Differentiation Class 11 Commerce Maths 1 Chapter 9 Miscellaneous Exercise 1 Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharati Maharashtra State Board 11th Commerce Maths Solution Book Pdf Chapter 9 Differentiation Miscellaneous Exercise 9 Questions and Answers.
Std 11 Maths 1 Miscellaneous Exercise 9 Solutions Commerce Maths
I. Differentiate the following functions w.r.t.x.
Question 1.
x
5
Solution:
Let y = x
5
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
dy dx=ddxx5=5x4
Question 2.
x
-2
Solution:
Let y = x
-2
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
dy dx=ddx(x−2)=−2x−3=−2x3
Question 3.
√x
Solution:
Let y = √x
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
dy dx=ddx√x=12√x

Question 4.
x√x
Solution:
Let y = x√x
∴ y = x32
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
dy dx=ddxx32=32x12
Question 5.
1√x
Solution:
Let y = 1√x
∴ y = x−12
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
dy dx=−12x−32=−12x32
Question 6.
7
x
Solution:
Let y = 7
x
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
dy dx=ddx7x=7xlog7
II. Find dydx if
Question 1.
y = x
2
+ 1x2
Solution:

Question 2.
y = (√x + 1)
2
Solution:


Question 3.
y = (√x+1√x)2
Solution:

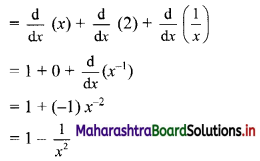
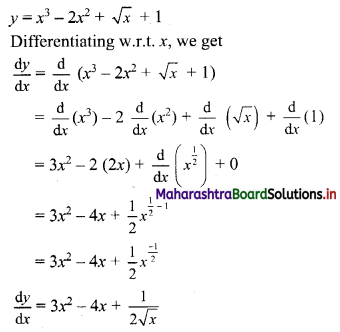
Question 4.
y = x
3
– 2x
2
+ √x + 1
Solution:
Question 5.
y = x
2
+ 2x – 1
Solution:

Question 6.
y = (1 – x)(2 – x)
Solution:

Question 7.
y = 1+x2+x
Solution:
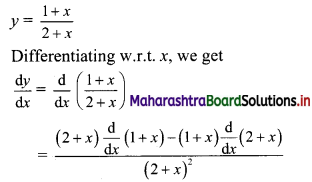
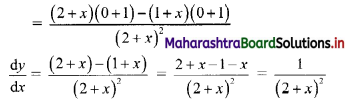

Question 8.
y = (logx+1)x
Solution:

Question 9.
y = exlogx
Solution:
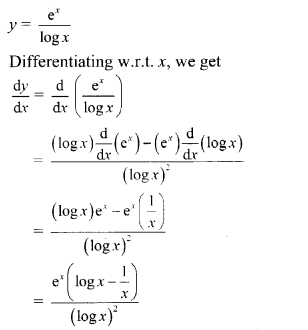
Question 10.
y = x log x (x
2
+ 1)
Solution:
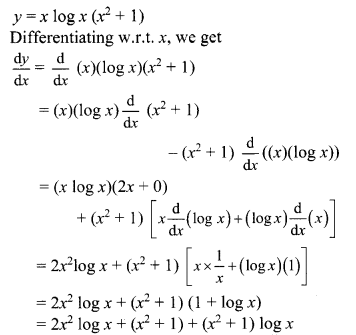
III. Solve the following:
Question 1.
The relation between price (P) and demand (D) of a cup of Tea is given by D = 12P. Find
the rate at which the demand changes when the price is ₹ 2/-. Interpret the result.
Solution:
Demand, D = 12P
Rate of change of demand
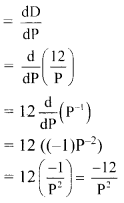
When price P = 2,
Rate of change of demand,
(dDdP)P=2=−12(2)2=−3
∴ When the price is 2, the rate of change of demand is -3.
∴ Here, the rate of change of demand is negative demand would fall when the price becomes ₹ 2.
Question 2.
The demand (D) of biscuits at price P is given by D = 64P3, find the marginal demand
when the price is ₹ 4/-.
Solution:
Given demand D = 64P3
Now, marginal demand
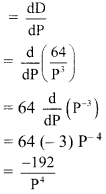
When P = 4
Marginal demand
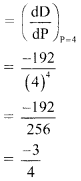

