Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 History Solutions Chapter 4 History of Indian Arts Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 10 History Chapter 4 Question Answer History of Indian Arts Maharashtra Board
Class 10 History Chapter 4 History of Indian Arts Question Answer Maharashtra Board
History Class 10 Chapter 4 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
(A) Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the statement.
(1) The arts of painting and sculpting are …………….……. .
(a) visual arts
(b) performing arts
(c) folk arts
(d) classical arts
Answer:
(a) visual arts

(2) The …………….……. saw the rise of Mathura school.
(a) Kushana period
(b) Gupta period
(c) Rashtrakuta period
(d) Maurya period
Answer:
(a) Kushana period
(B) Identify and write the wrong pair in the following set.
(1) Qutub Minar – Mehrauli
(2) Gol Gumbaz – Vijapur
(3) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus – Delhi
(4) Taj Mahal – Agra
Answer:
(3) Wrong Pair: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus – Delhi
Question 2.
Write short notes.
(1) Art
Answer:
- It is a natural instinct in humans to share their emotions, experience, wisdom acquired with others.
- This act of sharing, results in beautiful creation, called an ‘Art’.
- Art gives us an experience of different elements.
- These elements are expressed through sculpture, singing, painting and dance.
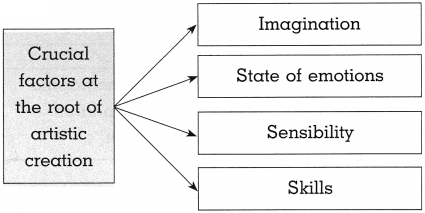
- The crucial factors which are at the root of artistic creation are the imagination power of the artist.
- The sensibility state of his emotions and skills.
(2) Hemadpanti style
Answer:
- Hemadpanti temples were primarily built in 12th- 13th century.
- The main feature of this style is its masonry. The walls are built without mortar, by locking stones, using the tenon and mortise joints technique.
- Hemadpanti temples are built in square¬shaped and star-shaped designs. In the star¬shaped plan, the outer walls of a temple has a zigzag design which gives interesting effect of alternating light and shadow.
- Tourists are attracted to see these beautiful designs. Hemadpanti temples are found at several places in Maharashtra.
(3) Maratha style of painting
Answer:
- The Maratha style of paintings began to develop in the later half of the 17th century.
- This style consists of coloured paintings which are in form of murals and miniatures used in manuscripts.
- Murals of Maratha style can be seen at the entrance of old wadas, in drawing rooms and on the ceilings of the temples.
- The Maratha style was influenced by the Rajput and European style of paintings.
- The Maratha style of paintings helps us to understand various things about the times in which it was developed such as lifestyle, attires, customs, etc.
Question 3.
Explain the following statements with reasons.
(1) An expert with deep understanding of art history is required in the art market.
Answer:
- There is an independent market for purchase and sale of art objects.
- The authenticity of the object, its standards can only be assessed by an expert.
- Only an artist can know the exact value of an art object or ensure if it is genuine or not.
- So, when art objects are assessed all the above points are considered.
- This requires special expertise. Hence an expert with deep understanding of art history is required for this task.
(2) It is necessary to preserve the tradition like Chitrakathi, which is on the verge of extinction.
Answer:
- The stories from Ramayana or Mahabharata narrated with the help of wooden puppets and paintings is known as Chitrakathi or Pinguli tradition.
- It is preserved by the Thakur community.
- As the Chitrakathi pictures are drawn on papers and painted using col9urs made from natural substances, they deteriorate rapidly if not maintained.
- Therefore it is necessarý to preserve the tradition like Chitrakathi as it is part of our glorious cultural heritage and is on the verge of extinction.
Question 4.
Complete the following table.
| Temple Architecture Naagara | Naagara | Draavida | Hemadpanti |
| Characteristics | |||
| Examples |
Answer:
| Styles of Temple Architecture | Nagara | Dravid | Hemadpanti |
| Characteristics |
(1) Series of miniature towers are arranged
(2) Towers taper towards the top (3) Tower appears to be continuously rising from the base of the temple to the top. |
(1) Temple towers resembled pyramid shape.
(2) Gopura (main entrance) was large and magnificent than the tower. (3) Mythological stories were carved on walls and ceilings. |
(1) The temple structure was star-shaped with outer walls having zigzag design.
