due to high velocity winds & heavy rains, these prove to be destructive.
(iv) The cyclones in the Caribbean Sea are known as ‘hurricanes’. These are also destructive in nature.
(v) During these storms, the minimum velocity of the wind is 60 km per hour.
(vi) Cyclones also originate in the temperate zone but they are not so powerful & hence are not destructive.
Question 3.
What are anticyclones?
Answer:
(i) Under specific atmospheric conditions, the air pressure in a particular region increases & the pressure in the surrounding areas remain low.
(ii) In this situation, winds blow from the centre towards the surrounding areas in a circular manner.
(iii) In the northern hemisphere, these winds blow in a clockwise direction whereas in the southern hemisphere they blow in an anticlockwise direction.
(iv) During anticyclone, the skies are clear, winds blow with lesser velocities and the weather is pleasant.
Can you tell?
Observe the picture given below and answer the following questions.:

Question 1.
Which are the winds in the northern hemisphere that blow from the mid latitudinal high pressure belt to the equatorial low pressure belt?
Answer:
Easterlies blow from mid latitudinal high pressure belt to equatorial low pressure belt in the northern hemisphere
Question 2.
What is the direction of the Westerlies in the southern hemisphere?
Answer:
Westerlies blow from north west to south east in the southern hemisphere
Question 3.
Which planetary winds blow from the mid-latitudinal high pressure belts to the subpolar low pressure belts in the northern hemisphere?
Answer:
The Westerlies blow from mid latitudinal high pressure belts to subpolar low pressure belts in the northern hemisphere
Question 4.
Why is the direction of polar winds not the same in both the hemispheres?
Answer:
The rotation of the earth causes the change in the direction of winds in both the hemisphere. So polar winds blow from northeast to south west in the northern hemisphere & from south east to north-west in the southern hemisphere.

Question 5.
Name the winds that blow in the southern hemisphere.
Answer:
Easterlies, Westerlies and Polar Winds blow in the southern hemisphere.
Question 6.
In which direction do the Easterlies blow in the Northern and Southern hemisphere?
Answer:
Easterlies blow from northeast to southeast in northern hemisphere & from southeast to northwest in the southern hemisphere.