Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Match the pairs and explain.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
|
(1) Growth of pollen tube towards ovules
(2) Growth of shoot system (3) Growth of root system (4) Growth towards the water |
(a) Gravitropic movement
(b) Chemotropic movement (c) Phototropic movement (d) Growth-irrelevant movement (e) Hydrotropic movement |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – a),
(4 – e).

2. Complete the paragraph.
The milk was on the stove. Rasika was engrossed in watching television. She smelled something burning. She ran towards the kitchen. The milk was boiling over. She held the vessel with her bare hands but, screaming, she let it go at once. This activity was controlled by ……………….. cells. Special ends of ……………….. in these cells collected the information, from where it was transferred to the ……………….. and then towards the terminal end of the ……………….. The chemicals produced at the terminal end passed through the minute space i.e. ………………. . In this way, ……………….. were conducted in the body and the process of ……………….. was completed by conducting the impulses from ……………….. to ………………
(Nerve, muscle cell, impulse, dendrite, synapse, axon, reflex action, cell body)
Answer:
nerve, dendrite, cell body, axon, synapse, impulses, reflex action, nerve, muscle cell.
3. Write notes on Root pressure, Transpiration, Nerve cell, Human brain, Reflex action
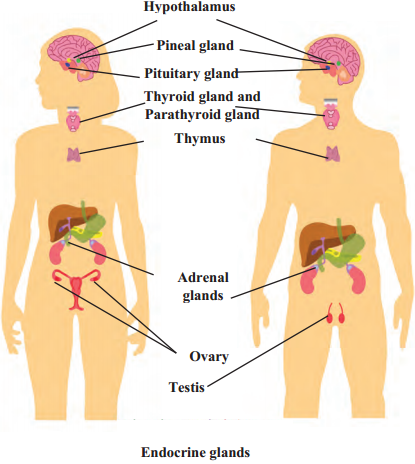
4. Name the hormones of the following endocrine glands and the function of each.
Pituitary, Thyroid, Adrenal, Thymus, Testis, Ovary.
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Question 1.
Pituitary:
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| (i) Growth hormone | Stimulates growth of bones. |
| (ii) Adrenocorticotropic hormone | Stimulates adrenal gland. |
| (iii) Thyroid-stimulating hormone | Stimulates thyroid gland. |
| (iv) Prolactin | Stimulates milk production. |
| (v) Follicle-stimulating hormone | Controls growth of gonads. |
| (vi) Luteinizing hormone | Controls menstrual cycle and ovulation. |
| (vii) Oxytocin | Contracts uterus during parturition. |
| (viii) Antidiuretic hormone | Regulates water-level in the body. |
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 2.
Thyroid
Answer:
| Hormone | Function | |
| (i) Thyroxine | Controls growth of body and metabolic activities. | |
| (ii) Calcitonin | Controls calcium metabolism and calcium level in blood. | |
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Exercise Question 3.
Adrenal
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| (i) Adrenalin and nor-adrenalin | Controls behaviour during crisis and emotional situation. |
| (ii) Corticosteroid | Maintains balance of Na + and K + and stimulates metabolism. |
9th Class Science Chapter 15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Exercise Question 4.
Thymus
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| Thymosin | Control the cells which give rise to immunity. |
Question 5.
Testis
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| Testosterone | Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characteristics like beard, mustache, hoarse voice etc. in men. |
Std 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 6.
Ovary
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| (i) Oestrogen | Stimulates growth of the endometrium. Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characteristics in women. |
| (ii) Progesterone | Prepares the endometrium for conception and maintains pregnancy. |
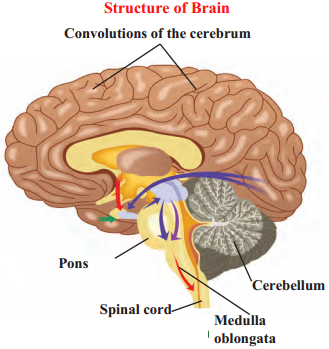
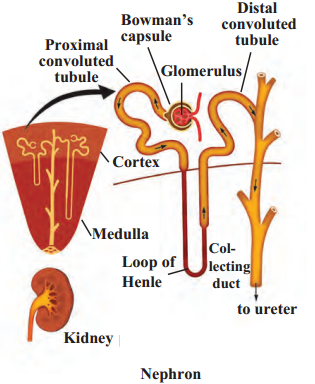
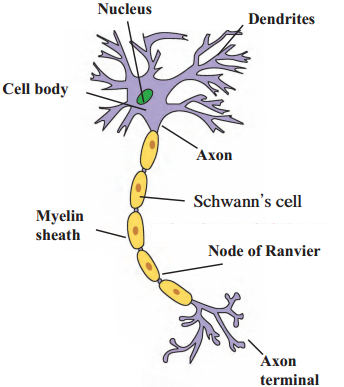
5. Draw and label the diagrams.
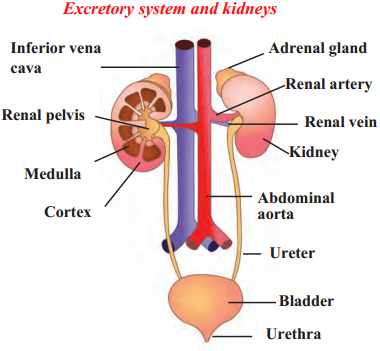
Human endocrine glands, Human brain, Nephron, Nerve cell, Human excretory system.
15. Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 1.
Human endocrine glands
Answer:
15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 2.
Human brain
Answer:
Life Processes In Living Organisms 9th Class Notes Question 3.
Nephron
Answer:
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Questions And Answers Question 4.
Nerve cell
Answer:
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Solutions Question 5.
Human excretory system
Answer:
6. Answer the following.
a. Explain chemical co-ordination in humans and give the names and functions of some hormones.
Answer:
Chemical co-ordination in humans :
- In humans chemical co-ordination is brought about with the help of certain chemical substances called hormones.
- Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands. These glands are also called ductless glands.
- These glands do not have any arrangement of their own to either store or carry their secretions. So, the hormones are directly released into the blood circulation.
- Though the endocrine glands are present at specific locations in our body, their secretions reach all parts of the body via the blood.
-
Endocrine glands along with the nervous systems are responsible for control and co-ordination in our body.
These two systems help each other to control and integrate the various activities of the body. - A marked difference between these two systems is that nerve impulses are fast but short-lived whereas the actions of hormones are very slow but long-lasting.
- It is very important that hormones are secreted only in the required quantity and there is a special mechanism which controls the quantity and timing of hormone secretion.