(2) The walls were built without using any mortar. (3) The stones were locked by using the technique of tenon and mortise joints. |
| Examples |
(1) Konark Sun Temple
(2) Lingraj Temple of Bhubaneshwar (3) Kandariya Mahadev temple at Khajuraho |
(1) Meenakshi Temple at Madurai
(2) Chariot Temple at Mahabalipuram (3) Brihadeeshvara temple at Thanjavur (4) Tirupati Temple |
(1) Gondeshwar temple at Sinnar
(2) Ambreshwar temple at Ambarnath (3) Aundha Nagnath temple at Hingoli (4) Kopeshwar temple at Khidrapur |
Question 5.
Answer the following questions in detail.
(1) Write in detail about folk styles of painting.
Answer:
- The art of rock painting dates back to Stone Age. These rock paintings have preserved the style of folk painting.
- Rock paintings usually depict humans, animals and geometric figures.
- The style of rock paintings seems to be changing according to the cultural changes from Stone age to the beginning of agriculture.
- Man started depicting flora and fauna in a different style and also figures.
- There was difference in colours too. Black and Red were used in rock paintings.
- Colours extracted from natural substances were used.
- The man started using the knowledge he got from the surroundings and nature and depicted it in the pictures.
- In the later stage of development, man started customs such as decorating the walls and courtyards (Rangawali).
- By drawing various figures and symbols or using panels of painting to narrate stories. It helped in the development of folk paintings.
(2) Explain the characteristics of the Islamic architecture in India by giving examples.
Answer:
A blend of Persian, Central Asian, Arabic and pre Islamic native Indian styles created the Islamic architecture of India.
Following are the characteristics of Islamic architecture developed in the medieval period under the patronage of Muslim sultanates:
- Built in Islamic style, the Kutub Minor is the highest minaret in the world. It is 73 metres (240 ft) in height.
- The Taj Mahal built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jah’an is looked’ upon as the paramount* example of Islamic’architecture.
- The Gol Gumbaz at Bijapur in Karnataka built in 17th century is known for its echo which can be heard many times.
- The forts at Agra and Delhi are known for their massive walls of redstone.
- The walls are interrupted by graceful curves and lofty bastions. Red sandstone, domes, arches, minarets, magnificance all combined form characteristics of Islamic architecture.
(3) What kind of professional opportunities are available in the field of arts?
Answer:
Various opportunities are available in different fields of art:
- Art historian can work in field of journalism. Art students can work in museums, archives, libraries. Information Technology, archaeological research and Indology contribute to recently developed fields like Heritage Management and Cultural Tourism.
- An expert in art is required to assess the exact value of an art object and also in its sale and purchase. Experts are required in the field of manufacturing of objects for home decoration.
- Ornaments, artistic creations of metals, earthen pots with colourful designs, objects made from cane and bamboo, beautiful glass objects, attractive textiles and clothing all come are under applied arts.
- These fields require experts in manufacturing and sales. Hence many opportunities of employment are available in the field of arts.
(4) Observe the illustration of Warli painting on p. 23 and write about:
(a) Depiction of nature
(b) Drawings of human figures
(c) Depiction of occupations
(d) Houses
Answer:

The traditions of Warli painting and Pingul or Chitra Katha
in Maharashtra are among the finest examples of folk style of paintings. Divya Somya Mashe, the artist in Thane district has played a great role in making the Warli style of paintings very popular. He has been honored with a number of national and international awards for his paintings. In the year 2011, he was awarded ‘Padmashree’.
Name of the painting tradition:
This picture is from Warli tradition.
Nature’s description:
Artist has sketched trees, leaves and shrubs in the picture. A fish is also drawn.
Sketch of human activities:
Women dancing in a circular pattern is also sketched in the picture.
Designing features:
Pictures of men, women and children are sketched. Warli paintings do not portray the exact objects but only a sketch. Human figures are drawn with the help of a triangle, circle and square which are placed at the tip.
Project
(1) Collect additional information of the World Heritage sites in India.
(2) Observe the sculptors or image-makers at work in your locality and interview them.
