Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 17 Effects of Light Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 Science Chapter 17 Effects of Light Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 7 Science Chapter 17 Effects of Light Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Fill in the blanks.
Question a.
When the beams from the headlights of a car fall on an object in the night, the shadows – called ………. and ………… . can be seen.
Answer:
umbra, penumbra
Question b.
During a lunar eclipse the shadow of the …………. falls on the ………. .
Answer:
earth, moon

Question c.
During a solar eclipse the shadow of the ………. falls on the ………… .
Answer:
moon, earth
Question d.
Various shades of colour are seen in the sky at sunrise and sunset due to ……….. .
Answer:
scattering of light
2. Give reasons.
Question a.
Space beyond the earth’s atmosphere appears dark.
Answer:
- Space beyond the earth’s atmosphere does have some gas and cosmic dust but there is not any atmosphere.
- As there are no particles to scatter the sunlight, the space appears black.

Question b.
We are able to read while sitting in the shade.
Answer:
- We are able to read because the sun light which falls on the book is scattered and reaches our eyes.
- While sitting in the shade our eyes adjust to the environment and to amount of light available. That is how we are able to read.
Question c.
We should not observe the solar eclipse with naked eyes.
Answer:
- During a solar eclipse ultra-violet rays which are harmful to us reach the earth and may lead to eclipse blindness or retinal bums and cataracts.
- In order to protect our eyes a solar eclipse should never be watched with the naked eye.
- A special type of goggles should be used for this.

3. Give some examples of scattering of light that we come across in day to day life.
Question a.
Give some examples of scattering of light that we come across in day to day life.
Answer:
- The formation of rainbow, shift in position of stars, increased day time, mirage, inverted image, glittering of diamond, the working of lens and prism, bending of pen in water are examples of scattering of light.
- The blue colour of the sky is due to the scattering of sunlight by the molecules of air.
- During sunrise and sunset, sunlight has to travel greater distance, so shorter wavelength gets scattered off and removed and only orange and red with longer wavelengths reach us.
- So during sunrise and sunset, sky appears fed and orange.
4. Why is the shadow of a bird flying high not seen on the earth?
Question a.
Why is the shadow of a bird flying high not seen on the earth?
Answer:
- Birds flying high in the sky do cast their shadow but because they are shading an area that is very tiny the shadow is not visible.
- The higher the bird flies, the smaller the shadow it casts.
- Also when the bird flies high, the dark part of the shadow that is called Umbra does not reach the ground so we do not see its shadow.

5. Why is a penumbra not obtained from a point source?
Question a.
Why is a penumbra not obtained from a point source?
Answer:
- The umbra, penumbra are the distinct parts of a shadow, created by any light source after striking on an opaque object.
- For a point source, only the umbra is cast sharp dark shadow and not penumbra, because all the light of the point source will be blocked by any shadowing object.
- Whereas penumbra forms only when some of the light from the source gets blocked by the shadowing object and not all of it does.

6. Answer the following questions in your own words.
Question a.
What is meant by scattering of light?
Answer:
- Scattering of light is the deviation of light rays from its straight path.
- As light propagates through the atmosphere, it travels in a straight path until it is obstructed by bits of dust or gas molecules in the atmosphere
- The process in which light gets deflected by the particles in the medium through which the light passes is called scattering, e.g. The blue colour of the sky is due to the scattering of sunlight by the molecules of air.
Question b.
Does the shadow really vanish in the zero shadow condition?
Answer:
1. Yes, the day on which the sun reaches exactly overhead, at noon, shadow completely disappears.
‘This event can be seen in the region between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N) and Tropic of Capricorn (23.5°S).
2. The shadow diminishes and eventually disappears for a while only to reappear later.