- For example, whenever there is an increase in blood glucose level, certain cells in the pancreas get stimulated and as a response, they release a greater quantity of insulin, thus bringing down the sugar level to normal.
| Hormone | Function |
| (1) Growth hormone | Stimulates growth of bones. |
| (2) Luteinizing hormone | Controls menstrual cycle and ovulation. |
| (3) Thyroxine | Controls growth of body and metabolic activities. |
| (4) Insulin | Stimulates liver to convert excess blood glucose to glycogen. |
| (5) Testosterone | Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characters like beard, mustache, hoarse voice, etc. in men. |
Names and functions of some hormones:
b. Explain the difference between the excretory system of humans and plants.
Answer:
| Excretory system of humans | Excretory system of plants |
| (i) In humans, the excretory system carries out the function of the removal of waste from the body. | (i) In plants, there is no special system or organ for excretion. |
| (ii) Waste substances are generally eliminated out of the body | (ii) Most of the waste substances are stored in the leaves, flowers, fruits and bark of the stem. |
| (iii) The excretory products are urea, uric acid, ammonia, etc. | (iii) The excretory products are gum, resin, latex of rubber, etc. |
c. Explain co-ordination in plants with the help of suitable examples.
Answer:
- Plants do not have systems like the nervous system or muscular system.
- In plants, movements are mainly in the form of responses given to the stimuli.
- Plants show two types of movements – growth relevant movements and growth irrelevant movements.
- Movement or growth of any part of the plant in response to an external stimulus is called tropism or tropic movement.
- Examples of growth-relevant movements are :
- The shoot system of any plant responds to the light stimulus i.e., it grows towards the source of light. This is called phototropic movement.
- The root system of plants responds to stimuli like gravitation and water. These responses are called gravitropic movement and hydrotropic movement respectively.
- Movement shown by plants in response to specific chemicals is called chemotropic movement.
- For example, the growth of the pollen tube towards the ovule.
- Some specific movements of the plants do not lead to the plant growth.
- Such movements are called growth-irrelevant movements.
- As a response to changes in the surroundings, plant hormones bring about various movements in plants.
- Examples of growth irrelevant movements are closing of leaflets of Touch-me-not (Mimosa) plant on touch.
- In the plant called Venus fly trap, when an insect visits the flower like trap, the trap closes up and the trapped insect is digested by the plant.
- The lotus flower opens during day-time while that of the tuberose opens at night.
- In plants like Touch-me-not (Mimosa), movement also occurs at places other than where it has been touched.
- Hence, we can infer that the information about the touch must have been released within the plant from one place to another.
- Plants use electrochemical impulses for transfer of information from one place to another.
- Plant cells change their shape by increasing or decreasing the water content and thereby, bring about the movements of plants.
7. Explain in your own words with suitable examples.
a. What is meant by co-ordination?
Answer:
- Several different organ systems function in multicellular organisms.
- Their life goes on smoothly if there is co-ordination between different organ systems or organs and the stimuli in the surrounding.
- Depending upon this, we can say that systematic regulation of different processes can be called control and bringing about the different processes in the proper sequence is called co-ordination.
- If any activity in the body is to be completed successfully, proper co-ordination between different systems, and organs participating at different steps of that activity is necessary.
- If due to lack of co-ordination, there is confusion at any step, the activity may not get completed. There should be no randomness at any step.
- There should be proper co-ordination between internal activities of the body resulting from various factors like body temperature, water- level, enzyme-level, etc. or stimuli arising in the surrounding environment.
- Proper co-ordination between various systems of an organism helps to maintain a state of equilibrium called homeostasis which is necessary for the optimal efficiency of the body.
b. How does excretion occur in human beings?
Answer:
- Removal of wastes from the body is very important and it is the excretory system that carries out this function.
- The human excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, the urinary bladder and the urethra. Urine is formed by the kidneys by separating the waste and unwanted excess substances from the blood.
- The functional unit of the kidney that performs the basic function of filtration is called a nephron. The urea produced in the liver comes into the blood.
- When the urea-containing blood comes into the glomerulus, it is filtered through capillaries and urea and other similar substances are separated from it.
- Water molecules and small molecules of some other substances can cross the semipermeable membrane of Bowman’s capsule.
- The solution accumulated in the cavity of Bowman’s capsule passes into the tubular part of the nephron. Here, molecules of water and some other useful substances are reabsorbed into the blood.
- Urine is formed from the remaining solution which is full of waste materials. The urine is carried by the ureters and stored in the urinary bladder. Afterwards, urine is given out through the urethra.
c. How is excretion in plants useful to human beings?
Answer:
- Plants give out oxygen during photosynthesis by diffusion which is useful to human beings for respiration.
- Some waste materials of plants for example, gum, resin, latex of rubber, etc. are useful to humans.
d. Describe the transportation system in plants.
Answer:
- Plants have two types of conducting tissues i.e., xylem which conducts water and phloem which conducts food.
- During transpiration, water is released into the atmosphere.
- As a result, water level is the epidermal layer of the leaf decreases.
- Water is brought up to the leaves through the xylem so as to compensate for the lost water.
- Transpiration helps in absorption of water and minerals and distribution to all parts of the plant whereas root pressure preforms the important role of pushing the water up at night time.
- The food produced by leaves is transported to each cell of the plant through phloem.
- When the food material like sucrose is transported towards a part of the plant through phloem, using ATP, the water concentration in that part decreases.
- As a result, water enters the cell by diffusion. The pressure on the cell wall increases due to increase in the cellular contents.
- Due to the increased pressure, food is pushed into the neighboring cells where the pressure is low.
- This process helps the phloem to transport the materials as per the need of the plant.
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms Intext Questions and Answers
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Exercise Question 1.
How do the digestive system and respiratory system work?
Answer:
(a) Digestive system:
- The digestive system is responsible for digestion of food. i.e. breaking down complex insoluble food into simpler soluble form.
- The digestive system is made up of alimentary canal and digestive glands.
- The alimentary canal is a long and muscular tube of varying diameter which extends from the mouth to the anus.
- The digestive glands associated with alimentary canal are salivary glands, gastric glands, liver and pancreas.
- The process of digestion includes various stages wherein the food passes through the different organs of the alimentary canal and there it is digested part by part with the help of various enzymes secreted from the digestive glands.
- After the food is digested, the important nutrients are absorbed into the blood and the undigested food and residue of digested food is removed out of the body through the anus.
(b) Respiratory system:
- Respiration is the process of release of energy from the assimilated food.
- The respiratory system consists of nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs (alveoli).
- Oxygen enters our body through breathing.
- This oxygen is taken to the cells and with the help of oxygen, food is oxidized into the cells to release energy in the form of ATR
- During this process, carbon dioxide and water vapour are given out as by-products which are given out during breathing.
Thus, the digestive and respiratory systems work in co-ordination with each other to produce energy from food.
Life Processes In Living Organisms Exercise Question 2.
