Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 17 Introduction to Biotechnology Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 9 Science Chapter 17 Introduction to Biotechnology Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Science Chapter 17 Introduction to Biotechnology Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Each of the following statements is wrong. Rewrite them correctly by changing either one or two words.
a. Simple squamous epithelium is present in the respiratory tract.
b. Glandular epithelium is present in kidneys.
c. Chlorenchyma helps the plant to float in water.
d. Striated muscles are also called involuntary muscles.
e. Chloroplast is present in permanent tissue.
Answer:
a. False. Ciliated columnar epithelium is present in respiratory tract.
b. False. Cuboidal epithelium is present in kidneys.
c. False. Aerenchyma helps the plant to float in water.
d. False. Striated muscles are also called voluntary muscles.
e. False. Chlorenchyma is present in permanent tissue.

2. Identify the odd word and explain why it is odd.
a. Xylem, phloem, permanent tissue, meristematic tissue.
Answer:
Meristematic tissue. It has the ability to divide whereas the others have lost the ability to divide.
b. Epithelium, Muscle fibre, nerve fibre, the epidermis.
Answer:
Epidermis. It is a plant tissue whereas the others are animal tissues.
c. Cartilage, bone, tendon, cardiac muscle.
Answer:
Cardiac muscle. It is a muscular tissue whereas the others are connective tissues.
3. Write the names of the following tissues.
a. Tissue lining inner surface of mouth.
Answer:
Squamous epithelium.
b. Tissue joining muscles and bones.
Answer:
Tendon
c. Tissue responsible for increasing height of plants.
Answer:
Apical meristem.
d. Tissue responsible for increasing girth of stem.
Answer:
Lateral meristem.

4. Write the differences.
Simple tissue and complex tissues in plants.
Answer:
| Simple Tissue in plants | Complex Tissues in plants |
| (i) They are made up of only one type of cells. | (i) They are made up of more than one type of cells. |
| (ii) They are found in all parts of the plant. | (ii) They are found in the vascular regions of the plant. |
| (iii) They perform different functions like storage | (iii) They mainly perform the function of |
| of food, support, giving strength etc. | conduction of water and food. |
| (iv) Examples – Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma. | (iv) Example – Xylem and phloem. |
5. Write short notes.
a. Meristematic tissue.
Answer:
- Meristematic tissue is present in specific parts of a plant where growth takes place.
- Cells of meristematic tissue contain thick cytoplasm, a conspicuous nucleus and a thin cell wall and are compactly packed together.
- Vacuoles are usually absent in these cells and they are highly active.
- The main function of meristematic tissue is to bring about plant growth.
- According to the location, meristematic tissues are of three types: Apical meristem, intercalary meristem and lateral meristem.
b. Xylem
Answer:
- Xylem is a complex permanent tissue in plants.
- It consists of thick-walled dead cells.
- The type of cells in xylem are trachieds, vessels, xylem fibres (dead cells) and xylem parenchyma (living cells).
- Its structure is like interconnected tubes conduct water and minerals only in upward direction.
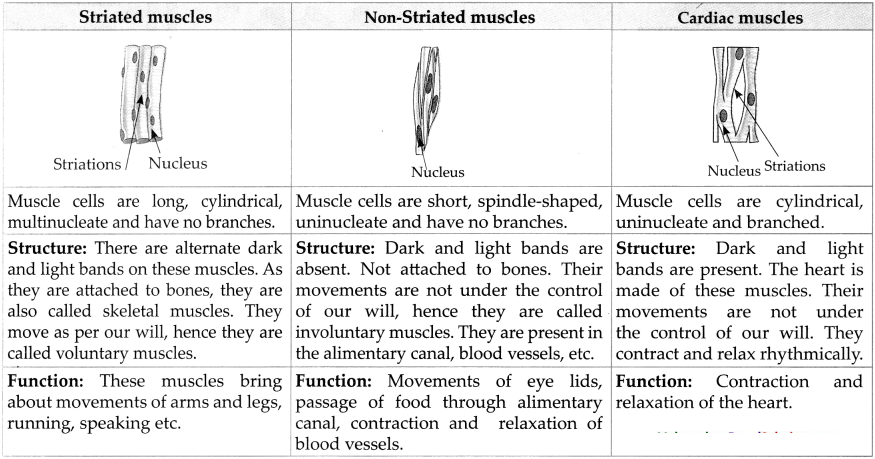
c. Striated muscles.
Answer:
- The cells of striated muscles are long, cylindrical, multinucleate and have no branches.
- These are alternate dark and light bands on these muscles.
- As they are attached to bones, they are also called skeletal muscles.
- They move as per our will, hence they are called voluntary muscles.
- Striated muscles bring about movements of arms and legs, running, speaking etc.
d. Agro-complementary business.
Answer:
(i) The business that are complementary to agriculture and generate supplementary income for the farmers are called agro complementary business.

