Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Political Science Solutions
Chapter 1 Post World War Political Developments Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 9 Political Science Chapter 1 Post World War Political Developments Textbook Questions and Answers
1A. Choose the right option and rewrite the sentence:
Question 1.
A system of independent and sovereign states ___.
(a) Political system
(b) International system
(c) Social system
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) International system

Question 2.
The main responsibility of the United Nations ____.
(a) to avoid war
(b) independence of colonies
(c) improving the economics of different nations
(d) disarmament
Answer:
(a) to avoid war
Question 3.
The Cold War ended with the event, _____.
(a) Establishment of the United Nations
(b) Disintegration of the Soviet Union
(c) Creation of Military Organisations
(d) Cuban Missile Crisis
Answer:
(b) Disintegration of the Soviet Union
2. Explain with reasons whether the following statements are true or false:
Question 1.
The League of Nations was established after the First World War.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
The world became unipolar due to the Cold War.
Answer:
False.
Question 3.
The policies of Mikhail Gorbachev gave an impetus to democratisation.
Answer:
True.

3. Explain the following concepts:
Question 1.
Cold War
Answer:
(i) America and the Soviet Union, who were allies in the Second World War became competitors, as soon as the war was over.
(ii) The cooperation between them gave way to rivalry. This rivalry occupied a period of 40-45 years of international politics
(iii) There was no open war between these two countries; but there was such tension in their relations, that it seemed that a war would erupt any time.
(iv) The concept of Cold War is used to describe the condition where there is no actual war, but there are such tensions in the circumstances, that they may be responsible to cause war.
(v) In this period, America was already a super power, but the Soviet Union also tried to become a super power by making nuclear weapons and by increasing its military might.
(vi) The struggle for power, arms race, differences in ideologies, attitude of checkmating each other by strategies and counter-strategies gave rise to the Cold War.
Question 2.
Non-Aligned Movement
Answer:
(i) In the period of the Cold War, while the world was becoming bipolar, there were some countries which did not want to join the super power rivalry. Such nations decided to stay out of the cold war rivalry. Their policy is known as non-alignment.
(ii) The Asian and African countries, which became independent after the Second World War supported the idea of non-alignment.
(iii) This movement started from 1961 under the leadership of India’s Prime Minister Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, President of Yugoslavia Marshall Tito, President of Egypt Gamal Abdal Nasser, President of Indonesia Dr. Sukarno and Prime Minister of Ghana Dr. Kwame Nkrumah.
(iv) The non-aligned Movement has opposed colonialism, imperialism and racism. It has encouraged the resolution of international disputes by peaceful means.
(v) India led this movement under the guidance of Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru. India continued to actively support the movement afterwards as well.
(vi) Even after the end of the Cold War, the importance of the movement has not reduced. The non-aligned movement is based on eternal principles of humanism, global peace and equality.
(vii) It has inspired the less developed countries to come together. It has encouraged the resolution of international disputes by peaceful means.
(viii) While taking a firm stand on disarmament, fostering human rights, the non-aligned movement put forth the problems of poor, undeveloped countries firmly. This movement made a demand of a New International Economic Order (NIEO).
Question 3.
Interdependence
Answer:
(i) All the countries of the world are dependent on each other for one reason or the other. However big, prosperous or developed a nation may be, it can never be self-sufficient to fulfill all its needs.
(ii) Even big nations have to depend upon other big and small nations. Thus, interdependence is an important feature of the international system, i.e. today’s global system.
Question 4.
Bipolarisation
Answer:
During the Cold War, most countries of the world joined either of the two super power blocks. Such a division of the nations of the world in two groups is bipolarisation.
Question 5.
Globalization
Answer:
(i) After the end of the Cold War, trade and economic relations between countries became more open. As it has been mentioned before, capital, labour, markets and information began circulating globally.
(ii) The give and take of ideas among people all over the world grew.
(iii) Due to the revolution in information technology, different events and developments began to be known everywhere.
(iv) The boundaries between nations did not remain as sacrosanct as they were before. All these processes are together called globalisation.
(v) Just as globalisation has brought us benefits, it has also caused losses. For example, as the economies of different countries got linked with each other, trade increased, economic unification grew, plenty of products became available in the markets; but (at the same time) the gap between the poor and rich nations did not reduce.