Question c.
Will the laser beam be seen if it passes through a glass box which contains a lighted incense stick?
Answer:
Yes, it will be seen.
7. Discuss and write:
Question a.
Write a science based paragraph on ‘What if the sun did not rise’?
Answer:
- The sun is a star and the centre of our solar system. Everything in our solar system revolves around the sun.
- If the sun were to suddenly disappear, Earth and the other planets would retain their forward motion, effectively flying off into outer space in a straight line.
- If the Sun didn’t rise means the Earth’s rotation had come to a screeching halt.
- Sunrise and sunset are a result of the earth’s rotation so we will not get to see sunrise or sunset. Earth’s spinning generates the magnetic field at the core and it is saving us from harmful rays from the sun.
- Without sun it would be very dark. No sun means no plants and no animals. Of course, without sun none of us would even exist.
- Moon will disappear, because the moon dose not produce light. We only see the moon because sunlight is reflected by the moon.
- Without the sun’s warmth, Earth would quickly become a much colder place. Life would be difficult, oceans will freeze.
- Without sun rays, all photosynthesis on earth would stop. All plants would die.
- All animals that rely on plants for food, including humans would die.

Question b.
What efforts will you make to remove the misconceptions about eclipses?
Answer:
Solar, lunar eclipse have been traditionally observed as an ominous sign and therefore superstitions are prevalent in association with these natural phenomena.
1. All these misconceptions should be removed by explaining scientifically the process of eclipse how it happens: (a) Explain with the help of diagram and models of sun, moon and earth, (b) Explain how special glasses which will protect us from UV rays, and excess heat can be used to observe eclipses safely.
2. Also inform that eclipses are natural phenomena and can be predicted in advance.
Question c.
Various eclipses and the conditions during that period.
Answer:
There are two eclipses:
- Solar eclipse
- Lunar eclipse
1. Solar eclipse:
There are two types of Solar eclipse, (a) Total solar eclipse (b) Partial solar eclipse
a. Total solar eclipse: In total solar eclipse, the moon is between the sun and the earth and the moon shadow covers the sun disc fully by perfect alignment. The part of the earth that lies in the umbra of the moon experiences total solar eclipse.
b. Partial solar eclipse: In partial solar eclipse, the moon is between the sun and the earth arid the moon shadow does not cover the sun disc fully, because of imperfect alignment. The part of the earth that lies in the penumbra of the moon experiences partial solar eclipse.
c. The solar eclipse occur on a new moon day.
d. Solar eclipse last for few minutes.
2. Lunar eclipse:
There are two types of Lunar eclipse, (a) Total lunar eclipse (b) Partial lunar eclipse
a. Total lunar eclipse: In total lunar eclipse, the earth comes in between the sun and the moon and the earth’s shadow covers the moon’s surface fully because of perfect alignment.
b. Partial lunar eclipse: In partial lunar eclipse, the earth’s shadow does not cover the moon’s surface fully because of inperfect alignment. A small part of the moon’s surface is covered by umbra part of earth’s shadow.
c. The lunar eclipse occurs on a full moon night.
d. Lunar eclipse last for few hours.

8. Explain the difference:
Question a.
Point sources and Extended sources.
Answer:
| Point sources | Extended sources |
| 1. A source of radiation light that is concentrated at a point and considered as having no spatial extension. | 1. An extended source is a source consisting of many point sources separated internally. |
| 2. Shadow we get from a point source is dark called umbra. | 2. Shadow we get from extended source of light is faint called penumbra and dark called umbra |

Question b.
Umbra and Penumbra.
Answer:
| Umbra | Penumbra |
| 1. The umbra is a central core of darkness which tapers away. | 1. The penumbra is an outer cone of partial shadow which diverges, instead of tapering. |
| 2. Umbra is shadow formed from a point source of light. | 2. It is the shadow formed from the extended source of light. |
| 3. It is dark | 3. It is faint |
| 4. Umbra is the area of total shadow | 4. Penumbra is the area of partial shadow. |

Project:
Question a.
Obtain information about the special goggles used to watch a solar eclipse.
Class 7 Science Chapter 17 Effects of Light Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
During solar eclipse ………….. comes between the sun and earth.
Answer:
moon
Question 2.
A solar eclipse is seen only on a ………….. day.
Answer:
new moon day
Question 3.
During lunar eclipse ……………. comes between the sun and the moon.
Answer:
earth

Question 4.
A lunar eclipse is seen only on a ………….. night.
Answer:
full moon
Question 5.
The day on which the sun reaches exactly overhead is called the …………… .
Answer:
zero shadow day
Question 6.
As seen from the earth, when a planet or star passes behind the moon, that state is called a ………….. .
Answer:
occultation
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Sky appears blue to us.
Answer:
- Sunlight is scattered by the molecules of gases like nitrogen, oxygen in the atmosphere.
- The blue colour in the sunlight which is at shorter wavelength is scattered the most than other colours and therefore the sky appears blue.