Previously you have performed the activity of observing a branch covered in a plastic bag. What did you observe in that activity?
Answer:
- When a branch is covered in a plastic bag, we observe that small droplets of water accumulate on the inner side of the plastic bag.
- This shows that leaves release water in the form of vapour through the stomata during transpiration. These vapours get condensed to form water droplets and accumulate inside the bag.
Life Process In Living Organism Exercise Question 3.
Which are the sensory organs of an organism? What is their function?
Answer:
- Sensory organs of an organism are eyes, ears, tongue, skin and nose.
- The eyes help the organism to perceive the sensation of light to see the objects around it.
- The ears help the organism to perceive the sensation of sound and also perceive the sensation of pressure.
- The tongue helps to perceive different tastes and also in chewing the food.
- The skin helps to perceive the sensation of touch, pain, pressure etc.
- Some insects also possess antennae for sensing the changes in the environment.
15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Question 4.
Where are the gustatory and olfactory nerves to be found?
Answer:
- Gustatory nerves are concerned with sense of taste whereas olfactory nerves are concerned with the sense of smell.
- Gustatory nerves are found in the tongue from where they carry impulses to the gustatory cortex in the brain.
- Whereas the olfactory nerves are found in the nasal passage from where they carry impulses to the olfactory lobes in the brain.
Answer the following questions:
15.Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 1.
Why do we eat fruits and vegetables? Do the plants also need minerals like we do?
Answer:
- We eat fruits and vegetables to get nutrients like carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and fibers. These nutrients are important for the proper functioning of the body .
- Plants too need minerals for their growth and development.
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Notes Question 2.
From where do plants get inorganic substances other than carbon dioxide and oxygen?
Answer:
Plants get inorganic substances like nitrogen, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, sodium etc. from the soil. Soil is the nearest and richest source of these elements.
9th Std Science Chapter 15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 3.
At least a small quantity of garbage or waste is produced every day in each house. What will happen if you keep this garbage for many days in your house?
Answer:
- If we keep garbage for many days in our house, it will start decaying due to the growth of decomposers like fungi and bacteria.
- This will result in foul odour and will also lead to spread of diseases.
Life Processes In Living Organisms Exercise Class 9 Question 4.
Sometimes, while eating we bite our own finger or tongue by mistake.
Answer:
- Sometimes, while eating we over-fill our mouth causing the bite to misalign, thus we bite our own finger or tongue by mistake.
- If we are dehydrated, the muscles of the mouth and tongue do not function properly causing us to bite our own tongue.
- If we are distracted with other activities while eating, it can cause us to bite our tongue or finger.
- Thus, due to lack of co-ordination sometimes while eating, we bite our own finger or tongue by mistake.
9th Class Science 15 Chapter Life Processes In Living Organisms Question 5.
Sometimes, we choke while eating in a hurry.
Answer:
- There is an elastic flap at the starting of the wind-pipe called epiglottis which opens whenever we breathe in air and closes to prevent the entry of food into the respiratory system.
- While eating in hurry, due to lack of co-ordination, the epiglottis opens to take in air but food too enters in causing us to choke.
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Extra Questions Question 6.
An injury to the medulla oblongata can lead to death. Why?
Answer:
- The medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities like the beating of the heart, blood circulation, breathing etc.
- An injury to the medulla oblongata will stop these activities, leading to death.
Life Processes In Living Organisms Class 9 Maharashtra Board Question 7.
You may have seen how a drunken person struggles to maintain his body balance. An excess of alcohol in the body causes one to lose control over it. Why does this happen? Find out the reason with help of the internet.
Answer:
- The cerebellum co-ordinates voluntary movements and maintains balance of the body.
- An excess of alcohol causes dysfunctioning of the cerebellum.
- It results in primary loss of co-ordinated movements and loss of balance.
9th Life Processes In Living Organisms 5 Question 8.
Why does this happen?
(a) Leaves of plants fall off in a particular season.
Answer:
- Plants lose water through their leaves by transpiration. So some plants shed their leaves in dry season to reduce transpiration and conserve water.
- In plants, the waste substances are stored in the vacuoles of leaf-cells which are then shed along with the leaves in a specific season.
(b) Fruits, flowers fall off after a certain period of time.
Answer:
- In plants, waste substances are stored in the vacuoles of fruits and flowers. So, they fall off after some time to excrete these wastes.
- Also, when fruits and flowers mature, the supply of nutrients to mature fruits and flowers is blocked. This causes abscission in that part of the plant leading to their detachment from the plant body and falling off.
(c) Substances like resin, gum, etc. are given out of the plant body.
Answer:
- Resin, gum etc. are the waste products of plants. They are given out after some time as a process of excretion in plants.
- Many plants, particularly, woody plants produce resin and gum in response to injury. These resin and gum act as bandage protecting the plants from invading insects and pathogens.
15 Life Processes In Living Organisms Exercise Question 9.
Which waste products are produced in our body through metabolic activities?
Answer:
The waste products formed in our body through metabolic activities are urea, uric acid, ammonia, carbon dioxide etc.
Life Processes In Living Organisms 9th Class Exercise Question 10.
As compared to the monsoons and winter a very small quantity of urine is produced in the summer season. Why is it so?
Answer:
In summer, we sweat more due to excess heat. So, the body tries to conserve water by reducing urine formation. This is to prevent dehydration.
Question 11.
In adults, the process of urination is under their control but not in infants. Why is it so?
Answer:
- In adults, the muscles of the bladder are under the voluntary control. So the process of urination is under control.
- In infants, the bladder muscles are not mature until about two years of age. So, the process of urination is not under control.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
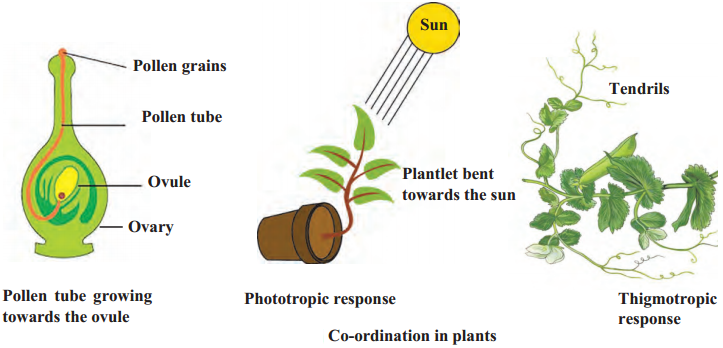
Observe the following figures carefully.
Answer:
Observations:
- Figure ‘A’ shows chemotropic movement. Pollen tube grows towards the ovule in response to specific chemicals released by the ovule.
- Figure ‘B’ shows phototropic movement. Shoot grows towards the Sun in response to stimulus of light.