4. Give your opinion on the following topics:
Question 1.
What measures should the League of Nations have taken to avoid the Second World War?
Answer:
(i) League of Nations should have organised a military wing with the help of member nations to keep a check over the aggressors like Germany and Japan.
(ii) League should have reconsidered implementation of harsh term of treaties imposed on the losers to avoid the revengeful policies of dictators like Adolf Hitler.
Question 2.
Non-Alignment was necessary during the Cold War.
Answer:
(i) Yes. This was important to keep newly independent countries of Asia and Africa away from the super power rivalry.
(ii) Since these countries did not officially show allegiance to any super power, they freed themselves from the dominance of USA and USSR and could independently frame their foreign policies.
(iii) This further promoted peace and co-operation.
Question 3.
Human welfare was neglected due to the Cold War.
Answer:
(i) Yes, due to military alliances the world was gripped in the fear of a possible Third World War, which would have annihilated the entire human race.
(ii) Moreover the Arms Race diverted the resources and harnessed science for destruction rather than human welfare.
Question 4.
Which countries can emerge as super powers, in competition with America in present times?
Answer:
India and China could be future super powers.
5. Write brief answers:
Question 1.
Compare the First World War and the Second World War with the help of the following points.
Answer:

Question 2.
What were the factors responsible for the end of Cold War?
Answer:
The factors responsible for the end of Cold War are:
(i) The Soviet Union adopted the policy of opening up the economy. The State loosened up its control of the economy.
(ii) The then President of the Soviet Union Mikhail Gorbachev implemented the policies of Perestroika (Restructuring) and Glasnost (Openness). Due to these policies, the control over the media reduced.
(iii) As the East European countries under the influence of the Soviet Union adopted the capitalist and democratic paths, the Soviet Union disintegrated and several new nations were created out of it.
Question 3.
What major changes occurred in global politics after the end of the Cold War?
Answer:
(i) Major changes took place in world politics after the end of the Cold War. For example, America remained the only super power in world politics.
(ii) A conducive atmosphere prevailed for the growth in trade and economic relations between and among nations.
(iii) As all nations of the world decided to give priority to trade relations, the idea of giving ‘aid’ to other nations fell behind.
(iv) The United Nations now had to take more concrete steps to maintain global peace and security.
(v) Environmental protection, fostering of human rights, gender equality and management of natural calamities now acquired a global dimension.
Class 9 Political Science Chapter 1 Post World War Political Developments Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option from the given options and rewrite the sentence:
Question 1.
President of Soviet Union who implemented ‘Perestroika’ and ‘Glasnost’ ______.
(a) Nikita Khrushchev
(b) Mikhail Gorbachev
(c) General Molotov
(d) Vladimir Lenin
Answer:
(b) Mikhail Gorbachev
Question 2.
Military organisation formed under dominance of USA ______.
(a) North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
(b) Warsaw Pact
(c) New International Economic Order
(d) Non-Aligned Movement
Answer:
(a) North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
Question 3.
Division of world into two power blocs is called ______.
(a) Globalisation
(b) Nuclear Escalation
(c) Bipolarisation
(d) Internationalism
Answer:
(c) Bipolarisation
Question 4.
Among the following ________ is not an Axis Power.
(a) Germany
(b) Italy
(c) Belgium
(d) Japan
Answer:
(c) Belgium
Question 5.
______ is an important event of the Cold War.
(a) Fashoda Incident
(b) Cuban Missile Crisis
(c) Wall Street Crash
(d) Red Menace
Answer:
(b) Cuban Missile Crisis

Question 6.
Non-aligned movement is opposed to ____.
(a) Racism
(b) Capitalism
(c) McCarthyism
(d) Nepotism
Answer:
(a) Racism
Question 7.
Non-aligned movement demanded establishment of _______.
(a) Association of South East Asian Nations
(b) League of Nations
(c) New International Economic Order (NIEO)
(d) European Union (EU)
Answer:
(c) New International Economic Order (NIEO)
Question 8.
The policy of Perestroika means restructuring and Glasnost means ______.
(a) strictness
(b) oneness
(c) massiveness
(d) openness
Answer:
(d) openness
State whether the following statements are True or False, with reasons:
Question 1.
A system of Independent States is called International System.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Interdependence is not an important feature of the International System.
Answer:
False.
Question 3.
The Second World War proved to be far more destructive than the First World War.
Answer:
True.