Question 2.
Solar eclipse is either partial or total.
Answer:
- When the moon comes in between the sun and the earth and the solar disc is corripletely covered by the moon, it is called total solar eclipse.
- When the solar disc is not covered fully by the moon, it is partial solar eclipse.
Explain the difference:
Question 1.
Solar eclipse and Lunar eclipse.
Answer:
| Solar eclipse | Lunar eclipse |
| 1. When the moon comes between the sun and the earth, a shadow of the moon is cast on the earth and sun cannot be seen from the part in shadow. This is called a solar eclipse. | 1. When the earth comes between the sun and the moon a shadow of the earth is cast on the moon and a part of the moon in covered this is called the lunar eclipse. |
| 2. A solar eclipse is seen only on a new moon day. | 2. A lunar eclipse is seen only on a full moon night. |
3. A solar eclipse should never be watched with the naked eye. because ultra violate rays which are harmful to us reach the earth
|
3. A lunar eclipse can be seen with the naked eye.
|
| 4. It can be seen for a few minutes only. | 4. It can be seen over a period of a few hours. |

Explain diagrams:
Question 1.
Explain Solar eclipse with diagram.
Answer:
Solar eclipse:
- During its revolution, when the moon comes between the sun and the earth, a shadow of the moon is cast on the earth and the sun cannot be seen from the part in the shadow. This is called a solar eclipse
- A solar eclipse is seen only on a new moon day.
- The solar eclipse may be either partial or total,
- Sometimes the solar disc is completely covered by the moon. This is the total solar eclipse.
- When the solar disc is not covered fully by the moon, we have a partial solar eclipse.
- During a solar eclipse, ultra-violet rays which are harmful to us reach the earth.
- A solar eclipse should never be watched with the naked eye.
- A special type of goggles should be used for this purpose.
- Solar eclipse can be seen for a few minutes only.
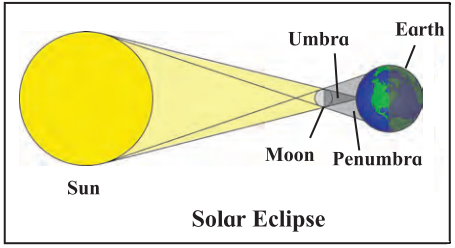

Question 2.
Explain Lunar eclipse with diagram
Answer:
Lunar eclipse:
- When the earth comes between the sun and the moon a shadow of the earth is cast on the moon and a part of the moon is covered. This is called the lunar eclipse.
- A lunar eclipse is seen only on a full moon night. If the whole moon comes in the shadow of the earth, it is a total lunar eclipse.
- When the shadow of the earth is cast only on a part of the moon, it is a partial lunar eclipse. You can watch a lunar eclipse with the naked eye.
- A lunar eclipse can be seen over a period of a few hours.
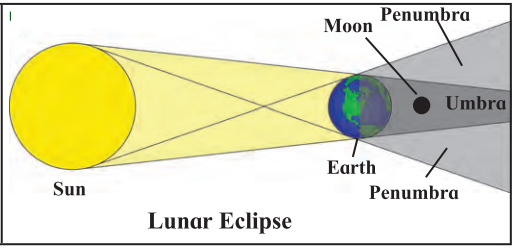

Question 3.
Write a short note on Zero Shadow Day.
Answer:
- The day on which the sun reaches exactly overhead is called zero shadow day.
- On this day, at noon, shadow completely disappears.
- This event can be seen in the region between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5°N) and at tropic of Capricon (23.5°S).
- The shadow diminishes and eventually disappears for a while only to reappear later
- This phenomenon occurs twice every year Mumbai got to witness it on May 14, 2018 last year.