(ii) These include:
- Animal Husbandry: It is practiced for milk production and for using the cattle as help in farming operations, e.g. cows and buffaloes are raised for milk whereas bulls and male buffaloes for pulling heavy loads.
- Poultry farming: It is the rearing of egg and meat yielding chickens. Chickens raised for eggs are called layers while those raised for meat are called broilers.
- Sericulture: It is the rearing of silkworms (moths) for silk production. The silk fibres obtained are processed, reeled and then woven into fabric.
e. Genetic engineering
Answer:
- Genetic engineering is the deliberate modification of the characteristics of an organism by manipulating its genetic material.
- An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is called a genetically modified organism (GMO).
- Genetic engineering is applied in many fields like research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology and medicine.
- In agriculture, genetic engineering is used in the production of cash crops, improvement in varieties of cash crops, increase in ability of plants to withstand environmental stresses.
- In medicine, genetic engineering is used for vaccine production, early diagnosis of congenital disease, organ transplant, cancer research, production of artificial skin, cartilage etc. in laboratories.
f. Sericulture
Answer:
- Sericulture is the rearing of silkworms (moths) for production of silk.
- Bombyx mori is the most commonly used variety of silkworm for this purpose.
- The life cycle of silkworm consist of four stages namely egg, larva, pupa and adult.
- Thousands of eggs deposited by female moths are incubated artificially to shorten the incubation period.
- Larvae hatching out of eggs are released on mulberry plants.
- Larvae are nourished by feeding on mulberry leaves.
- After feeding for 3-4 days, larvae move to branches of mulberry plant.
- The silk thread is formed from the secretion of their salivary glands.
- Larvae spin this thread around themselves to form a cocoon. The cocoon may be spherical in nature.
- Ten days before the pupa turns into an adult, all the cocoons are transferred into boiling water.
- Due to the boiling water, the pupa dies in the cocoon and silk fibres become loose.
- These fibres are unwound, processed and reeled. Various kinds of fabric is woven from silk threads.

6. Explain the meaning of biotechnology and its impact on agricultural management with suitable examples.
Answer:
The techniques of bringing about improvements in living organisms by artificial genetic changes and by hybridization for the welfare of human beings, are together called biotechnology. Impact of biotechnology on agricultural management:
- Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are being produced by introducing changes in DNA of natural crops.
- Normally such varieties are not found in nature.
- Thus, new varieties are produced artificially Different useful characters are introduced in such varieties.
- Some naturally occurring varieties cannot withstand environmental stress like frequently changing temperature.
- Wet and dry famines, changing climates etc. However, GM crops can grow in any of such adverse conditions.
- As GM crops are resistant to insect pests, pathogens, chemical weedicides, etc. the use of harmful chemicals like pesticides can be avoided.
- Due to use of seeds of GM crops, there is improvement in nutritive value and decrease in loss of crops.
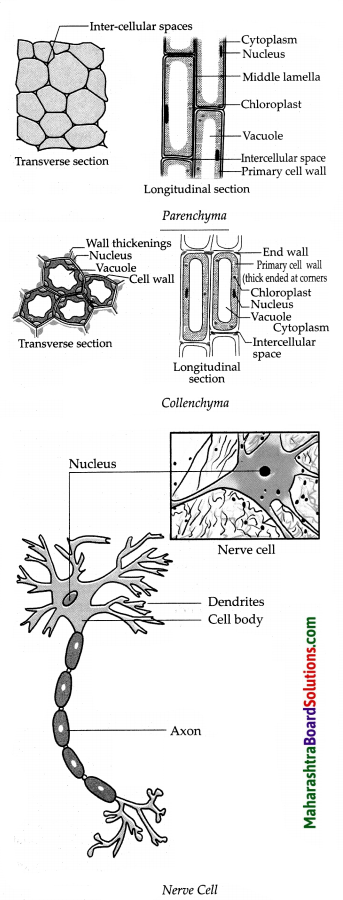
Draw neat and labelled diagrams of the following:

