Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Science Solutions
Chapter 16 Natural Resources Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Natural Resources Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Describe natural resources with reference to the following 3 types:
Question a.
Mineral resources
Answer:
Mineral wealth has an important place among natural resources. The rocks on the earth are mainly made of minerals. These minerals can be obtained by mining. Minerals that contain a high proportion of metals are ores, (i) Minerals are formed from the magma in the earth’s crust and the lava from the eruption of volcanoes when they cool and get transformed into crystals e.g. magnetite, mica, (ii) Minerals get transformed from one form into another due to large changes in temperature and pressure e.g. Diamond, Graphite, (iii) There are 3 types of minerals according to their properties Non-metal minerals: e.g. mica, sulphur, potash, diamond.
Some important minerals and ores are Iron ore, manganese, bauxite, copper and mica.

Question b.
Forest resources
Answer:
Question c.
Ocean resources
Answer:

2. Write answers to the following questions in your own words.
Question a.
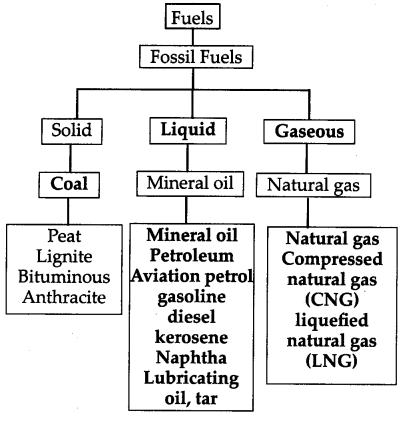
What is meant by fossil fuel? What are their types?
Answer:
a. Coal:
b. Mineral oil:
c. Natural gas:

Question b.
Make a list of the components we obtain from mineral oil.
Answer:
Question c.
What do we get from forest?
Answer:

Question d.
What are the items included in ocean resources? What are their uses?
Answer:
Bio-resources in oceans
Mineral resources from oceans

Question e.
Why should we prevent the wastage of fuels used for vehicles?
Answer:
Question f.
Why is the diversity of plants and animals in the forests declining?
Answer:

Question g.
Write the names of five minerals and the useful substances obtained from them.
Answer:
Some important minerals and ores are:

Question h.
Name the two important stages in the process of obtaining metals from ores.
Answer:
The two important stages in the process of obtaining metals from ores are extraction and purification.
3. What steps are taken for protection and conservation of natural resources?
Question a
What steps are taken for protection and conservation of natural resources?
Answer:

4. Complete the Flow Chart:
Question a.
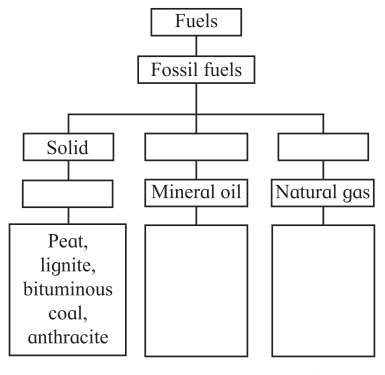
Answer:
5. How does the economic condition of a nation depend on its natural resources?
Question a.
How does the economic condition of a nation depend on its natural resources?
Answer:
1. Natural resources are a necessary condition for economic growth.
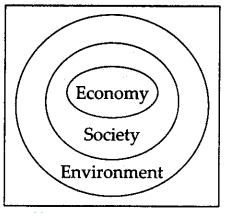
2. Three circles enclosed within one another shows how both economy and society are subsets of our planetary ecological system.
3. Natural resource economics deals with the supply, demand and allocation of the Earth’s natural resources.
4. Economic growth is an increase in the value of goods and services produced in an economy.
5. The natural resources of a country depend on the climatic and environmental conditions.
6. Countries having plenty of natural resources enjoy good growth than countries with small amount of natural resources.
7. A country having skilled and educated work force with rich natural resources takes the economy on the growth path, because skilled and educated people can efficiently utilize or exploit natural resources, e.g. Saudi Arabia: their economic growth is high, because they have oil wells.
8. All countries import fuel or oil from them so Saudi Arabia is economically a rich country.
6. Which medicinal plants will you grow on your school premises and near your house? Why?
Question a.
Which medicinal plants will you grow on your school premises and near your house? Why?
Answer:
1. I will grow tulsi, neem, lemon grass, bel, adulsa, periwinkle, cinnamon, ashwagandha, shatavari, amla, hirda, behda.
2. These plants are used for treatment of various diseases.