Answer:
Memory Map
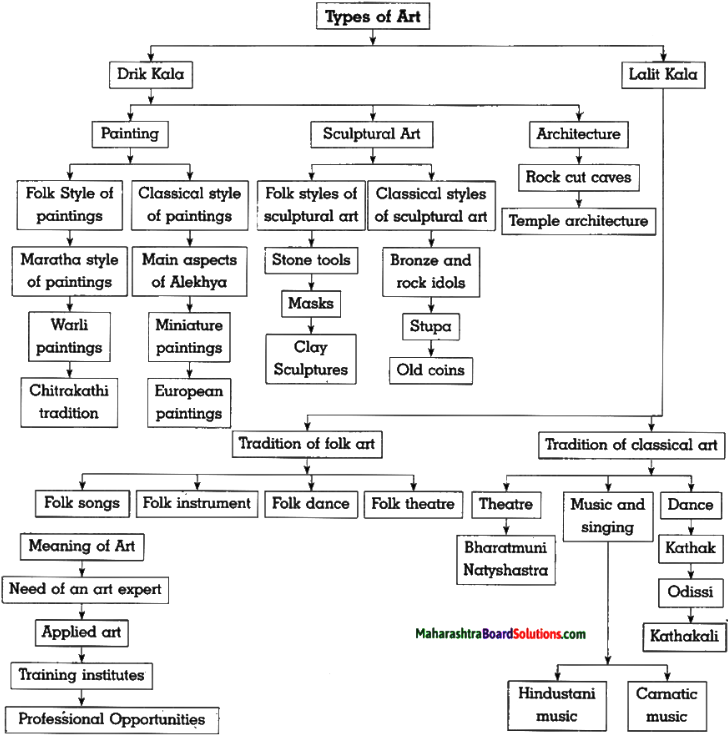
Question 6.
Complete the sentences by choosing a correct option:
(a) Lalit Kala is also known as …………………… .
(a) Folk art
(b) Aangik Kala
(c) Drik Kala
(d) Nagara art
Answer:
(b) Aangik Kala
(b) Jivya Somya Mashe, an artist in the Thane district played a great role in making the …………………… style of painting very popular.
(a) Chitrakathi
(b) Maratha
(c) Warli
(d) Classical
Answer:
(c) Warli
(c) The Chalukya King, Someshvara, mentioned in …………………… book the tradition of Chitrakathi.
(a) Natyashastra
(b) Kitab-e-Navras
(c) Paintings of Ajanta
(d) Manasollas
Answer:
(d) Manasollas.
(d) The ancient Indian texts mentioned …………………………. styles of Classical Art.
(a) Nine
(b) Thirty-six
(c) Sixty-four
(d) Eighty-four
Answer:
(c) Sixty-four
(e) During the reign, of Mughal Emperor …………………………., the Mughal miniature style showing a blend of Indian and Persian was developed.
(a) Akbar
(b) Aurangzeb
(c) Jahangir
(d) Babur
Answer:
(a) Akbar
(f) Some of the drawings of Gangaram Tambat are preserved in …………………………. university.
(a) Stanford
(b) Cambridge
(c) Oxford
(d) Yale
Answer:
(d) Yale
(g) …………………………. is the characteristic of European style of painting.
(a) Sketching
(b) Exact portrayal of object
(c) Natural colours
(d) Landscape
Answer:
(b) Exact portrayal of object
(h) Replicas of Ajanta paintings was made by
(a) Pestonji Bomanji
(b) Gangaram Tambat
(c) Raja Ravi Verma
(d) James Wales
Answer:
(a) Pestonji Bomanji.
(i) The lion capital of the Ashoka pillar found at …………………………. is the national emblem of India.
(a) Bodhgaya
(b) Patliputra
(c) Sanchi
(d) Sarnath
Answer:
(d) Sarnath
(j) The stupa at …………………………. in Indonesia is the largest stupa in the world.
(a) Ubud
(b) Sigiran
(c) Borobudur
(d) Palembang
Answer:
(c) Borobudur
(k) The …………………………. school of art laid the foundation of Indian iconography.
(a) Gandhar
(b) Nagara
(c) Dravid
(d) Mathura
Answer:
(d) Mathura
(l) The temple architecture developed in India around 4th century C.E. during the …………………………. period.
(a) Kushana
(b) Rashtrakuta
(c) Gupta
(d) Chola
Answer:
(c) Gupta
(m) …………………………. is a blend of Nagara style of architecture of North India and Dravid style of South India.
(a) Gandhar
(b) Mathura
(c) Bhoomija
(d) Vesara
Answer:
(d) Vesara.
(n) The two main branches of the Indian classical music are ………………………… .