7. Which two main techniques are used in biotechnology? Why?
Answer:
- The two main techniques used in biotechnology are – Genetic engineering and tissue culture.
- These techniques are used to bring about improvements in living organisms by artificial genetic changes and by hybridization for the welfare of human beings.
- Its uses are in the production of cash crops, improvement in varieties of cash crops, early diagnosis of congenital diseases, organ transplant, cancer research, production of artificial skin, cartilage etc. in laboratories.
8. Discuss ‘Agritourism’ in the class and write a project on an agrotourism centre nearby. Present it in the class in groups.
Answer:
- In agritourism, plantlets of flowering, medicinal, ornamental, vegetable plants and fruit trees are produced on a large scale by tissue culture technique.
- By growing some of the plants fully, an agritourism centre can be developed.
- If sufficient land is available, the emerging field of agritoursim would be a good business.
-
An agritourism centre consists of following:
(a) Mango, chikoo (sapota), guava, coconut, custard apple and some other regional fruit trees.
(b) Shade giving local or exotic attractive plants.
(c) Ornamental and flowering plants.
(d) Butterfly garden.
(e) Medicinal plant garden.
(f) Organic vegetables and fruits. - People visit places with such attraction in large numbers.
- Selling plantlets/seedlings, fruits, vegetables at such places can be quite profitable.
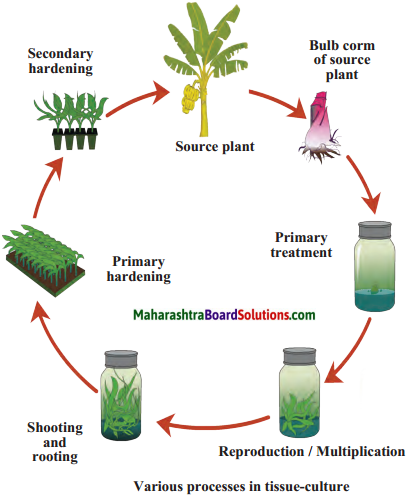
9. Define the term tissue and explain the concept of tissue culture.
Answer:
A group of cells having the same origin, same structure and same function is called tissue. Concept of tissue culture:
- Ex vivo growth of cells or tissues in an aseptic and nutrient-rich medium is called tissue culture.
-
Nowadays, a complete organism can be developed from a single cell or from tissue with the help of the tissue culture technique.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- A liquid, solid or gel-like medium prepared from agar, which supplies nutrients and energy necessary for tissue culture is used in this technique.
- Tissue culture can be used to grow plants on a large scale, which bear flowers, fruits of excellent quality, in shorter durations and are disease free.
- The various processes involved in tissue culture are:
10. ‘Rearing of sheep is a livestock’. Justify this statement.
Answer:
- The term livestock refers to animals reared for profit or for use.
- Sheep provides us with wool, skin, meat and milk.
- Therefore, rearing of sheep is a livestock.
Class 9 Science Chapter 17 Introduction to Biotechnology Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which components bring about important processes in the living organisms?
Answer:
Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems bring out important processes in living organisms.
Question 2.
Which is the smallest structural and functional unit of the body of living organisms?
Answer:
Cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of the body of living organisms.
Question 3.
Which type of muscle is the diaphragm of the respiratory system?
Answer:
Diaphragm is a skeletal muscle. It is an involuntary muscle that regulates breathing, although some voluntary control can be achieved.

Question 4.
What is the main difference between the growth of animals and plants?
Answer:
- Growth in animals is uniform whereas the growth in plants occurs in specific parts of the body.
- Growth in animals occurs for a certain period of life whereas the growth in plants occur throughout their life.
Question 5.
Why does the growth of a plant occur only at specific parts of the plant body?
Answer:
Growth of a plant occurs only at specific parts of the body due to the presence of meristematic tissues which contain dividing cells.
Question 6.
Suppose you want to grow a garden like the one shown in the picture, around your home or school. What would you do to achieve that? By which methods will you cultivate the seedlings?

Answer:
- To grow a garden around the school or home, one must cultivate seedlings of different plants and those seedlings must be watered regularly and nurtured properly.
-
Seedlings can be cultivated by the following methods:
(a) Seed sowing: Seeds are sown, watered and allowed to germinate.
(b) Transplantation: Seeds are sown somewhere else and then the seedlings are transplanted in the garden.
Question 7.
You must have seen flowers of same variety but of 2 or 3 different colours borne by same plant. How is this possible?
Answer:
- The different coloured flowers borne by the same plant are due to the pigments like anthocyanins, carotenoids etc. according to the genetic makeup of the plant.
- Also, by using the latest techniques of biotechnology and tissue culture, it is possible to manipulate the genes for flower colour and get the desired flower colour.