Question 4.
Efforts towards arms control and disarmament happened during the Cold War.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Non-alignment was an important movement during the Cold War.
Answer:
True.
Explain the concept:
Question 1
Military Organisation
Answer:
(i) During the Cold War, power struggle between USSR and USA created need for nations who will support their ideologies.
(ii) Thus, organisations were created for helping nations militarily and thus dragging them into either of the super power blocs for their hegemony.
(iii) The respective super powers took up the responsibility of the security of the countries joining the military organisations led by them.
(iv) NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organisation) was a military organisation under the dominance of America, while the Warsaw Pact was a military organisation, under the command of the Soviet Union.
Do as directed/instructed:
Complete the charts.
Question 1.
Answer:

Question 2.
Answer:
Question 3.
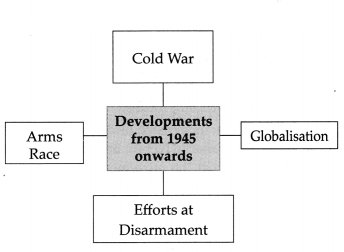
Answer:
Answer in brief:
Question 1.
What were the effects of World War I?
Answer:
(i) The First World War was fought between 1914 and 1918. The war caused a tremendous loss of life and property. The countries which joined the war suffered tremendous economic losses.
(ii) Even the countries which did not join the war were impacted by the war. The economies of the victorious as well as the losing countries collapsed.
(iii) Earlier empires in Europe collapsed and new nations came into being.
(iv) Independence movements in European colonies changed hegemony of European Nations.
(v) League of Nations was established.
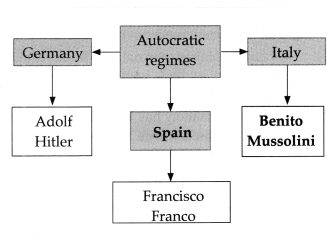
(vi) Autocratic regime came up in Germany Spain, Italy and other countries.
Question 2.
Describe America’s role in the Second World War.
Answer:
(i) America played a major role in the Second World War. It had manufactured nuclear weapons.
(ii) In order to end the war, it dropped two nuclear weapons on two cities of Japan – Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6th and 9th August 1945 respectively.

Question 3.
What gave rise to the Cold War?
Answer:
(i) America was already a super power, but the Soviet Union also tried to become one, by making nuclear weapons and by increasing its military might.
(ii) The struggle for power, arms race, differences in ideologies, attitude of checkmating each other by strategies and counter-strategies gave rise to the Cold War.
Question 4.
Describe extreme differences among USA and USSR.
Answer:
(i) The U.S.A was a democratic State, advocating capitalism, while the Soviet Union advocated socialism and a one party authoritarian system.
(ii) Both the super powers wanted to expand their own dominance in the world.
(iii) America wanted to spread capitalism, while the Soviet Union wanted to spread socialism.
Question 5.
What is meant by Non-Aligned Movement and who were its founding fathers?
Answer:
(i) The Asian and African countries, which became independent after the Second World War supported the idea of non-alignment.
(ii) This movement started from 1961 under the leadership of India’s Prime Minister Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, President of Yugoslavia Marshall Tito, President of Egypt Gamal Abdal Nasser, President of Indonesia Dr. Sukarno and Prime Minister of Ghana Dr. Kwame Nkrumah.
Question 6.
Evaluate the Non-Aligned Movement.
Answer:
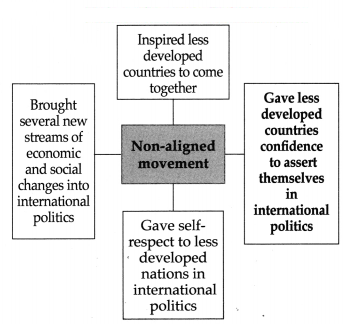
(i) The Non-Aligned Movement has opposed colonialism, imperialism and racism.
(ii) It has encouraged the resolution of international disputes by peaceful means.
(iii) The Non-Aligned movement is based on eternal principles of humanism, global peace and equality.
(iv) It has inspired the less developed countries to come together.
(v) While taking a firm stand on disarmament, fostering human rights, the Non-Aligned movement put forth the problems of poor, undeveloped countries firmly.
(vi) This movement made a demand of a New International Economic Order (NIEO).
Chapter 1 Post World War Political Developments Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 9 Political Science Chapter 1 Post World War Political Developments Textbook Questions and Answers
1A. Choose the right option and rewrite the sentence:
Question 1.
A system of independent and sovereign states ___.
(a) Political system
(b) International system
(c) Social system
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) International system