(a) Folk music and Vocal
(b) Dadraa and Thumri
(c) Bhajans and Qawwalis
(d) Hindustani music and Carnatic music
Answer:
(d) Hindustani music and Carnatic music
(o) The text of …………………………. written by Bharatmuni is supposed to be the earliest one discussing music and theatre.
(a) Manasollas
(b) Abhilasha Chintamani
(c) Natyashastra
(d) Rasratnakar
Answer:
(c) Natyashastra
(p) Every year the …………………………. festival is held in Pune.
(a) Kala Ghoda
(b) Gunidas
(c) Savai Gandharva
(d) Gharapuri
Answer:
(c) Savai Gandharva
(q) The ruler of Bijapur, Ibrahim Adilshah wrote …………………………. text in Persian language.
(a) Tuzuk-i-Babari
(b) Padmavat
(c) Akbarnama
(d) Kitab-e-Navras
Answer:
(d) Kitab- e-Navras
(r) …………………………. is a prominent name among artists who created a new style of fusion of Indian and Western dance.
(a) Pandit Shivkumar Sharma
(b) Pandit Hariprasad Chaurasia
(c) Pandit Uday Shankar
(d) Ustad Zakir Hussain
Answer:
(a) Pandit Uday Shankar.
Question 7.
Identify the wrong pair in the following and write it:
(1)
| Architectural structure | Place |
| (1) Kutub Minar | (a) Mehrauli |
| (2) Gol Gumbaz | (b) Bijapur |
| (3) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus | (c) Delhi |
| (4) Taj Mahal | (d) Agra |
Answer:
Wrong pair: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus – Delhi
(2)
| Picture | Style |
| (1) Murals seen in the old wadas at Wai, Menavali | (a) Miniature style |
| (2) Bhimbetka | (b) Folk painting |
| (3) Pictures narrating Ramayana and Mahabharata story | (c) Chitrakathi |
| (4) Painting style in Thane district | (d) Warli painting |
Answer:
Wrong pair: Murals seen in the old wadas at Wai, Menavali – Miniature style
(3)
| Architectural structure | Style |
| (1) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus | (a) Gothic architecture |
| (2) Gol Gumbaz | (b) Muslim architecture |
| (3) Temples in South India | (c) Nagara architecture |
| (4) Gondeshwar Temple | (d) Hemadpanti architecture |
Answer:
Wrong pair: Temples in South India – Nagara architecture
(4)
| Monument | Emperors |
| (1) Completed Kutub Minar | (a) Altmash |
| (2) Construction of Taj Mahal | (b) Emperor Akbar |
| (3) Gol Gumbaz | (c) Mohammed Adilshah |
| (4) Built Sanchi Stupa | (d) Emperor Ashoka |
Answer:
Wrong pair: Construction of Taj Mahal – Emperor Akbar
Question 3.
Do as directed:
(A) Complete the following concept chart:
(1)
Answer:
(2)
Answer:
(3)
Answer:
(4)
Answer:
(5)
Answer:
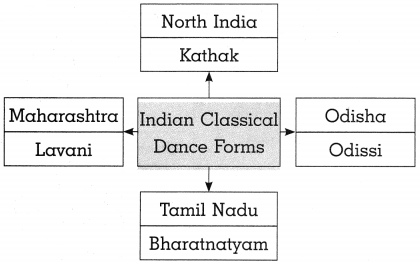
(6)
Answer:
(B) Prepare a flow chart on the Development of Indian Iconography.
Answer:

Question 8.
Explain the following concepts:
(a) Style in Art:
Answer:
- Every artist has its own method of working which becomes his style.
- When this style is repeated by several artists over a prolonged period of time it becomes a tradition.
- This tradition is known as an art ‘style’.
- Such traditions are established in every art style. Various art styles are developed over the years in every culture.
- The specific art styles indicate the characteristic of a certain region and period.
- They help us to learn the history of arts of these civilizations.