Question 8.
What keeps the various organs and organ systems separate from each other? Why?
Answer:
The epithelial tissue keeps the various organs and organ systems separate from each other by forming a layer on the organs.
Question 9.
Why are epithelial tissues said to be simple tissues?
Answer:
Epithelial tissues are said to be simple tissues as they are made up of only one type of cells.
Question 10.
Why do slim persons feel more cold in winter than those who are obese?
Answer:
- Below the skin, there is a tissue called adipose tissue.
- The cells of these tissue are filled with fat droplets.
- Due to storage of fat, it acts as an insulator and helps to retain heat in the body.
- Obese people have more fat deposited in the adipose tissue as compared to slim persons. Therefore, slim persons feel more cold in winter than those who are obese.
Question 11.
Why can bones not be folded?
Answer:
- Bone cells called osteocytes are embedded in solid ground substance made up of calcium phosphate.
- This makes the bone hard, rigid and non- flexible. Therefore, bones cannot be folded.
Question 12.
Which other industries can be started as an extension of the plant nursery business?
Answer:
Businesses like Agritourism, Ecotourism, forest resorts and organic fruit gardens, yoga and meditation centres can be started as an extension of the plant nursery business.
Question 13.
To which places do people choose to go on vacation in order to relax when they are tired of crowds and stressful life?
Answer:
People choose to go to hill stations, beaches, forest resorts and places where there is lot of greenery to relax when they are tired of crowds and stressful life.
Question 14.
What is the inter-relationship between the two questions (7 and 8) above?
Answer:
The inter-relationship between the above two questions is that businesses like agritourism, ecotourism, forest resorts etc. can fetch a huge profit as people look for these kind of places to relax, to be away from the hustle and bustle of city life and feel close to nature.

Question 15.
Why are the cocoons transferred to boiling water before the pupa develops into an adult?
Answer:
- Once the pupa develops into an adult, it will secrete a fluid to dissolve the silk and emerge out.
- Hence the cocoons are transferred to boiling water before the pupa develops in to an adult to kill the silkworms before transformation is complete.
Question 16.
Why we cannot see our organs like the heart, blood vessels and intestines?
Answer:
We cannot see our organs like the heart, blood vessels and intestines as they are located inside the body.
Question 17.
What is meant by white revolution? Who was its pioneer? What benefits did it bring?
Answer:
- White revolution was the programme launched by the National Dairy Development Board to increase the milk production in India.
- Dr. Verghese Kurien was the pioneer of white revolution.
- It transformed India from a milk-deficient nation to the largest producer of milk. It also helped the dairy farmers in directing their own development and empowering them.
It also helped to reduce the malpractices carried out by milk traders and merchants.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Collect information about GM varieties of crops in your area and make a note of them. Also find out if there are adverse effects of GM crops on human beings and environment.
Answer:
-
Some of the GM crops are:
(a) Maize: MON 810, MON 863
(b) Rice: Golden rice
(c) Brinjal: BT brinjal
(d) Cotton: BT cotton - Effects of GM Crops on human beings: GM crops may cause toxicity and allergic reactions in humAnswer:
-
Effects of GM Crops on environment:
(a) GM crops may be toxic to pollinators and non-target species like butterflies.
(b) Many GM crops may be a threat to soil ecosystem as they secrete their toxins into the soil.

Question 2.
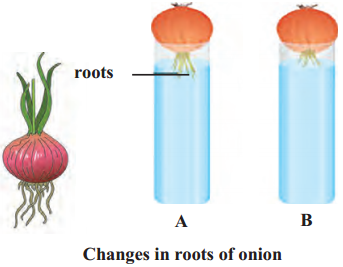
As shown in the figure, place an onion on each gas jar in such a way that its base (roots) will remain dipped in water. Measure and record the length of the roots of both onions on the first, second and third day. On the fourth day, cut off 1 cm of the roots of the onion in flask B Measure the length of the roots of both onions for the next five days and record your observations in the following table.
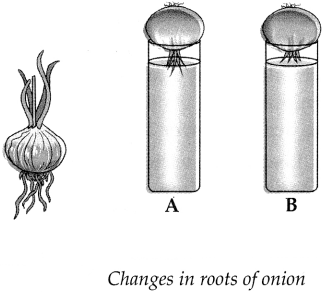
| Length (cm) | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 |
| Flask A | |||||
| Flask B |
Answer:
(Students are expected to record their observation in the given table).
(a) Which onion has longer roots? Why?
Answer:
The onion in jar Ahas longer roots as it continues to grow due to the presence of meristematic tissue at root tip which had dividing cells.
(b) Why did the roots of the onion in jar B stop growing?
Answer:
The roots of onion in jar B stopped growing as the meristematic tissue present in the root tips were cut off.
Question 3.
Take a fresh and fleshy leaf of Rhoeo, lily or any other plant. Pull and press it, tearing it obliquely in such a way that its transparent epidermis will be visible at the cut margins. Take the transparent epidermis with the forceps and keep it in dilute safranin solution for 1 minute. Spread it on a slide, cover it with a cover-slip and observe it under a compound microscope.
Answer:
- The cells of the epidermis are flat and polygonal and there are no intercellular spaces between them.
- A single continuous layer is formed.
- The epidermis is covered by a waxy cuticle.