Project:
Question 1.
Collect conches and shells of various shapes and colours and make a decorative article.
Question 2.
Collect information about the mines of various minerals.
Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Natural Resources Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
………….. is the major raw material for biogas.
Answer:
cow dung
Question 2.
Atomic energy is obtained by using ores of ………….. .
Answer:
Uranium

Question 3.
Biogas generation is mainly based on the principle of ………….. .
Answer:
Fermentation
Question 4.
Floods can be prevented by ………….. .
Answer:
Afforestation
Question 5.
Coal, petroleum, natural gas are ………….. resources.
Answer:
non-renewable
Question 6.
The total percent of land of world under forest cover is ………….. .
Answer:
30%
Question 7.
A naturally occurring substance ………….. .
Answer:
minerals
Question 8.
Minerals that contain a high proportion of metal are called ………….. .
Answer:
ore

Question 9.
Coal, mineral oil and natural gas are ………….. .
Answer:
fossil fuel
Question 10.
Deposits of common salt are also found in the earth. This salt is called ………….. .
Answer:
rock salt
Question 11.
………….. is the liquid fuel formed by the decomposition of organic substances.
Answer:
Mineral oil
Question 12.
The underground mineral oil is extracted through ………….. .
Answer:
oil wells

Question 13.
Mineral oil is also known as ………….. or ………….. .
Answer:
petroleum, crude oil
Question 14.
………….. are the preserved remains of dead organisms in rock.
Answer:
Fossil
Question 15.
Coal can be formed from ………….. .
Answer:
Fossils
Question 16.
Impurities of sand and soil in ore are called ………….. .
Answer:
Gangue
Question 17.
Coal mainly contains ………….. .
Answer:
carbon

Question 18.
Petroleum is formed from ………….. .
Answer:
organisms in sea
Question 19.
Separation of various fractions of petroleum is called ………….. .
Answer:
Refining
Question 20.
We can obtain minerals from rocks by ………….. .
Answer:
mining
Question 21.
………….. is the most important ore of aluminium
Answer:
Bauxite
Question 22.
………….. is the coal of the highest grade.
Answer:
Anthracite

Question 23.
Metals are obtained from their ore by ………….. and ………….. .
Answer:
extraction, purification
Question 24.
………….. is the largest oil and gas research and production company in India.
Answer:
ONGC
Question 25.
Natural gas is transformed under high pressure into ………….. and ………….. .
Answer:
LNG and CNG

Question 26.
The main component of Natural gas is ………….. .
Answer:
Methane
Question 27.
………….. and ………….. are used for adding fragrance in soaps and incense sticks.
Answer:
Sandalwood and oil of Encalyptus
Question 28.
………….. is a natural herbal medicine for cough and cold.
Answer:
Adulsa

Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is meant by natural resources?
Answer:
Question 2.
What are alternative fuels?
Answer:
Hydrogen, biofuels, methanol or wood alcohol, ethanol or green alcohol are some of the alternative fuels.

Question 3.
What is meant by fuels?
Answer:
Question 4.
Which natural resources do we use as fuels?
Answer:
We use coal, mineral oil and natural gas as fuels.
Question 5.
What is meant by forests?
Answer:
An extensive area of land covered by a variety of plants is called a forest. A forest is a natural habitat of plants, animals and microbes.

Question 6.
What are the uses of forests?
OR
Write short note on forest and its uses.
Answer:
Question 7.
Are minerals to be found in seas and on the seabed as they are found inside the earth?
Answer:
Yes, there are very large reserves of tin chromium, phosphates, copper, zinc, iron, lead, manganese, sulphur, uranium etc. in the ocean and seabed.