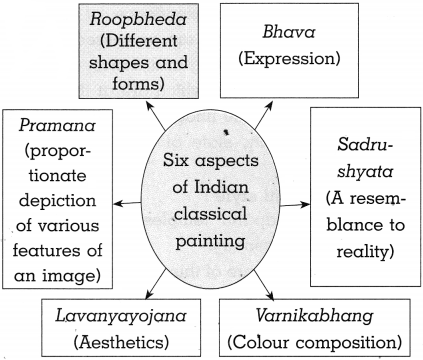
(b) Classical Style of Paintings:
Answer:
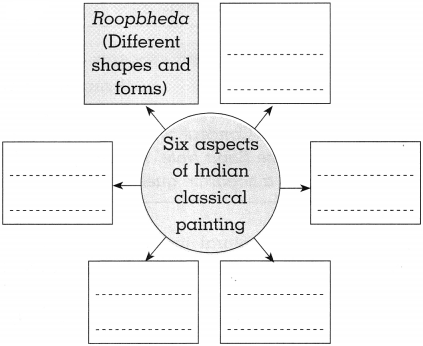
- Art which is expressed within an established frame of consistent rules is known as classical art. The ancient Indian texts mentioned altogether 64 arts.
- The aft of painting is mentioned as alekhyam or alekhya vidya in these texts.
- This alekhya vidya has six main aspects of paintings (Shadange).
- They are shapes and forms (Roopbheda), expressions (Bhava).
- Proportionate depiction of various features of an image (Pramana).
- Aesthetics (Lavanyayojana), resemblance to reality (Sadrushyata) and colour composition (Varnikabhang).
- Agama text of Jainism and in Puranas various arts like painting, sculpting are explained in context of temple architecture.
Question 9.
Write short notes:
(a) Chitrakathi:
Answer:
- The tradition of narrating stones from Ramayana and Mahabharata with the help of wooden puppets and paintings is known as Chitrakathi. It is also known as Pinguli.
- This tradition is mentioned in Manasollas, a book written by the Chalukya King Someshvara in the 12th century. People belonging to Thakur community stifi practise this art They are frm village, Pinguli near Kudal in Maharashtra.
- The Chitrakathi pictures are drawn on paper and painted with natural substances. To complete the narration of a single story it takes around 30 to 50 pictures.
- These pictures are preserved and are passed on from one generation to another. The artists and government are trying to preserve this tradition which is on the verge of extinction.
(b) Miniature Painting:
Answer:
- Painting in a small size square is called Miniature painting.
- The miniature reached people through manuscripts. The earlier period of miniature painting shows the influence of Persian style.
- The Deccan miniature style was developed under the patronage of the Deccan Sultanate.
- Mughal miniature painting style of painting’ was developed during the reign of Mughal Emperor Akbar. ¡t shows a blend of Indian and Persian style.
(c) Western style of painting:
Answer:
- Indian artists came under the influence of European style of painting during the British period.
- An art school at Shaniwar Wada at Pune was established under the leadership of Scottish artist James Wales.
- J. J. School of art and industry was established in 1857 to offer the courses in European style of painting.
- Pestonji Bomanji made replicas of Ajanta paintings.
- lames Wales had done a portrait of Savai Madhavrao and Nana Phadnavis.
- Exact portrayal of the object of the painting is a characteristic of European style.
(d) Gangaram Tambat:
Answer:
- An art school was established under the leadership of Scottish artist James Wales at Shanivar Wada in Pune.
- Marathi artist Gangaram Tambat worked with James Wales.
- He made drawings of rock-cut caves at Verul and Karle.
- Some of his drawings are preserved in the Yale Centre of British Art of Yale University.
(e) Temple architecture:
Answer:
- Temple architecture began to develop in India around 4th century C.E. during the Gupta period. In the initial stage of the Gupta period, the temples had only the Sanctum Sanctorum (Garbhagriha) and a Veranda with four columns.
- Temple architecture reached its peak by the 8th century C. E. and its example is the Kailas temple of Verul. By medieval period various types of temple architecture had developed in India.
- The styles of tower (Shikar) determined various styles of temple architecture in India. The Nagara style of North India and Dravid style of South India are two prominent styles of Indian temple architecture. A blend of Nagara and Dravid is known as Vesara style.
- Bhoomija style seen in temples of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh has very close resemblance to ‘Nagara’ style.
(f) Indo-Gothic Architecture:
Answer:
- During the British period, a new architectural style arose in India which was a blend of Indian and Gothic known as Indo-Gothic style of architecture.
- During the British period, buildings like churches, government offices, residences of top officials, railway stations were built in Indo-Gothic style of architecture.
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus in Mumbai is the finest example of Indo- Gothic style of architecture.
(g) Ttitab-e-Navras:
Answer:
- Ibrahim Adilshah II, the ruler of Bijapur, wrote a book in Persian language entitled ‘Kitab- e-Navras’. This text is about Indian classical music.