- Figure ‘C’ shows thigmotropic movement. Tendrils of climbers are sensitive to touth. When they come in contact with an object, they entwine around the object and cling to it.
- All the above movements are related to growth. Hence, they are called growth relevant movements.
Question 2.
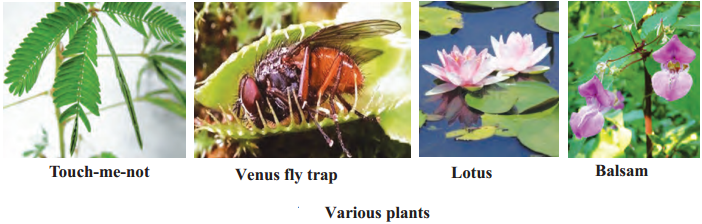
Observe the pictures carefully and think about them.
Answer:
- Figure ‘A’ shows touch-me-not (Mimosa) plant. In this plant, the leaflets close in response to stimulus of touch.
- Figure ‘B’ shows Venus fly trap. In this plant, there is a trap that appears and smells like a flower and deceives the insect. When an insect visits that flower-like trap, the trap closes up and the trapped insect is digested by the plant,
- Figure ‘C’ shows lotus plant. The lotus flower opens during day-time.?
- Figure ‘D’ shows Balsam plant. In this plant, the ripened fruit dehisces (bursts open) at the right time to disperse the seeds.
Question 3.
As you watch the match being played on your school ground, you will see the control and co-ordination among the movements of the players. Make a list of all such different actions.
Answer:
In an inter-house basketball match, control and co-ordination is seen in dodging the ball, jumping, running, passing it to the team mates and dribbling the ball.
Question 4.
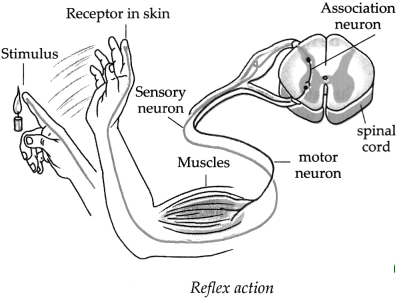
Observe the figure carefully and as per the numbers in that figure, answer the following questions.
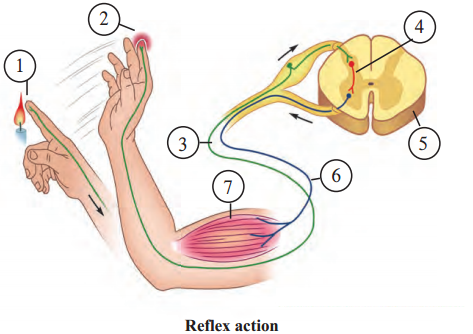
(a) What is happening at 1 and 2?
Answer:
At 1 stimulus of heat is received by thermo-receptors in the skin. At 2, the hand is withdrawn instantly.
(b) Which nerve carried the impulse to the point marked 3? In which direction is it conducting the impulse?
Answer:
Sensory nerve carried the impulse to the point marked 3. The impulse is conducted from the skin towards the spinal cord.
(c) Which is the nerve shown by 4?
Answer:
The nerve shown by 4 is association neuron. It is present in the gray matter of the spinal cord. It receives the sensory impulse, interprets it and generates impulse.
(d) Which is the organ marked as 5?
Answer:
Spinal cord.
(e) At 6, which nerve is conducting the response impulse?
Answer:
Motor nerve.
(f) At 7, where has the impulse reached? What is its effect?
Answer:
At 7, the impulse has reached the muscles of the hand. As a result, the muscles contract and the hand is withdrawn instantly in response to the stimulus of heat.
Question 5.
Sketch and label:
Answer:
- Stimulus
- Hand is withdrawn
- Sensory neuron
- Association neuron
- Spinal cord
- Motor neuron
- Muscles
(6) Observe the figure and list down functions for ‘A’ and ‘B’
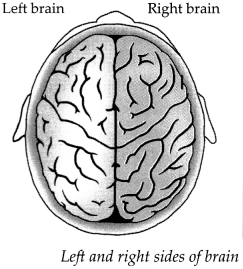
Answer:
| Functions of Left Brain | Functions of right brain |
| (i) Analytical thinking | Holistic thinking |
| (ii) Logical thinking | Intuition |
| (iii) Language | Creativity |
| (iv) Science and Mathematics | Art and music |
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Take a small plant like balsam or tuberose with its roots intact. Wash and clean its roots. As shown in the fig, keep it in the water containing a stain like safranin or eosin. Observe the stem and the veins of the leaves after 2-3 hours.
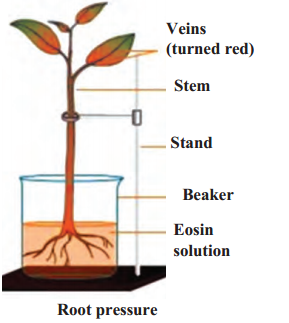
Answer:
- The stem and veins of the leaves appear pinkish in colour.
- Due to the root pressure generated, eosin solution is continuously pushed upward.
- As a result water reaches xylem and the water column is pushed forward.
Question 2.
Take a transverse section of the stem of a plant and observe the stained xylem under a compound microscope.
Answer:
The xylem elements appear pinkish as the eosin solution is conducted upwards through the xylem. From this we infer that the xylem is responsible for the conduction of water and minerals in the plant.
Question 3.
Observe your mother while she cuts the elephant’s foot (Amorphophallus) or arum leaves. Your hands may also begin to itch if you try to cut these leaves. Why does this happen? Try to find out. Ask your mother what she does to prevent the itching.
Answer:
- In some plants like elephant foot (Amorphophallus) or arum, waste materials are in the form of crystals of calcium oxalate. They are called raphides.
- As they are needle-shaped, they prickle and cause irritation of the skin leading to itching.
- This can be prevented by applying tartaric acid (tamarind) or citric acid (lemon) on the hands while cutting these vegetables as the acids dissolve the crystals of calcium oxalate.
Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Life Processes in Living Organisms Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose and write the correct options.
Question 1.
The transport of food produced in leaves to each cell in the plant body is called …………………………… .
(a) Transpiration
(b) Root pressure
(c) Translocation
(d) Ascent of sap
Answer:
(c) translocation
Question 2.
Kidneys filter blood about ……………………………. times every day.
(a) 100
(b) 200
(c) 300
(d) 400
Answer:
(d) 400
Question 3.
About ……………………………. of blood is sent through the dialysis machine at one time.
(a) 500 ml
(b) 5 l
(c) 200 ml
(d) 400 ml
Answer:
(a) 500 ml
Question 4.
The movement of plant towards the source of light is called ……………………………. movement.
(a) chemotropic
(b) hydrotropic
(c) phototropic
(d) gravitropic
Answer:
(c) phototropic
Question 5.