Question 8.
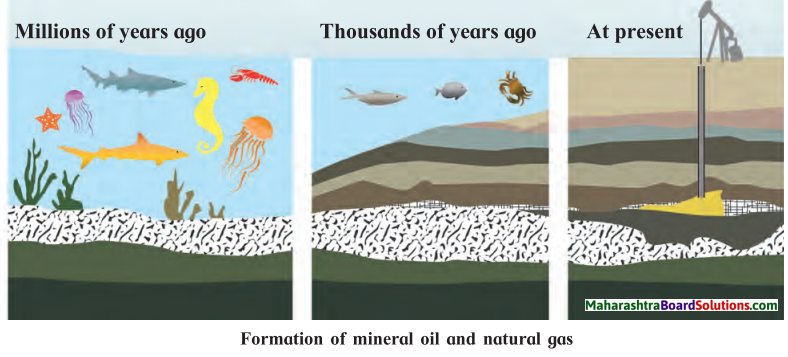
How is mineral oil formed?
Answer:

Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Why are all minerals not ores?
Answer:
Question 2.
What is meant by metal mineral and non¬metal mineral?
Answer:

Question 3.
Why is mineral oil called ‘liquid gold’?
Answer:
Because of its high price and value and its economic need, the mineral oil is called liquid gold. It’s reserve is less and demand is more.
Question 4.
Why is coal called black gold?
Answer:
Question 5.
What would happen if underground mineral resources are exhausted?
Answer:

Question 6.
Why is natural gas an eco-friendly fuel?
Answer:
Question 7.
What useful things will we have to do without if rubber is no longer available?
Answer:

Question 8.
What are the adverse effects of clearing of forest or cutting down trees?
Answer:
Find out:
Question 1.
How did the various ages of the prehistoric period get their names on the basis of the uses of metals.
Answer:
1. The three-age system in history archaeology, and physical anthropology is a methodological concept adopted during the 19th century by which artifacts and events of late prehistory and early history could be ordered into a recognizable chronology.
2. Initially developed by C. J. Thomson, director of the Royal Museum of Nordic Antiquities, Copenhagen – as a means to classify the museum’s collection according to whether the artifacts were made of stone, bronze or iron.
3. Depending-upon the use of stone, bronze, iron, that period was known as stone age, bronze age, and iron age, respectively.

Answer the following:
Question 1.
Write down the difference between Metal minerals and Non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
Question 2.
Write down the different types of coal.
Answer:
Peat, lignite (brown coal), bituminous coal and anthracite are various types of coal.
Anthracite is the coal of the highest grade.

Question 3.
Write down the characteristics of Compressed Natural Gas.
Answer:
Characteristics of CNG:
Observe the pictures and answer the question.

Question a.
What is the process shown in the given picture?
Answer:
The process shown is formation of mineral oil and natural gas.

Question b.
Explain the process.
Answer:
Question c.
What are the gaseous substances formed in the above process?
Answer:
Natural gas is also formed along with mineral oil. It contains methane, ethane, propane and butane gases.

Question d.
When the products of the process is refined, what other components are produced?
Answer:
When mineral oil is refined by fractional distillation products produced are petrol, diesel, kerosene, naphtha lubricating oil, tar, etc.
Chapter 16 Natural Resources Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Natural Resources Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Describe natural resources with reference to the following 3 types:
Question a.
Mineral resources
Answer:
Mineral wealth has an important place among natural resources. The rocks on the earth are mainly made of minerals. These minerals can be obtained by mining. Minerals that contain a high proportion of metals are ores, (i) Minerals are formed from the magma in the earth’s crust and the lava from the eruption of volcanoes when they cool and get transformed into crystals e.g. magnetite, mica, (ii) Minerals get transformed from one form into another due to large changes in temperature and pressure e.g. Diamond, Graphite, (iii) There are 3 types of minerals according to their properties Non-metal minerals: e.g. mica, sulphur, potash, diamond.
Some important minerals and ores are Iron ore, manganese, bauxite, copper and mica.