Question 4.
Establish your own plant nursery near your school or home. Prepare the seedlings of flowering plants, fruit plants, and ornamental plants being grown in your area. Can you start a business in the future with the help of this activity? Think it over.
Answer:
(Students are expected to do this activity on their own.)
Yes, we can start a business of plant nursey in future. If sufficient land is available, the emerging field of agritourism would be a good business.
Question 5.
Observe the skin of the back of your hand with the help of a magnifying lens. Do you see the closely attached squarish and pentagonal shapes?
Answer:
Yes, we can see the squarish and pentagonal shapes. This is the stratified squamous epithelium present on the outer layer of skin.
Question 6.
Observe a permanent slide of blood smear under a compound microscope. What did you see?
Answer:
- A permanent slide of blood smear under a compound microscope shows different types of cells like RBCs, WBCs and platelets.
- The different types of WBCs that can be seen are eosin mphocytes.
Question 7.
Visit a modern cowshed nearby and record the following points – The number of cattle, their variety, total milk production, cleanliness in cattle-shed, arrangements for health care of cattle.
Answer:
Students are expected to do this activity on their own.

Question 8.
Collect more information about animal husbandry.
Answer:
- The branch of agriculture which deals with the feeding, shelter, health and breeding of domestic animals is called animal husbandry.
- It is a scientific and systematic management of livestock.
-
Animal husbandry practices include:
(a) Proper food and clean drinking water.
(b) Proper shelter
(c) Proper methods of breeding
(d) Prevention and cure of disease. - Animal husbandary practices serve as an alternative income for the farmers and help to satisfy the need of food for man.
Question 9.
Find out from the internet the average daily milk yield from local and exotic varieties of cow.
Answer:
- Milk yield from local cow : 12-15 litres/day.
- Milk yield from exotic cow: 15-30 litres/day.
Question 10.
Are the structure and functions of the bodies of plants and animals the same?
No. The structure and functions of the bodies of plants and animals are not the same. Some differences between plants and animals:
Answer:
| Plants | Animals |
| Plants continue to grow throughout their life. | Animals grow only for a specific period of life. |
| Growth in plants in not uniform. | Growth in animals is uniform. |
| Plants have dividing and non-dividing tissues. | Animals do not have different dividing and nondividing tissues. |
| Plants are sedentary. | Animals generally move from place to place in search of food, shelter and partners. |
| Energy needs of plants are less. | Energy needs of animals are greater. |
| Plants can prepare their own food by photosynthesis. | Animals cannot prepare their own food. They depend on plants and other animals for their food. |
Class 9 Science Chapter 17 Introduction to Biotechnology Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose and write the correct option:
Question 1.
Protective coverings in the animal body are called tissues.
(a) meristematic
(b) muscular
(c) epithelial
(d) bone
Answer:
(c) epithelial

Question 2.
Epithelial tissue is present in
(a) skin
(b) inner surface of blood vessels
(c) walls of the alveoli
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 3.
helps in selective transport of substances.
(a) Squamous epithelium
(b) Stratified epithelium
(c) Cuboidal epithelium
(d) Columnar epithelium
Answer:
(a) Squamous epithelium
Question 4.
helps in secretion of digestive juice, absorption of nutrients.
(a) Glandular epithelium
(b) Columnar epithelium
(c) Cuboidal epithelium
(d) Ciliated epithelium
Answer:
(b) Columnar epithelium

Question 5.
supports internal organs
(a) Areolar tissue
(b) Adipose tissue
(c) Lymph
(d) Tendon
Answer:
(a) Areolar tissue
Question 6.
tissue helps in insulation, supply of
Answer:
(b) Adipose tissue
Question 7.
connect muscles to bones.
(a) Ligaments
(b) Tendons
(c) Cartilages
(d) Nerves
Answer:
(b) Tendons
Question 8.
join two bones to each other.
(a) Cartilages
(b) Tendons
(c) Ligaments
(d) Muscles
Answer:
(c) Ligaments

Question 9.
meristem increases the length of root and stem.
(a) Intercalary
(b) Apical
(c) Lateral
(d) Permanent
Answer:
(b) Apical
Question 10.
showed that cells and tissues can be grown ex vivo.
(a) Frederick Campion Steward
(b) Gregor Johann Mendel
(c) Frederick Miescher
(d) Robert Brown
Answer:
(a) Frederick Campion Steward
Question 11.
is an example of genetically modified maize.
(a) Vaishali
(b) Vistive Gold
(c) MON 810
(d) Amflora
Answer:
(c) MON 810
Question 12.
is an exotic variety of cow.
(a) Holstein
(b) Gir
(c) Sahiwal
(d) Dangi
Answer:
(a) Holstein