- It includes the verses suitable for singing. It is a composition of excellent poetry expressed through Dhrupad style giving the experience of ecstasy to the interested audience.
- The Ncrvras mentioned in Sanskrit literature are explained in this text.
Question 10.
Explain the following sentences with reasons:
(a) Indian performing arts were enriched over time.
Answer:
- A constant stream of rulers like the Greeks, Arabs, Mughals and the British came to India.
- During their rule, Indian people came into contact with their styles of folk art.
- The culture which they brought along lasted and blended with existing streams of Indian performing arts.
- As a result, many styles of classical vocal music, instrumental music and dance came into existence.
- Therefore Indian performing arts enriched over time.
(b) The field of Applied Arts needs professionals.
Answer:
- An artistic creation is combined with utilitarian purpose to make it economically viable in applied arts.
- Many stages of production are reached before the concept of creation becomes a reality.
- Each field in applied arts requires detailed planning and meticulous management at each stage of production.
- Ornaments, earthen pots with colourful designs, objects made from Cane and Bamboo, beautiful glass objects.
- Attractive textiles and clothing all listed under applied arts essentially require trained and skilled individuals at every stage.
- Some of the production processes of artistic objects have a history of certain traditions. It is important to have knowledge of those traditions.
Hence, it is essential to have trained and skilled professionals at every stage.
Question 11.
Answer the following question in 25-30 words:
(a) Write about follk traditions of sculptural art.
Answer:
- The tradition of folk art dates back to the Stone Ages.
- The custom of making clay images for rituals has been prevalent in India since Harappcin times.
- It has continued even today in many regions of Bengal, Bihar, Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- During the festivals, Ganesh idols are made along with the masks of Goddess Gauri.
- Bull figurines are made for the festival of Bailpola.
- Wooden memorials, Veergals (memorial stones), the decorated clay storage bins, etc.
- Are examples of folk tradition of sculptural art.
- The sculptures made for religious and festival reasons became masterpieces of artists’ creation.
(b) Write about Gandhara School of Art.
Answer:
- The regions around Afghanistan showed great influence of Greeks and Persians from 2nd century B.C.E.
- Gandhara style of art was a fusion of Greek- Roman and Indian style.
- Gandhara school was heavily influenced by Greek methodologies.
- The materials used to make sculptures were Grey sandstone. Mud, Lime and Stucco.
- Grey sandstone is more prominently used in Gandhara School of Art.
- The Gandhara school images are known for their anatomical accuracy, spatial depth and foreshortening.
- The sculptures in Gandhara style are found in Taxila, Peshawar and on the North West Frontier.
(c) Write about development of Indian Iconography.
Answer:
- The Kushana period from the 1st – 3rd century C.E. saw the rise of Mathura School of Art.
- The Mathura School of Art laid the foundation of Indian iconography style.
- The Kushana Kings made use of images of various deities on their coins.
- During the Gupta period, the ieonographic rules were formulated and standards for sculptural- art were set.
- The art of making bronze images was developed under the patronage of Chola Kings during 9th-13tji century.
- Bronze idols of gods and goddesses like Siva-Parvati, Natraj, Lakshmi, Vishnu, etc. were made.
(d) Give information about the rock-cut caves in India.
Answer:
- The tradition of rock-cut caves originated in India in the 3rd century B.C.E.
- The entire composition of a rock-cut cave represents a union of architecture and sculptural art.
- The entrances of such rock-cut caves, interiors with its carved columns and images are excellent specimens of sculptural art.
- The paintings on the walls and ceilings have survived till today.
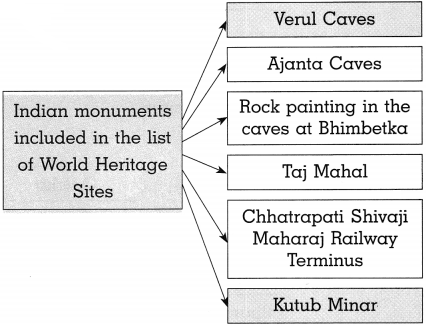
- The rock-cut caves at Ajanta and Verul in Maharashtra were declared as World Heritage Sites in 1983.
(e) Elaborate on the development of temple architecture.
Answer:
- The temple architecture began to develop in India during the Gupta period in 4th century C.E.