The movement of root system towards stimulus of gravity is called ……………………………. movement.
(a) phototropic
(b) gravitropic
(c) hydrotropic
(d) chemotropic
Answer:
(b) gravitropic
Question 6.
The movement of root system towards stimulus of water is called ……………………………. movement.
(a) Phototropic
(b) Gravitropic
(c) Hydrotropic
(d) Chemiotropic
Answer:
(c) hydrotropic
Question 7.
Hormone ……………………………. helps in stem elongation.
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Abscisic acid
Answer:
(b) Gibberellin
Question 8.
Hormone ……………………………. helps in cell division.
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Abscisic acid
Answer:
(c) Cytokinin
Question 9.
The hormone ……………………………. is effective in prevention and retardation of growth, leaf wilting, etc.
(a) Auxin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Gibberellin
(d) Abscisic acid
Answer:
(d) Abscisic acid
Question 10.
……………………………. neurons conduct impulses from the sensory organs to the brain and the spinal cord,
(a) Sensory
(b) Motor
(c) Association
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Sensory
Question 11.
The brain of an adult human weighs about …………………………… .
(a) 500 – 600 grams
(b) 2 – 3 kilograms
(c) 1300 -1400 grams
(d) 1500 -1600 grams
Answer:
(c) 1300 – 1400 grams
Question 12.
……………………………. is the largest part of the brain.
(a) Cerebrum
(b) Cerebellum
(c) Medulla oblongata
(d) Spinal cord
Answer:
(a) Cerebrum
Question 13.
There are two triangular swollen structure called ……………………………. on the upper side of the medulla oblongata.
(a) Ventricles
(b) Meninges
(c) Pyramids
(d) Pons
Answer:
(c) Pyramids
Question 14.
Control of voluntary movements is done by …………………………… .
(a) Cerebrum
(b) Cerebellum
(c) Medulla oblongala
(d) Spinal cord
Answer:
(a) Cerebrum
Question 15.
Co-ordination of voluntary movements is done by …………………………… .
(a) cerebrum
(b) cerebellum
(c) medulla oblongata
(d) spinal cord
Answer:
(b) cerebellum
Question 16.
Control of involuntary activities like the beating of the heart, blood circulation, breathing etc. are controlled by …………………………… .
(a) Spinal cord
(b) Cerebrum
(c) Cerebellum
(d) Medulla oblongata
Answer:
(d) Medulla oblongata
Question 17.
The function of cerebrum is to …………………………… .
(a) control of voluntary movements
(b) co-ordination of voluntary movements
(c) control of involuntary activities
(d) maintaining the body balance
Answer:
(a) control of voluntary movements
Question 18.
The function of cerebellum is …………………………… .
(a) to control of voluntary movements
(b) to maintain the body balance
(c) to control of involuntary activities
(d) to co-ordinate of voluntary movements
Answer:
(b) to maintain the body balance
Question 19.
Hormone ……………………………. stimulates the liver to convert excess blood glucose into glycogen.
(a) Glucagon
(b) insulin
(c) Somatostatin
(d) Pancreatic polypeptide
Answer:
(a) Glucagon
Question 20.
Hormone ……………………………. controls behaviour during crisis and emotional situation.
(a) Thyroxine
(b) Parathormone
(c) Adrenalin and Nor adrenalin
(d) Somatostatin
Answer:
(c) Adrenalin and Nor adrenalin
Question 21.
……………………………. controls menstrual cycle and ovulation.
(a) Prolactin
(b) Oxytocin
(c) Luteinizing hormone
(d) Progesterone
Answer:
(c) Luteinizing hormone
Question 22.
……………………………. stimulates growth of secondary sexual characteristics in men.
(a) Thymosin
(b) Testosterone
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Thyroxine
Answer:
(b) Testosterone
Question 23.
……………………………. occurs through stomata.
(a) Translocation
(b) Perspiration
(c) Transpiration
(d) Conduction
Answer:
(c) Transpiration
Question 24.
……………………………. performs the important role of pushing the water up during the night time.
(a) Translocation
(b) Root pressure
(c) Transpiration pull
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Root pressure
Question 25.
In plants, gaseous substances are given out by …………………………….
(a) Root pressure
(b) Osmosis
(c) Diffusion
(d) Translocation
Answer:
(c) diffusion
Question 26.
Each kidney has approximately ……………………………. nephrons.
(a) 1 lakh
(b) 10,000
(c) 10 lakh
(d) 50 lakh
Answer:
(c) 10 lakh
Question 27.
Insulin is secreted by the ……………………………. of the pancreas.
(a) Alpha cells
(b) Beta cells
(c) Delta cells
(d) F cells
Answer:
(b) Beta cells
Select the odd man out:
Question 1.
Skin, Brain, Kidneys, Lungs.
Answer:
Brain – It is a controlling organ whereas the others are excretory orgAnswer:
Question 2.
Gum, Resin, Urea, Latex
Answer:
Urea – It is an excretory product of animals whereas the others are excretory products of plants.
Question 3.
Gibberellin, Auxin, Thyroxine, Cytokinin.
Answer:
Thyroxine – It is a hormone in animals whereas the others are hormones in plants.
Question 4.
Dendrite, Cell body, Axon, Synapse.
Answer:
Synapse – It is a minute space between two adjacent neurons whereas the others are parts of the neuron.
Question 5.
Thyroxine, Calcitonin, Insulin, Auxin.
Answer:
Auxin – It is a plant hormone whereas the others are hormones in human beings.
Complete the Analogy:
(1) Water : Xylem :: Food : …………………………….
(2) Movement of root system : Gravitropic :: Movement of shoot system : …………………………….
(3) Brain: Cranial Cavity :: Spinal Cord : …………………………….
(4) Cavities of the brain : Ventricles :: Cavities of the spinal cord : …………………………….
(5) Involuntary activities : Medulla oblongata : : Balance of the body : …………………………….
(6) Stem elongation: Gibberellin :: Cell division : …………………………….
(7) Control of voluntary movements : Cerebrum :: Co-ordination of voluntary movements : …………………………….
(8) Converts glucose to glycogen : Insulin :: Converts glycogen to glucose : …………………………….
(9) Secondary sexual characters in males : Testosterone :: Secondary sexual characters in females : …………………………….
Answer:
(1) Phloem
(2) Phototropic
(3) Vertebral column
(4) Central canal
(5) Cerebellum
(6) Cytokinin
(7) Cerebellum
(8) Glucagon
(9) Oestrogen
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
|
(1) Gibberellins
(2) Cytokinins (3) Abscisic acid (4) Auxin |
(a) Enlargement of cells
(b) Helps in stem elogation (c) Cell division (d) Wilting of leaf |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – d),
(4 – a).