Question 2.
The main responsibility of the United Nations ____.
(a) to avoid war
(b) independence of colonies
(c) improving the economics of different nations
(d) disarmament
Answer:
(a) to avoid war
Question 3.
The Cold War ended with the event, _____.
(a) Establishment of the United Nations
(b) Disintegration of the Soviet Union
(c) Creation of Military Organisations
(d) Cuban Missile Crisis
Answer:
(b) Disintegration of the Soviet Union
2. Explain with reasons whether the following statements are true or false:
Question 1.
The League of Nations was established after the First World War.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
The world became unipolar due to the Cold War.
Answer:
False.
Question 3.
The policies of Mikhail Gorbachev gave an impetus to democratisation.
Answer:
True.

3. Explain the following concepts:
Question 1.
Cold War
Answer:
(i) America and the Soviet Union, who were allies in the Second World War became competitors, as soon as the war was over.
(ii) The cooperation between them gave way to rivalry. This rivalry occupied a period of 40-45 years of international politics
(iii) There was no open war between these two countries; but there was such tension in their relations, that it seemed that a war would erupt any time.
(iv) The concept of Cold War is used to describe the condition where there is no actual war, but there are such tensions in the circumstances, that they may be responsible to cause war.
(v) In this period, America was already a super power, but the Soviet Union also tried to become a super power by making nuclear weapons and by increasing its military might.
(vi) The struggle for power, arms race, differences in ideologies, attitude of checkmating each other by strategies and counter-strategies gave rise to the Cold War.
Question 2.
Non-Aligned Movement
Answer:
(i) In the period of the Cold War, while the world was becoming bipolar, there were some countries which did not want to join the super power rivalry. Such nations decided to stay out of the cold war rivalry. Their policy is known as non-alignment.
(ii) The Asian and African countries, which became independent after the Second World War supported the idea of non-alignment.
(iii) This movement started from 1961 under the leadership of India’s Prime Minister Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, President of Yugoslavia Marshall Tito, President of Egypt Gamal Abdal Nasser, President of Indonesia Dr. Sukarno and Prime Minister of Ghana Dr. Kwame Nkrumah.
(iv) The non-aligned Movement has opposed colonialism, imperialism and racism. It has encouraged the resolution of international disputes by peaceful means.
(v) India led this movement under the guidance of Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru. India continued to actively support the movement afterwards as well.
(vi) Even after the end of the Cold War, the importance of the movement has not reduced. The non-aligned movement is based on eternal principles of humanism, global peace and equality.
(vii) It has inspired the less developed countries to come together. It has encouraged the resolution of international disputes by peaceful means.
(viii) While taking a firm stand on disarmament, fostering human rights, the non-aligned movement put forth the problems of poor, undeveloped countries firmly. This movement made a demand of a New International Economic Order (NIEO).
Question 3.
Interdependence
Answer:
(i) All the countries of the world are dependent on each other for one reason or the other. However big, prosperous or developed a nation may be, it can never be self-sufficient to fulfill all its needs.
(ii) Even big nations have to depend upon other big and small nations. Thus, interdependence is an important feature of the international system, i.e. today’s global system.
Question 4.
Bipolarisation
Answer:
During the Cold War, most countries of the world joined either of the two super power blocks. Such a division of the nations of the world in two groups is bipolarisation.
Question 5.
Globalization
Answer:
(i) After the end of the Cold War, trade and economic relations between countries became more open. As it has been mentioned before, capital, labour, markets and information began circulating globally.
(ii) The give and take of ideas among people all over the world grew.
(iii) Due to the revolution in information technology, different events and developments began to be known everywhere.
(iv) The boundaries between nations did not remain as sacrosanct as they were before. All these processes are together called globalisation.
(v) Just as globalisation has brought us benefits, it has also caused losses. For example, as the economies of different countries got linked with each other, trade increased, economic unification grew, plenty of products became available in the markets; but (at the same time) the gap between the poor and rich nations did not reduce.