Question b.
Forest resources
Answer:
Question c.
Ocean resources
Answer:

2. Write answers to the following questions in your own words.
Question a.
What is meant by fossil fuel? What are their types?
Answer:
a. Coal:
b. Mineral oil:
c. Natural gas:

Question b.
Make a list of the components we obtain from mineral oil.
Answer:
Question c.
What do we get from forest?
Answer:

Question d.
What are the items included in ocean resources? What are their uses?
Answer:
Bio-resources in oceans
Mineral resources from oceans

Question e.
Why should we prevent the wastage of fuels used for vehicles?
Answer:
Question f.
Why is the diversity of plants and animals in the forests declining?
Answer:

Question g.
Write the names of five minerals and the useful substances obtained from them.
Answer:
Some important minerals and ores are:

Question h.
Name the two important stages in the process of obtaining metals from ores.
Answer:
The two important stages in the process of obtaining metals from ores are extraction and purification.
3. What steps are taken for protection and conservation of natural resources?
Question a
What steps are taken for protection and conservation of natural resources?
Answer:

4. Complete the Flow Chart:
Question a.

Answer:

5. How does the economic condition of a nation depend on its natural resources?
Question a.
How does the economic condition of a nation depend on its natural resources?
Answer:
1. Natural resources are a necessary condition for economic growth.
2. Three circles enclosed within one another shows how both economy and society are subsets of our planetary ecological system.

3. Natural resource economics deals with the supply, demand and allocation of the Earth’s natural resources.
4. Economic growth is an increase in the value of goods and services produced in an economy.
5. The natural resources of a country depend on the climatic and environmental conditions.
6. Countries having plenty of natural resources enjoy good growth than countries with small amount of natural resources.
7. A country having skilled and educated work force with rich natural resources takes the economy on the growth path, because skilled and educated people can efficiently utilize or exploit natural resources, e.g. Saudi Arabia: their economic growth is high, because they have oil wells.
8. All countries import fuel or oil from them so Saudi Arabia is economically a rich country.
6. Which medicinal plants will you grow on your school premises and near your house? Why?
Question a.
Which medicinal plants will you grow on your school premises and near your house? Why?
Answer:
1. I will grow tulsi, neem, lemon grass, bel, adulsa, periwinkle, cinnamon, ashwagandha, shatavari, amla, hirda, behda.
2. These plants are used for treatment of various diseases.

Project:
Question 1.
Collect conches and shells of various shapes and colours and make a decorative article.
Question 2.
Collect information about the mines of various minerals.
Class 7 Science Chapter 16 Natural Resources Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
………….. is the major raw material for biogas.
Answer:
cow dung
Question 2.
Atomic energy is obtained by using ores of ………….. .
Answer:
Uranium

Question 3.
Biogas generation is mainly based on the principle of ………….. .
Answer:
Fermentation
Question 4.
Floods can be prevented by ………….. .
Answer:
Afforestation
Question 5.
Coal, petroleum, natural gas are ………….. resources.
Answer:
non-renewable
Question 6.
The total percent of land of world under forest cover is ………….. .
Answer:
30%
Question 7.
A naturally occurring substance ………….. .
Answer:
minerals
Question 8.
Minerals that contain a high proportion of metal are called ………….. .
Answer:
ore

Question 9.
Coal, mineral oil and natural gas are ………….. .
Answer:
fossil fuel
Question 10.
Deposits of common salt are also found in the earth. This salt is called ………….. .
Answer:
rock salt
Question 11.
………….. is the liquid fuel formed by the decomposition of organic substances.
Answer:
Mineral oil
Question 12.
The underground mineral oil is extracted through ………….. .
Answer:
oil wells

Question 13.
Mineral oil is also known as ………….. or ………….. .
Answer:
petroleum, crude oil
Question 14.
………….. are the preserved remains of dead organisms in rock.
Answer:
Fossil
Question 15.
Coal can be formed from ………….. .
Answer:
Fossils
Question 16.
Impurities of sand and soil in ore are called ………….. .
Answer:
Gangue
Question 17.
Coal mainly contains ………….. .
Answer:
carbon

Question 18.
Petroleum is formed from ………….. .
Answer:
organisms in sea
Question 19.
Separation of various fractions of petroleum is called ………….. .
Answer:
Refining
Question 20.
We can obtain minerals from rocks by ………….. .
Answer:
mining
Question 21.
………….. is the most important ore of aluminium
Answer:
Bauxite
Question 22.
………….. is the coal of the highest grade.
Answer:
Anthracite