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
|
(1) Cerebrum
(2) Cerebelleum (3) Medulla oblongata (4) Spinal cord |
(a) Control of involuntary activities
(b) Decision – making, memory and intellectual activities. (c) Centre for coordination of reflex actions (d) Maintaining body’s balance |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – d),
(3 – a),
(4 – c).
State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements.
Question 1.
Plants need less energy as compared to animals.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Xylem conducts food whereas phloem conducts water.
Answer:
False. Xylem conducts water whereas phloem conducts food.
Question 3.
The loss of water from the plants is known as translocation.
Answer:
False. The loss of water from the plants is known as transpiration.
Question 4.
Calcium oxalate crystals present in some plants are called resins.
Answer:
False. Calcium oxalate crystals present in some plants are called raphides.
Question 5.
Root pressure helps to push the water up in plants during night time.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
Translocation is carried out by phloem in downward direction.
Answer:
False. Translocation is carried out by phloem in both upward and downward direction.
Question 7.
In unicellular organisms, waste materials are directly eliminated across the cell surface.
Answer:
True
Question 8.
Urea is produced in the liver.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
Systematic regulation of different processes is called co-ordination.
Answer:
False. Systematic regulation of different processes is called control.
Question 10.
A hormone auxin produced in the apical part of the shoot helps in enlargement of cells.
Answer:
True
Question 11.
Gibberellin helps in prevention and retardation of growth, leaf wilting etc.
Answer:
False. Abscisic acid helps in prevention and retardation of growth, leaf wilting etc.
Question 12.
The movement shown by venus fly trap while trapping an insect is a growth relevant movement.
Answer:
False. The movement shown by venus fly trap while trapping an insect is a growth irrelevant movement.
Question 13.
The lotus flower opens during night time while that of tuberose (polyanthus) opens during day time.
Answer:
False. The lotus flower opens during day time while that of tuberose (polyanthus) opens during night time.
Question 14.
Sensory neurons conduct impulses from the brain and the spinal cord to effector organs like muscles or glands.
Answer:
False. Sensory neurons conduct impulses from the sensory organs to the brain and the spinal cord.
Question 15.
There are 31 pairs of cranial nerves.
Answer:
False. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
Question 16.
Activities like heart beat, blood circulation, breathing, sneezing, etc. are controlled by cerebellum.
Answer:
False. Activities like heart beat, blood circulation, breathing, sneezing, etc. are controlled by cerebellum.
Question 17.
Spinal nerves are associated with head, thorax and abdomen.
Answer:
False. Spinal nerves are associated with arms, legs, skin and some other parts of the body.
Question 18.
Nerve impulses are slow and long lasting whereas action of hormones is fast and short lived.
Answer:
False. Nerve impulses are fast and short lived whereas action of hormones is slow and long lasting.
Question 19.
Reflex actions are controlled by cerebellum.
Answer:
False. Reflex actions are controlled by spinal cord.
Question 20.
Thyroid stimulating hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland.
Answer:
True
Question 21.
The hormone thymosin is secreted by the thyroid gland.
Answer:
False. The hormone thymosin is secreted by the thymus gland.
Question 22.
Parathormone controls metabolism of calcium and phosphorns.
Answer:
True
Question 23.
The right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney.
Answer:
True
Name the following:
Question 1.
The structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Answer:
Newtron.
Question 2.
The network of capillaries in the Bowman’s capsule.
Answer:
Glomerulus.
Question 3.
The minute space between two adjacent nervous.
Answer:
Synapse.
Question 4.
The special cells which bring about control and co-ordination.
Answer:
Neurons.
Question 5.
The cavities present in various parts of the brain.
Answer:
Ventricles.
Question 6.
The long tubular cavity of the spinal cord.
Answer:
Central Canal.
Question 7.
The thread like fibrous structure at the end of the spinal cord.
Answer:
Filum terminale.
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
It is necessary to remove harmful and waste substances from the body.
Answer:
- Many harmful and waste substances like urea, uric acid, ammonia, etc. are produced in living organisms.
- If these substances accumulate in the body or are retained in the body for long, it can lead to serious harm or even death.
- Hence, it is necessary to remove such harmful and waste substances from the body.
Question 2.
In plants like Touch-me-not (Mimosa), movement also occurs at the places other than where it has been touched.
Answer:
- In plants like Touch-me-not (Mimosa), the information about the touch is relayed within the plant from one place to another.
- Plants use electro-chemical impulses for transfer of information from one place to another.
- Plant cells change their shape by increasing or decreasing their water content and thereby, bring about the movements of plants.
- Hence, in plants like Touch-me-not (Mimosa) movement also occurs at the places other than where it has been touched.
Question 3.
Endocrine glands are also called ductless glands.
Answer:
- Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands.
- These glands do not have any arrangement of their own to store or carry their secretions.
- Hence, as soon as hormones are produced, they are directly released into the blood circulation.
- Thus, though these endocrine glands are present at specific locations in our body, their secretions reach all parts of the body via blood.
- Therefore, endocrine glands are also called ductless glands.
Define the following:
Question 1.
Transportation
Answer:
The process by which a substance either synthesized or absorbed in one part of the body reaches another is called as transportation.
Question 2.
Control
Answer:
Systematic regulation of different processes is called as control.
Question 3.
Coordination
Answer:
Bringing about the different processes in the proper sequence is called as co-ordination.
Question 4.
Tropism or Tropic movement
Answer:
Movement or growth of any part of the plant in response to an external stimulus is called as tropism or tropic movement.
Question 5.
Excretion
Answer:
Removal of waste or harmful substances from the body is called excretion.
Question 6.
Dialysis
Answer:
The process of separating the nitrogenous waste from the blood with the help of a man?made machine is called dialysis.
Question 7.
Reflex action
Answer:
An immediate and involuntary response given to a stimulus from the environment is called a reflex action.
Question 8.
Homeostasis
Answer:
Proper co-ordination between various systems of an organism helps to maintain a state of equilibrium called homeostasis.
Question 9.
Tropism
Answer:
Movement or growth of any part of the plant in response to an external stimulus is called tropism.
Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Nervous control and Chemical control
Answer:
| Nervous Control | Chemical Control |
| (i) Nervous control is brought about by special types of cells called neurons. | (i) Chemical control is brought about by chemical substances called hormones. |
| (ii) It involves the nervous system i.e., brain, spinal cord and nerves. | (ii) It involves the endocrine glands. |
| (iii) Nerve impulses are fast and short-lived. | (iii) Actions of hormones are very slow and long-lasting. |
Question 2.