Question 13.
is a layer chicken.
(a) Brahma
(b) Leghorn
(c) Cochin
(d) Aseel
Answer:
(b) Leghorn
Question 14.
is a broiler chicken.
(a) Leghorn
(b) Lehman
(c) Aseel
(d) Minorca
Answer:
(c) Aseel
Question 15.
is a broiler chicken.
(a) Minroca
(b) Ancona
(c) Leghorn
(d) Cochin
Answer:
(d) Cochin
Question 16.
Cartilage is found
(a) all around the cells in body
(b) in nose, ear, larynx, trachea
(c) between the muscles and skin
(d) around the blood vessels
Answer:
(b) in nose, ear, larynx, trachea

Question 17.
Which of the following is an exotic variety of COW?
(a) Plymouth Rock
(b) New Hampshire
(c) Black Rock
(d) Brown Swiss
Answer:
(d) Brown Swiss
Question 18.
epithelium is present in the inner surface of respiratory tract.
(a) Stratified
(b) Columnar
(c) Ciliated
(d) Cuboidal
Answer:
(c) Ciliated
Question 19.
Bones consist of osteocytes embedded in solid ground substance made up of
(a) calcium bicarbonate
(b) calcium carbonate
(c) calcium phosphate
(d) calcium sulphate
Answer:
(c) calcium phosphate

Question 20.
helps in growth of branches, formation of leaves and flowers.
(a) Lateral meristem
(b) Apical meristem
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) Xylem
Answer:
(c) Intercalary meristem
Question 21.
tissue is present in the hard coat of seeds, outer covering of coconut.
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Xylem
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Sclerenchyma
Answer:
(d) Sclerenchyma
Question 22.
The cells of tissue are dead.
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Sclerenchyma

Question 23.
Cuboidal epithelium is found in
(a) inner surface of mouth, blood vessels
(b) inner layer of skin
(c) tubules of kidney, salivary gland
(d) inner surface of respiratory tract
Answer:
(c) tubules of kidney, salivary gland
Find the odd man out:
Question 1.
Cell body, muscle fibre, axon, dendrites.
Answer:
Muscle fibre. It is a muscle cell whereas the others are parts of nerve cell.
Question 2.
Tracheids, vessels, companion cells, xylem fibres.
Answer:
Companion cells. It is an element of phloem whereas the others are elements of xylem.
Question 3.
Sieve tubes, tracheids, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres.
Answer:
Tracheids. It is an element of xylem whereas the others are elements of phloem.
Question 4.
Holstein, Brown swiss, Bombyx mori, Jersey.
Answer:
Bombyx mori. It is a variety of silkworm whereas the others are varieties of cows.
Complete the analogy:
(1) Inner surface of mouth : Squamous epithelium :: Inner surface of intestine :
(2) Glandular epithelium : Secretion of sweat, oil :: Cuboidal epithelium:
(3) Respiratory tract: Ciliated columnar epithelium :: Kidney tubules:
(4) Outer layer of skin : Stratified epithelium :: Inner layer of skin :
(5) Muscular tissue : Movement :: Nervous tissue :
(6) Tendons : Join muscles to bones :: Ligaments :
Answer:
(1) Columnar epithelium
(2) Secretion of saliva
(3) Cuboidal epithelium
(4) Glandular epithelium
(5) Conduction of excitation
(6) Join two bones to each other

Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Squamous epithelium | (a) Secretion of digestive juice |
| (2) Cuboidal epithelium | (b) Selective transport of substances |
| (3) Columnar epithelium | (c) Protection of organs |
| (4) Stratified epithelium | (d) Secretion of saliva |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – d),
(3 – a),
(4 – c)
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Brahma | (a) Local variety of cow |
| (2) Jersey | (b) Layer chicken |
| (3) Devin | (c) Exotic variety of cow |
| (4) Lehman | (d) Broiler chicken |
Answer:
(1 – d),
(2 – C),
(3 – a),
(4 – h)

Question 3.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Potato | (a) Vistive Gold |
| (2) Maize | (b) Amflora |
| (3) Soybean | (c) Vaishali |
| (4) Tomato | (d) MON 863 |
Answer:
(1-b),
(2-d),
(3-a),
(4-c)
Answer the following:
Question 1.
Explain the different types of muscular tissues.
Answer:

Question 2.
Explain the types of complex permanent tissues.
Answer:
| Name of tissue | Xylem | Phloem |
| Characteristics | Consists of thick-walled dead cells | Consists of cytoplasm containing living cells. |
| Types of cells | Tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres – dead cells. Xylem parenchyma – living cells. | Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma – living cells. Phloem fibres – dead cells. |
| Function | A structure like interconnected tubes, conduct water and minerals only in upward direction. | Tubes joined to each other, conduct sugar and amino acids from leaves to various parts in upward and downward direction |
State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statement:
Question 1.
Lateral meristem increase girth(diameter) of the root and stem.
Answer:
True

Question 2.
Due to use of seeds of GM crops, there is decrease in nutritive value and increase in loss of crops.
Answer:
False. Due to use of seeds of GM crops there is improvement in nutritive value and decrease in loss of crops.
Question 3.
In a bioreactor, cells can be grown in a more nutritive medium and protected from pathogens.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Rare and endangered plants can be grown by tissue culture and can be protected from extinction.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
The silk thread is formed from the secretion of the sweat glands of silkworm.
Answer:
False. The silk thread is formed from the secretion of the salivary glands of silkworm.
Question 6.
Rhode Island Red, New Hampshire, Plymouth Rock, Black Rock are varieties of chicken reared for both eggs as well as meat.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
Phloem consists of thick-walled dead cells.
Answer:
False. Phloem consists of living cells containing cytoplasm.
Question 8.
Stratified squamous epithelium is present in inner surface of mouth, oesophagus, blood vessels and alveoli.
Answer:
False. Stratified squamous epithelium is present in the outer layer of skin.
Question 9.
Broiler chickens are raised for eggs.
Answer:
False. Broiler chickens are raised for meat.

Question 10.
Non-striated muscles bring about contraction and relaxation of heart.
Answer:
False. Cardiac muscles bring about contraction and relaxation of heart.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Tissue responsible for growth of branches, formation of leaves and flowers.
Answer:
Intercalary meristem.
Question 2.
Tissue that helps in insulation, supply of energy, storage of fats.
Answer:
Adipose tissue.
Question 3.
Tissue present in outer layer of skin.
Answer:
Glandular epithelium.
Question 4.
Tissue present in nose, ear, larynx, trachea.
Answer:
Cartilage.

Question 5.
Dead cells in xylem.
Answer:
Tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres.
Question 6.
Living cells in xylem.
Answer:
Xylem parenchyma.
Question 7.
Living cells in phloem.
Answer:
Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma.
Question 8.
Dead cells in phloem.
Answer:
Phloem fibres.
Question 9.
GM crops.
Answer:
BT cotton, Amflora, Golden Rice.
Question 10.
Local Indian varieties of cow.
Answer:
Sahiwal, Sindhi, Lai kandhari, Devni, Khillari, Dangi.

Question 11.
Exotic varieties of cow.
Answer:
Jersey, Brown swiss, Holstein.
Question 12.
Layers.
Answer:
Leghorn, Minorca, Ancona, Lehman.
Question 13.
Broilers.
Answer:
Brahma, Long, Cochin, Aseel.
Question 14.
Chickens reared for both eggs and meat.
Answer:
Rhode Island Red, New Hampshire, Plymouth Rock, Black Rock.
Give scientific reason.
Question 1.
Blood is a complex tissue.
Answer:
- A complex tissue is made up of more than one type of cells.
- In blood, cells of different types, colour and shapes are mixed together.
- Blood contains erythrocytes (RBCs), leucocytes (WBCs) and platelets in a liquid plasma.
- Therefore, blood is a complex tissue.
Define the following:
Question 1.
Tissue
Answer:
A group of cells having the same origin, same structure and same function is called tissue.

Question 2.
Differentiation
Answer:
When cells acquire a specific structure, shape and location and perform a specific function, it is called differentiation.
Question 3.
Biotechnology
Answer:
The techniques of bringing about improvements in living organisms by artificial genetic changes and by hybridization for the welfare of human beings, are together called ‘Biotechnology’.
Question 4.
Tissue culture
Answer:
Ex vivo growth of cells or tissues in an aseptic and nutrient-rich medium’ is called tissue culture.
Write short notes
Question 1.
Animal husbandry
Answer:
- In India, animal husbandry is practised for milk production and for using the cattle as help in farming operations.
- Example – Cows and buffaloes are raised for milk and bulls and male buffaloes for pulling the heavy loads.
- Local Indian varieties of cows like Sahiwal, Sindhi, Gir, Lai kandhari, Devni, Khillari, Dangi, etc. and exotic varieties like Jersey, Brown swiss, Holstein, etc. are kept for their milk.
-
Proper care of cattle is necessary for a clean and high yield of milk which includes:
(a) A balanced diet, i.e. all constituents of food should be given to cattle. It must include fibre- rich coarse food, fodder, and sufficient water.
(b) The cattle-shed should be clean and dry with proper ventilation and a roof.
(c) Cattle should be regularly vaccinated.