- The temples built at the beginning of the Gupta period had only the sanctum sanctorum (Garbhagriha) and a veranda with four columns.
- The magnificent structure of the Kailas temple of Verul gives testimony that temple architecture had reached its peak by the 8th century C.E.
- Different styles of temple architecture were developed by the medieval period. Some of them are Nagara, Dravid, Vesara and Bhoomija.
(f) What efforts were taken in India to make dance and classical music easily accessible to common people?
Answer:
The following efforts were taken to make dance and music easily accessible to people:
- Dance programmes and musical festivals were organised at various places.
- Many people attend these festivals including Indians and foreigners.
- The Savai Gandharva festival of Pune is very famous.
(g) Write about the work of Pandit Uday Shankar.
Answer:
- Pandit Uday .Shankar created a fusion of Indian classical dance and European operti.
- New styles of dancing were developed.
- He also included various folk dances in his style of fusion.
Thus, the scope of Indian performing arts seems to be constantly expanding.
(h) Which fields are related to applied arts ?
Answer:
- An artistic creation with a utilitarian purpose is called applied arts. Industry and advertisement. Interior Design and production of ornamental objects, Art Design of stage backdrops, Art Direction for films and television are the fields of applied arts.
- Layout of books, magazines, production of greeting cards, invitation cards, gift objects, calligraphy are also related to applied arts.
- Still and animated graphics, created with the help of computers are used for various purposes. This field needs experts with technical knowledge.
- In short, whichever art is known and is applied to create something new becomes applied art.
Question 12.
Read the following passage and answer the questions:
(a) In which states of India are the sites of rock paintings found?
Answer:
The sites of rock paintings are found in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Uttarakhand, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
(b) How old is the tradition of rock paintings?
Answer:
The tradition of rock painting dates back to the Stone Age.
(c) What are the features of rock paintings?
Answer:
- Rock paintings depict humans, animals, geometric figures, flora and fauna in various figures and also in colour.
- Natural colours in black and fed are used in them which are extracted from natural substances.
- The style of rock paintings seems to be changing according to the cultural changes from Stone Age to the beginning of agriculture.
- We get to know about ancient people, their natural surroundings and also the way they exploited available natural resources.
Question 13.
Answer the following questions in detail:
(a) Give information on Indian classical sculptural art.
Answer:
The development of folk styles of sculptural art led to the formation of rules for classical sculptural art and it evolved.
- The folk style of sculpture-making began during the Harappan period. Seals, stones and bronze statues that were made, gives a testimony that the art of sculpture was known to the Indians.
- It is about 5000 years old or even older tradition.
- The tradition of the erected stupa started in the times of Ashoka. The stupa at Borobudur in Indonesia is the largest stupa in the world.
- Gandhara style of sculptural art came to being in the 2nd century B.C.E. and has Greek and Persian influences.
- During the Kushana reign, Mathura School of art evolved which was a blend of Gandhara School of Art and indigenous art.
- The rules of Indian iconography was laid during the rule of the Gupta empire. Thus, Indian sculptural tradition has developed into a rich classical sculptural art.
(b) Differentiate between Classical and Folk: art.:
Answer:
Some differences are noted between Classical and Folk art. They are as follows: Classical Art Folk Art
| Classical Art | Folk Art |
| 1. Classical art does not have such a long tradition. | 1. The tradition of folk art has continued from the prehistoric times. |
| 2. Classical art is not connected to everyday life. | 2. Folk art is an integral part of everyday life. |
| 3. It takes a very long time period to master classical art. | 3. The creation of folk art has taken place naturally because of people’s involvement. |
| 4. Classical art developed within the established frame of rules. | 4. Folk art developed as an integral part of the religious festivals and social life. |
| 5. As classical art follows set rules, different types of styles, methods and schools are developed. | 5. Folk art is not bound by any rules. |
Brain Teaser
Across:
- Temples built in Maharashtra in 12-13th centuries in this style
- The text written by the ruler of Bijapur, Ibrahim Adilshah II
- Artist who created a fusion of Indian classical dance and European opera
- His drawings are preserved in the Yale Centre of British Art of Yale University
Down:
- The temple of Kailas at Verul
- An art school was established under his leadership in the times of Savai Madhavrao Peshwe
- The art of painting is mentioned as … in ancient Indian text
- Murals of Maratha style of painting can be seen at this place