Question 4.
Explain the phenomenon of scattering of light with the help of an experiment.
Answer:
- When the sun rises our surroundings appear illuminated. The entire sky appears bright.
- This happens because of the dust and other tiny particles in the air. This is the scattering of sunlight by the tiny particles of the various constituents of air.
- Had there been no atmosphere, the sky would have appeared dark during the day and of course, the sun would be directly seen.
- This has been verified by observations from the rockets and satellites which go out of the earth’s atmosphere.
Apparatus: A table lamp with a 60 or 100 W milky bulb (LED will not do), thick black paper, sticking tape, a packing needle, 100/200 ml. glass beaker, milk or milk powder, dropper, spoon, etc.
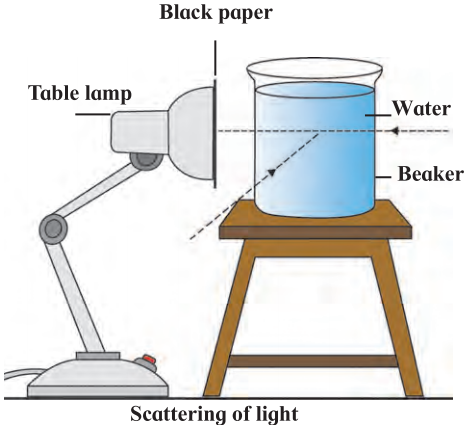
Procedure: Cover the mouth of the lampshade properly with black paper, using sticking tape. Prick a hole of 1 to 2mm diameter in the center of the paper with the help of the packing needle.
- Take clear water in the beaker. Light the bulb and place the beaker in contact with the hole.
- Observe from the front and at an angle of 90°.
- Now add 2-3 drops of milk to the water and stir. Observe again.
- A few more drops of milk may have to be added to make the water turbid.
- A blue tinge is seen when observed along the 90° angle. This is the scattered blue light.
- Because the blue light is scattered, a red-yellow light is seen from the front, and the hole appears reddish.

Question 5.
Short note on Shadow.
Answer:
- Shadow is a dark patch formed behind an opaque object when it is placed in the path of light.
- A shadow is formed only when a light source, an opaque object and a screen are present, e.g. during a lunar eclipse we see a part of the earth’s shadow on the surface of the moon.
- This happens when the earth, the sun, and the moon are in a straight line with the earth between sun and the moon.
- Here the sun acts as the light source, the earth as the opaque object and moon as the screen.
- Shadows are formed due the rectilinear propagation of light.
- The size and the shape of the shadow depend on the position and orientation of the opaque object between the source of light and the screen.
- If the distance of the object from the source is decreased, then the size of the shadow increases.
- If the object is moved away from the source, then the size of the shadow decreases.
- In older days shadows caused by objects placed in the sun were used to measure time. Such a device is called sun dial.

Use your brain power!
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Eclipses and transits which will occur recently.
Answer:
- January 6, 2019 – Partial solar eclipse
- January 21, 2019 – Total Lunar eclipse
- July 2, 2019 – Total solar eclipse
- July 16, 2019 – Partial Lunar eclipse
- December 26, 2019 – Annular solar eclipse.
Find Out:
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
If a few drops of milk are added in the experiment given the reddish colour seen from the front becomes an intense red. However, if many more drops are added the reddish colour is not seen. Why is this so?
Answer:
- As more and more milk is added, more particles of protein and fat scatter the light and the blue colour is scattered more and more than orange and red light and the beam appears blue from the sides.
- If few drops of milk are added, along with blue colour, orange and yellow also are scattered and only the intense red is seen from the front.
- But when many more drops are added, even the red colour is scattered and we do not see any colour from the front.

Question 2.
What is Occultation?
Answer:
As seen from the earth, when a planet or a star passes behind the moon, that state is called an Occultation.
Complete the Chart.
Question 1.
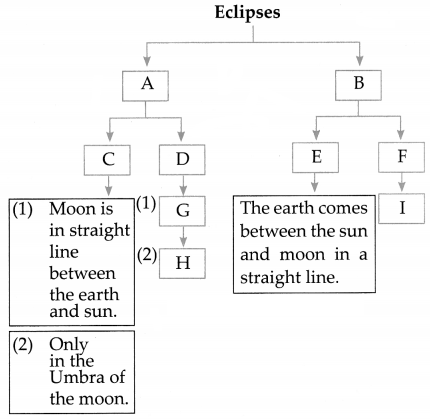
Answer:
- A – Solar B – Lunar
- C – Total Solar
- D – Partial Solar
- E – Total Lunar
- F – Partial Lunar
- G – Moon is not in a straight line between earth and sun
- H – It is in the penumbra region of the moon
- I – The earth comes in between the sun and moon and they are not in a straight line.