4. Give your opinion on the following topics:
Question 1.
What measures should the League of Nations have taken to avoid the Second World War?
Answer:
(i) League of Nations should have organised a military wing with the help of member nations to keep a check over the aggressors like Germany and Japan.
(ii) League should have reconsidered implementation of harsh term of treaties imposed on the losers to avoid the revengeful policies of dictators like Adolf Hitler.
Question 2.
Non-Alignment was necessary during the Cold War.
Answer:
(i) Yes. This was important to keep newly independent countries of Asia and Africa away from the super power rivalry.
(ii) Since these countries did not officially show allegiance to any super power, they freed themselves from the dominance of USA and USSR and could independently frame their foreign policies.
(iii) This further promoted peace and co-operation.
Question 3.
Human welfare was neglected due to the Cold War.
Answer:
(i) Yes, due to military alliances the world was gripped in the fear of a possible Third World War, which would have annihilated the entire human race.
(ii) Moreover the Arms Race diverted the resources and harnessed science for destruction rather than human welfare.
Question 4.
Which countries can emerge as super powers, in competition with America in present times?
Answer:
India and China could be future super powers.
5. Write brief answers:
Question 1.
Compare the First World War and the Second World War with the help of the following points.
| Points | First World War | Second World War |
| (1) Period | ||
| (2) Involved nations | ||
| (3) Impacts (Political and Economic) | ||
| (4) International Organisations established after the War |
| Points | First World War | Second World War |
| (1) Period | 1914-1918 | 1939 -1945 |
| (2) Involved nations | Allied Powers – Britain, France, Russia, Italy, America Central Powers – Germany, Austria, Hungary, Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria | Allied Powers – Britain, France, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, India, Soviet Union, China, America Axis powers – Germany, Japan, Italy |
| (3) Impacts (Political and Economic) | (i) Earlier empires in Europe collapsed and new nations came into being. | (i) Beginning of Cold War |
| (ii) Independence movements in European colonies changed hegemony of European Nations. | (ii) Destruction of public property on larger scale due to use of nuclear weapons | |
| (iii) League of nations was established. | ||
| (iv) Autocratic regime came up in Germany, Spain, Italy and other countries. | ||
| (v) Destruction of public property. | ||
| (4) International Organisations established after the War | League of Nations | United Nations Organisation |

Question 2.
What were the factors responsible for the end of Cold War?
Answer:
The factors responsible for the end of Cold War are:
(i) The Soviet Union adopted the policy of opening up the economy. The State loosened up its control of the economy.
(ii) The then President of the Soviet Union Mikhail Gorbachev implemented the policies of Perestroika (Restructuring) and Glasnost (Openness). Due to these policies, the control over the media reduced.
(iii) As the East European countries under the influence of the Soviet Union adopted the capitalist and democratic paths, the Soviet Union disintegrated and several new nations were created out of it.
Question 3.
What major changes occurred in global politics after the end of the Cold War?
Answer:
(i) Major changes took place in world politics after the end of the Cold War. For example, America remained the only super power in world politics.
(ii) A conducive atmosphere prevailed for the growth in trade and economic relations between and among nations.
(iii) As all nations of the world decided to give priority to trade relations, the idea of giving ‘aid’ to other nations fell behind.
(iv) The United Nations now had to take more concrete steps to maintain global peace and security.
(v) Environmental protection, fostering of human rights, gender equality and management of natural calamities now acquired a global dimension.
Class 9 Political Science Chapter 1 Post World War Political Developments Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option from the given options and rewrite the sentence:
Question 1.
President of Soviet Union who implemented ‘Perestroika’ and ‘Glasnost’ ______.
(a) Nikita Khrushchev
(b) Mikhail Gorbachev
(c) General Molotov
(d) Vladimir Lenin
Answer:
(b) Mikhail Gorbachev
Question 2.
Military organisation formed under dominance of USA ______.
(a) North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
(b) Warsaw Pact
(c) New International Economic Order
(d) Non-Aligned Movement
Answer:
(a) North Atlantic Treaty Organisation
Question 3.
Division of world into two power blocs is called ______.
(a) Globalisation
(b) Nuclear Escalation
(c) Bipolarisation
(d) Internationalism
Answer:
(c) Bipolarisation
Question 4.
Among the following ________ is not an Axis Power.
(a) Germany
(b) Italy
(c) Belgium
(d) Japan
Answer:
(c) Belgium
Question 5.
______ is an important event of the Cold War.
(a) Fashoda Incident
(b) Cuban Missile Crisis
(c) Wall Street Crash
(d) Red Menace
Answer:
(b) Cuban Missile Crisis