Question 23.
Metals are obtained from their ore by ………….. and ………….. .
Answer:
extraction, purification
Question 24.
………….. is the largest oil and gas research and production company in India.
Answer:
ONGC
Question 25.
Natural gas is transformed under high pressure into ………….. and ………….. .
Answer:
LNG and CNG

Question 26.
The main component of Natural gas is ………….. .
Answer:
Methane
Question 27.
………….. and ………….. are used for adding fragrance in soaps and incense sticks.
Answer:
Sandalwood and oil of Encalyptus
Question 28.
………….. is a natural herbal medicine for cough and cold.
Answer:
Adulsa

Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is meant by natural resources?
Answer:
Question 2.
What are alternative fuels?
Answer:
Hydrogen, biofuels, methanol or wood alcohol, ethanol or green alcohol are some of the alternative fuels.

Question 3.
What is meant by fuels?
Answer:
Question 4.
Which natural resources do we use as fuels?
Answer:
We use coal, mineral oil and natural gas as fuels.
Question 5.
What is meant by forests?
Answer:
An extensive area of land covered by a variety of plants is called a forest. A forest is a natural habitat of plants, animals and microbes.

Question 6.
What are the uses of forests?
OR
Write short note on forest and its uses.
Answer:
Question 7.
Are minerals to be found in seas and on the seabed as they are found inside the earth?
Answer:
Yes, there are very large reserves of tin chromium, phosphates, copper, zinc, iron, lead, manganese, sulphur, uranium etc. in the ocean and seabed.

Question 8.
How is mineral oil formed?
Answer:


Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Why are all minerals not ores?
Answer:
Question 2.
What is meant by metal mineral and non¬metal mineral?
Answer:

Question 3.
Why is mineral oil called ‘liquid gold’?
Answer:
Because of its high price and value and its economic need, the mineral oil is called liquid gold. It’s reserve is less and demand is more.
Question 4.
Why is coal called black gold?
Answer:
Question 5.
What would happen if underground mineral resources are exhausted?
Answer:

Question 6.
Why is natural gas an eco-friendly fuel?
Answer:
Question 7.
What useful things will we have to do without if rubber is no longer available?
Answer:

Question 8.
What are the adverse effects of clearing of forest or cutting down trees?
Answer:
Find out:
Question 1.
How did the various ages of the prehistoric period get their names on the basis of the uses of metals.
Answer:
1. The three-age system in history archaeology, and physical anthropology is a methodological concept adopted during the 19th century by which artifacts and events of late prehistory and early history could be ordered into a recognizable chronology.
2. Initially developed by C. J. Thomson, director of the Royal Museum of Nordic Antiquities, Copenhagen – as a means to classify the museum’s collection according to whether the artifacts were made of stone, bronze or iron.
3. Depending-upon the use of stone, bronze, iron, that period was known as stone age, bronze age, and iron age, respectively.

Answer the following:
Question 1.
Write down the difference between Metal minerals and Non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
| Metal minerals | Non-metallic minerals |
| 1. Metal minerals contain metal in raw form. | 1. Non-metallic minerals do not contain metal. |
| 2. These metals are generally associated with igenous rocks. | 2. These metals are generally associated with sedimentary rocks. |
| 3. They are usually hard and have shine of their own. | 3. They are not usually hard, have no shine of their own. |
| 4. e.g. Iron, copper tine, bauxite. | 4. e.g. Salt, coal, mica, clay. |
Write down the different types of coal.
Answer:
Peat, lignite (brown coal), bituminous coal and anthracite are various types of coal.
Anthracite is the coal of the highest grade.

Question 3.
Write down the characteristics of Compressed Natural Gas.
Answer:
Characteristics of CNG:
Observe the pictures and answer the question.

Question a.
What is the process shown in the given picture?
Answer:
The process shown is formation of mineral oil and natural gas.

Question b.
Explain the process.
Answer:
Question c.
What are the gaseous substances formed in the above process?
Answer:
Natural gas is also formed along with mineral oil. It contains methane, ethane, propane and butane gases.

Question d.
When the products of the process is refined, what other components are produced?
Answer:
When mineral oil is refined by fractional distillation products produced are petrol, diesel, kerosene, naphtha lubricating oil, tar, etc.