Growth relevant movements and growth irrelevant movements
Answer:
| Growth relevant movements | Growth irrelevant movements |
| (i) Growth relevant movements result in growth of the plants. | (i) Growth irrelevant movements do not result in growth of the plants. |
| (ii) They are also called as tropic movements. | (ii) They are also called as nastic movements. |
| (iii) They are in response to stimulus of light, water, gravity, chemicals, etc. | (iii) They are generally in response to stimulus of touch. |
| (iv) Examples : Bending of stem towards light, movement of roots towards gravity and water, etc. | (iv) Example : Closing of leaflets of Mimosa plant, closing of Venus fly trap, etc. |
Question 3.
Cerebrum and Cerebellum
Answer:
| Cerebrum | Cerebellum |
| (i) It is the largest part of the brain. | (i) It is the smaller part of the brain. |
| (ii) It occupies two thirds of the brain. | (ii) It is situated below the cerebrum at the back of the cranial cavity. |
| (iii) Its surface has deep, irregular ridges and grooves which are called convolutions. | (iii) Its surface shows shallow grooves instead of convolutions. |
| (iv) It controls voluntary movements, concentration, planning, decision-making, memory, intelligence and intellectual activities. | (iv) It co-ordinates voluntary movements and maintains the body’s balance. |
Write short notes:
Question 1.
Root Pressure
Answer:
- Root cells are in contact with water and minerals in the soil.
- Water and minerals enter the cells of the root surface due to difference in concentration. As a result, these cells become turgid.
- This is called root pressure.
- Under the effect of this pressure, water and minerals reach the xylem of the roots and to reduce this difference in concentration, they are continuously pushed forward.
- As a result of this continuous movement, a water column is formed, which is continuously pushed ahead.
- This pressure, is sufficient to lift the water up in shrubs, small plants and small trees.
Question 2.
Transpiration
Answer:
- Plants give out water in the form of water vapour through the stomata on their leaves. This is known as transpiration.
- Two cells called guard cells are present around the stomata. They control the opening and closing of stomata.
- Water is released into the atmosphere by leaves through the process of evaporation.
- As a result, water in the epidermal layer of the leaf decreases.
- Water is brought up to the leaves through the xylem to compensate for the lost water.
- Transpiration helps in absorption of water and minerals and distribution to all parts of the plant.
Question 3.
Nerve cell
Answer:
- Nerve cells also called as neurons are special types of cells which conduct impulses from one place to another in the body.
- Neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system.
- Nerve cells, the largest cell in the human body, may measure upto a few metres in length.
- Nerve cells have the ability to generate and conduct electrochemical impulse.
- The cells that support the nerve cells and help in their functioning are called neuroglia. Nerve cells and neuroglial cells together form nerves.
Question 4.
Reflex action
Answer:
- An immediate and involuntary response given to a stimulus from the environment is called a reflex action.
- Sometimes we react to an incident without any thinking on our part or control over the reaction.
- This is a response given to a certain stimulus from the surroundings.
- In such situations, proper control and co-ordination is achieved even without the intervention of the brain.
- For example, when our hand touches a hot object, the receptor in the skin detects the stimulus.
- The sensory neuron sends the impulse to the relay neuron in the spinal cord.
- The impulses are then sent to motor neurons which cause the muscles of the hand to contract and move away from the hot object.
- The spinal cord is the center of co-ordination for reflex actions.
Question 5.
Spinal cord
Answer:
- The spinal cord is the part of the central nervous system and it is held within the vertebral column.
- It is slightly thick but gradually tapers towards the end.
- There is a thread like fibrous structure at its end. It is called the filum terminale.
- The long tubular cavity of the spinal cord is called the central canal. It is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
- The spinal cord conducts impulses from the skin towards the brain and from the brain to the muscles and glands.
- It functions as a centre of co-ordination of reflex actions.
Question 6.
Dialysis
Answer:
- The efficiency of kidneys can be adversely affected by injury, infection or decreased blood supply.
- If this happens, excess of toxic substances accumulates in the body and it can lead to death.
- If kidneys fail, nitrogenous wastes are separated from the blood with the help of a man-made machine.
- The process of separating the nitrogenous waste from the blood with the help of this machine is called dialysis.
- About 500 ml of blood is sent at one time through this machine. Purified blood is reinfused into the body of the patient.
Draw neat and labelled diagrams:
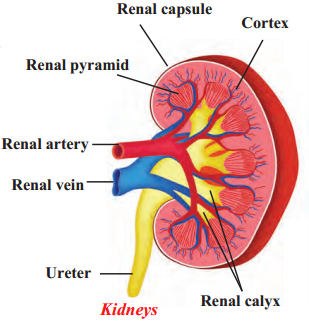
Question 1.
Vertical Section of Kidney
Answer:
Question 2.
Reflex action
Answer:
Name the hormones of the following endocrine glands and the function of each:
Question 1.
Parathyroid
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| Parathormone | Controls metabolism of calcium and phosphorus |
Question 2.
Pancreas
Answer:
| Hormone | Function |
| (i) Glucagon | Stimulates liver to convert glycogen into glucose. |
| (ii) Insulin | Stimulates liver to convert excess blood glucose into glycogen. |
| (iii) Somatostatin | Controls levels of insulin and glucagon. |
| (iv) Pancreatic Polypeptide | Controls movement of intestine and thereby glucose absorption. Controls secretion of pancreatic juice. |
Complete the following table of plant hormones with their functions:
Answer:
| Plant hormone | Functions |
| (i) Auxin |
Produced in the apical part of the shoot
Helps in enlargement of cells |
| (ii) Gibberellins | Help in stem elongation |
| (iii) Cytokinins | Help in cell division |
| (iv) Abscisic acid | Effective in prevention and retardation of growth, leaf wilting, etc. |
State the functions of different parts of the brain.
Answer:
| Parts of the Brain | Functions |
| Cerebrum | Control of voluntary movements, concentration, planning, decisionmaking, memory, intelligence, and intellectual activities. |
| Cerebellum |
(i) Co-ordination of voluntary movements.
(ii) Maintaining the body’s balance. |
| Medulla oblongata | Control of involuntary activities like the beating of the heart, blood circulation, breathing, sneezing, coughing, salivation, etc. |
| Spinal cord |
(i) Conduction of impulses from the skin towards the brain.
(ii) Conduction of impulses from brain to muscles and glands. (iii) Functions as centre of coordination of reflex actions. |
Answer the following:
Question 1.
How do plants bring about movements in them?
Answer:
- Plants use electro-chemical impulses for transfer of information from one place to another.
- Plant cells change their shape by increasing or decreasing their water content and thereby bring about the movement of plants.
Answer the following:
Question 1.
What are growth-irrelevant movements? Give examples.
Answer:
- Some specific movements of the plants do not lead to the plant growth. Such movements are called growth-irrelevant movements.