Question 3.
The supply S of electric bulbs at price P is given by S = 2p
3
+ 5. Find the marginal supply when the price is ₹ 5/-. Interpret the result.
Solution:
Given, supply S = 2p
3
+ 5
Now, marginal supply
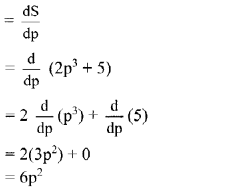
∴ When p = 5
Marginal supply = (dSdp)p=5
= 6(5)
2
= 150
Here, the rate of change of supply with respect to the price is positive which indicates that the supply increases.
Question 4.
The total cost of producing x items is given by C = x
2
+ 4x + 4. Find the average cost and the marginal cost. What is the marginal cost when x = 7?
Solution:
Total cost C = x
2
+ 4x + 4
Now. Average cost = Cx=x2+4x+4x
= x + 4 + 4x
and Marginal cost = dCdx=ddx(x
2
+ 4x + 4)
= ddx (x
2
) + 4ddx (x) + ddx (4)
= 2x + 4(1) + 0
= 2x + 4
∴ When x = 7,
Marginal cost = (dCdx)x=7
= 2(7) + 4
= 14 + 4
= 18
Question 5.
The demand D for a price P is given as D = 27P, find the rate of change of demand when the price is ₹ 3/-.
Solution:
Demand, D = 27P
Rate of change of demand = dDdP
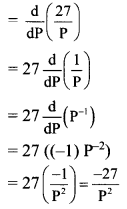
When price P = 3,
Rate of change of demand,
(dDdP)P=3=−27(3)2=−3
∴ When price is 3, Rate of change of demand is -3.

Question 6.
If for a commodity; the price demand relation is given as D = (P+5P−1). Find the marginal demand when price is ₹ 2/-
Solution:

Question 7.
The price function P of a commodity is given as P = 20 + D – D
2
where D is demand. Find the rate at which price (P) is changing when demand D = 3.
Solution:
Given, P = 20 + D – D
2
Rate of change of price = dPdD
= ddD(20 + D – D
2
)
= 0 + 1 – 2D
= 1 – 2D
Rate of change of price at D = 3 is
(dPdD)D=3 = 1 – 2(3) = -5
∴ Price is changing at a rate of -5, when demand is 3.
Question 8.
If the total cost function is given by C = 5x
3
+ 2x
2
+ 1; find the average cost and the marginal cost when x = 4.
Solution:
Total cost function C = 5x
3
+ 2x
2
+ 1
Average cost = Cx
= 5x3+2x2+1x
= 5x
2
+ 2x + 1x
When x = 4,
Average cost = 5(4)
2
+ 2(4) + 14
= 80 + 8 + 14
= 320+32+14
= 3534
Marginal cost = dCdx
= ddx (5x
3
+ 2x
2
+ 1)
= 5ddx (x
3
) + 2 ddx (x
2
) + ddx (1)
= 5(3x
2
) + 2(2x) + 0
= 15x
2
+ 4x
When x = 4, marginal cost = (dCdx)x=4
= 15(4)
2
+ 4(4)
= 240 + 16
= 256
∴ The average cost and marginal cost at x = 4 are 3534 and 256 respectively.

Question 9.
The supply S for a commodity at price P is given by S = P
2
+ 9P – 2. Find the marginal supply when the price is 7/-.
Solution:
Given, S = P
2
+ 9P – 2
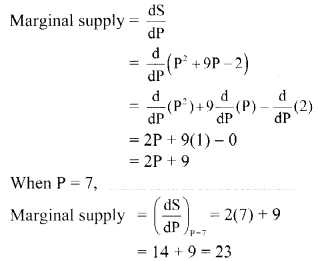
∴ The marginal supply is 23, at P = 7.
Question 10.
The cost of producing x articles is given by C = x
2
+ 15x + 81. Find the average cost and marginal cost functions. Find the marginal cost when x = 10. Find x for which the marginal cost equals the average cost.
Solution:
Given, cost C = x
2
+ 15x + 81
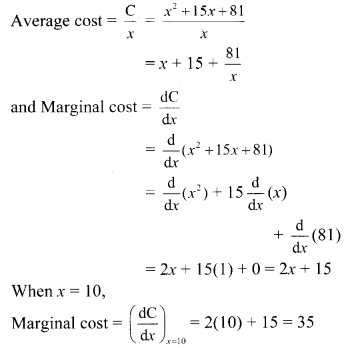
If marginal cost = average cost, then
2x + 15 = x + 15 + 81x
∴ x = 81x
∴ x
2
= 81
∴ x = 9 …..[∵ x > 0]