Question 6.
Non-aligned movement is opposed to ____.
(a) Racism
(b) Capitalism
(c) McCarthyism
(d) Nepotism
Answer:
(a) Racism
Question 7.
Non-aligned movement demanded establishment of _______.
(a) Association of South East Asian Nations
(b) League of Nations
(c) New International Economic Order (NIEO)
(d) European Union (EU)
Answer:
(c) New International Economic Order (NIEO)
Question 8.
The policy of Perestroika means restructuring and Glasnost means ______.
(a) strictness
(b) oneness
(c) massiveness
(d) openness
Answer:
(d) openness
State whether the following statements are True or False, with reasons:
Question 1.
A system of Independent States is called International System.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Interdependence is not an important feature of the International System.
Answer:
False.
Question 3.
The Second World War proved to be far more destructive than the First World War.
Answer:
True.

Question 4.
Efforts towards arms control and disarmament happened during the Cold War.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Non-alignment was an important movement during the Cold War.
Answer:
True.
Explain the concept:
Question 1
Military Organisation
Answer:
(i) During the Cold War, power struggle between USSR and USA created need for nations who will support their ideologies.
(ii) Thus, organisations were created for helping nations militarily and thus dragging them into either of the super power blocs for their hegemony.
(iii) The respective super powers took up the responsibility of the security of the countries joining the military organisations led by them.
(iv) NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organisation) was a military organisation under the dominance of America, while the Warsaw Pact was a military organisation, under the command of the Soviet Union.
Do as directed/instructed:
Complete the charts.
Question 1.

Answer:


Question 2.

Answer:

Question 3.

Answer:

Answer in brief:
Question 1.
What were the effects of World War I?
Answer:
(i) The First World War was fought between 1914 and 1918. The war caused a tremendous loss of life and property. The countries which joined the war suffered tremendous economic losses.
(ii) Even the countries which did not join the war were impacted by the war. The economies of the victorious as well as the losing countries collapsed.
(iii) Earlier empires in Europe collapsed and new nations came into being.
(iv) Independence movements in European colonies changed hegemony of European Nations.
(v) League of Nations was established.
(vi) Autocratic regime came up in Germany Spain, Italy and other countries.
Question 2.
Describe America’s role in the Second World War.
Answer:
(i) America played a major role in the Second World War. It had manufactured nuclear weapons.
(ii) In order to end the war, it dropped two nuclear weapons on two cities of Japan – Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6th and 9th August 1945 respectively.

Question 3.
What gave rise to the Cold War?
Answer:
(i) America was already a super power, but the Soviet Union also tried to become one, by making nuclear weapons and by increasing its military might.
(ii) The struggle for power, arms race, differences in ideologies, attitude of checkmating each other by strategies and counter-strategies gave rise to the Cold War.
Question 4.
Describe extreme differences among USA and USSR.
Answer:
(i) The U.S.A was a democratic State, advocating capitalism, while the Soviet Union advocated socialism and a one party authoritarian system.
(ii) Both the super powers wanted to expand their own dominance in the world.
(iii) America wanted to spread capitalism, while the Soviet Union wanted to spread socialism.
Question 5.
What is meant by Non-Aligned Movement and who were its founding fathers?
Answer:
(i) The Asian and African countries, which became independent after the Second World War supported the idea of non-alignment.
(ii) This movement started from 1961 under the leadership of India’s Prime Minister Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, President of Yugoslavia Marshall Tito, President of Egypt Gamal Abdal Nasser, President of Indonesia Dr. Sukarno and Prime Minister of Ghana Dr. Kwame Nkrumah.
Question 6.
Evaluate the Non-Aligned Movement.
Answer:
(i) The Non-Aligned Movement has opposed colonialism, imperialism and racism.
(ii) It has encouraged the resolution of international disputes by peaceful means.
(iii) The Non-Aligned movement is based on eternal principles of humanism, global peace and equality.
(iv) It has inspired the less developed countries to come together.
(v) While taking a firm stand on disarmament, fostering human rights, the Non-Aligned movement put forth the problems of poor, undeveloped countries firmly.
(vi) This movement made a demand of a New International Economic Order (NIEO).