- In the plant called venus fly trap, there is a trap that appears and smells like flowers and deceives insects. When an insect visits the flower-like trap, the trap closes up and the trapped insect is digested by the plant.
- Fibrils present on the leaves of the insectivorous plant Drosera, bend inward as soon as an insect lands on the leaves and surround the insects from all sides.
- In Balsam, the ripened fruit dehisces (bursts-open) at the right time to disperse the seeds.
Question 2.
Which are the different types of nerve cells or neurons?
OR
How are nerve cells classified according to their functions?
Answer:
According to their functions, nerve cells are classified into three types:
- Sensory neurons: They conduct impulses from the sensory organs to the brain and the spinal cord.
- Motor neurons : They conduct impulses from the brain or spinal cord to effector organs like muscles or glands.
- Association neurons : Association neurons perform the function of integration in the nervous system.
Question 3.
What are the different parts of the human nervous system?
Answer:
The human nervous system can be divided into the following three parts.
- Central nervous system (CNS) : It consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It controls and regulates all activities of the body.
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS) : The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves originating from the central nervous system which connect the central nervous system with all parts of the body. They are of two types cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
- Autonomic nervous system (ANS) : The autonomous nervous system consists of the nerves of involuntary organs like the heart, lungs, stomach etc. It is not under the control of our will.
Question 4.
Describe the structure of the central nervous system.
Answer:
- The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal card.
- The organization of the brain is extremely delicate and highly evolved.
- The brain is the main controlling part of the nervous system and is safely located in the cranial cavity. The spinal cord is protected by the vertebral column.
- In the space between the delicate central nervous system and its bony covering are the protective layers called the meninges.
- Cavities present in various parts of the brain are called ventricles whereas the long tubular cavity of the spinal cord is called the central canal.
- The ventricles, central canal and spaces between the meninges are filled with cerebro?spinal fluid.
- This fluid supplies nutrients to the central nervous system and protects it from shock.
Question 5.
Which are the two types of peripheral nerves?
Answer:
Peripheral nerves are of two types:
(a) Cranial nerves:
- Nerves originating from the brain are called cranial nerves.
- They are associated with various parts in the head.
- There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
(b) Spinal nerves:
- Nerves originating from the spinal cord are called spinal nerves.
- They are associated with arms, legs, skin and some other parts of the body.
- There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
Question 6.
How do plants get rid of their excretory products?
Answer:
- Excretion is a simpler process in plants. There is no special organ or system for excretion in plants.
- Gases are given out by diffusion.
- Most of the waste substances of plants are stored in vacuoles of leaf-cells and in flowers, fruits and the bark of the stem. After some time these parts fall off.
- Some other waste materials are stored in old and worn out xylem in the form of resin and gum.
- Some waste materials are also given out through roots in the surrounding soil.
Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Explain how food and other substances are transported in plants?
OR
Explain translocation in plants.
Answer:
- The food produced in leaves is transported to each cell in the plant body.
- Excess food, except amino acids, is stored in roots, fruits and seeds. This process is called translocation of materials.
- It is carried out in both the upward and downward directions by the phloem.
- Translocation is not a simple process, it requires energy. This energy is obtained from ATP.
- Whenever food material like sucrose is transported towards a part of a plant via the phloem with the help of ATP, the water concentration decreases in the part. As a result, water enters the cell by the process of diffusion.
- The pressure on the cell wall increases due to increase in cellular contents.
- Due to the increase pressure, food is pushed into the neighbouring cells where the pressure is low.
- This process helps the phloem to transport the materials as per the need of the plant. During flowering season, the sugar stored in roots or stem is transported towards the floral buds to make them open and blossom.
Question 2.
What is tropic movement? Describe the different types of tropic movements.
OR
What are growth relevant movements? Describe the different types of growth relevant movements.
Answer:
Movement or growth of any part of the plant in response to an external stimulus is called tropic movement or tropism.
The different types of tropic movements are:
- Phototropic movement : The shoot system of any plant responds to the light stimulus, i.e., it grows towards the source of light. The movement shown by plants towards the source of light is called phototropic movement.
- Gravitropic movement : The root system of plants responds to stimulus of gravity. This is called gravitropic movement.
- Hydrotropic movement : The root system of plants responds to the stimulus of water. This is called hydrotropic movement.
- Chemotropic movement : Movement shown by plants in response to specific chemicals is called chemotropic movement. For example, the growth of the pollen tube towards the ovule.
All the above-mentioned movements of plants are related with growth, hence are called growth relevant movement.
Question 3.
Write short note on : Human Brain
Answer:
- The brain is the main controlling part of the nervous system and is safely located in the cranial cavity.
- The brain is covered by protective layers called the Meninges.
- Cavities present in various parts of the brain are called ventricles.
- The ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid supplies nutrients to the brain and also protects it from shock.
- The brain of an adult human weighs about 1300 -1400 grams and consists of approximately 100 million neurons.
- The left side of our brain controls the right side of our body and right side of our brain controls left side of the body.
- In addition, the left side of the brain controls our speech and conversation, writing, logical thinking etc., whereas the right side controls artistic abilities.
Human brain is made up of following parts:
(a) Cerebrum:
- This is the largest part of the brain and consists of two cerebral hemispheres. These hemispheres are joined with each other with the help of tough fibres and nerve tracts.
- The cerebrum occupies two-thirds of the brain. Hence, it is also called as large brain.
- Its surface has deep, irregular ridges and grooves which are called convolutions, convolution increases the surface area of the cerebrum and therefore a large number of nerve cells can be accommodated.
(b) Cerebellum:
- This is the smaller part of the brain situated below the cerebrum at the back of the cranial cavity.
- Its surface shows shallow grooves instead of deep convolutions.
(c) Medulla Oblongata:
- This is the hind-most part of the brain.
- There are two triangular swollen structures called pyramids on the upper side of medulla oblongata.
- The medulla oblongata continues downwards the spinal cord.
(6) How are nerve impulses conducted in the body?
Answer:
- Special types of cells which conduct impulses from one place to another in the body are called neurons. Nerve cells have the ability to generate and conduct electro-chemical impulses.
- The cells that support the nerve cells and help in their functioning are called neuroglia.
- All the information about our surroundings is collected by the ends or dendrites of the neuron.
- The chemical process begins at those ends and electric impulses are generated which are conducted from the dendrites to the cell body, from the cell body to the axon and from the axon to its terminal.
- These impulses are then to be transferred from this nerve cell to the next.
- Now the impulse that reaches the terminal of an axon, stimulates the nerve cell to secrete certain chemicals.
- These chemicals pass through a minute space, called the synapse, between two adjacent neurons and generate the impulses in the dendrites of the next neuron.
- In this way, impulses are conducted in the body and these impulses are finally conveyed by nerve cells to muscles cells or glands.