Question 2.
Poultry farming.
Answer:
- Rearing of egg and meat yielding chickens is called poultry farming.
- Chickens raised for laying eggs are called layers . e.g. Leghorn, Minorca, Ancona, Lehman.
- Chickens raised for meat are called broilers, e.g. Brahma, Long, Cochin, Aseel.
- Rhode Island Red, New Hampshire, Plymouth Rock, Black Rock are varieties of chicken reared for both eggs as well as meat.
- The objectives behind development of new hybrid varieties from a cross between Indian varieties like Aseel and exotic varieties like Leghorn are to produce good quality chickens in large numbers.
- To develop the ability to withstand high temperature, to use by-products of agriculture as poultry feed, etc.
Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Xylem and Phloem
Answer:
| Xylem | Phloem |
| (i) Consists of mostly thick-walled dead cells. | (i) Consists of mostly living cells containing cytoplasm. |
| (ii) The types of cells include dead cells- tracheids, vessels and xylem fibres and living cells-Xylem parenchyma. | (ii) The types of cells include living cells – Sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and dead cells – phloem fibres. |
| (iii) Structure like interconnected tubes, conduct water and minerals only in upward direction. | (iii) Tubes joined to each other, conduct sugar and amino acids from leaves to various parts in both upward and downward direction. |
Question 2.
Striated muscles and Non-striated muscles.
Answer:
| Striated muscles | Non-striated muscles |
| (i) Muscle cells are long, cylindrical, multinucleate and have no branches. | (i) Muscle cells are short, spindle-shaped, uninucleate and have no branches. |
| (ii) There are alternate dark and light bands on these muscles and they are attached to bones. | (ii) Dark and light bands are absent. Not attached to bones. |
| (iii) They move as per our will, hence they are called voluntary muscles. | (iii) They are not under the control of our will, hence they are called involuntary muscles. |
| (iv) These muscles bring about movements of arms and legs, running, speaking etc. | (iv) These muscles bring about movement of eyelids, passage of food through alimentary canal, contraction and relaxation of blood vessels etc. |
Question 3.
Cartilage and Bone
Answer:
| Cartilage | Bone |
| (i) They are present in nose, ear, larynx, trachea. | (i) They form the skeleton of the body. |
| (ii) They contain cells supported by fibrous, flexible, jelly-like ground substance. | (ii) They contain osteocytes embedded in solid ground substance made up of calcium phosphate. |
| (iii) Lubricates the surface of bones, gives support and shape to organs. | (iii) Supports and protects different organs, helps in movement. |
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Close your eyes and try to identify different objects by feeling them with your hand. Why is it possible for you to identify things like a note-book, text-book, bench, compass-box, etc. only by touching them?
Answer:
- We can identify objects just by touching them because of the memory that we retain in our brain.
- The nervous tissue enables us to respond to the stimuli of touch.

Answer in detail:
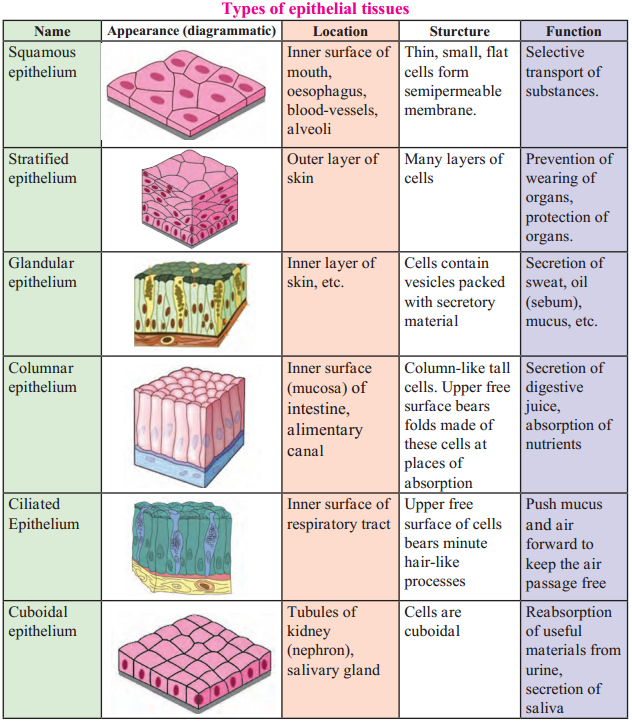
Question 1.
Write the location, structure and function of following epithelial tissues:
(a) Squamous epithelium
(b) Stratified epithelium
(c) Glandular epithelium
(d) Columnar epithelium
(e) Ciliated epithelium
(f) Cuboidal epithelium
Answer:
Question 2.
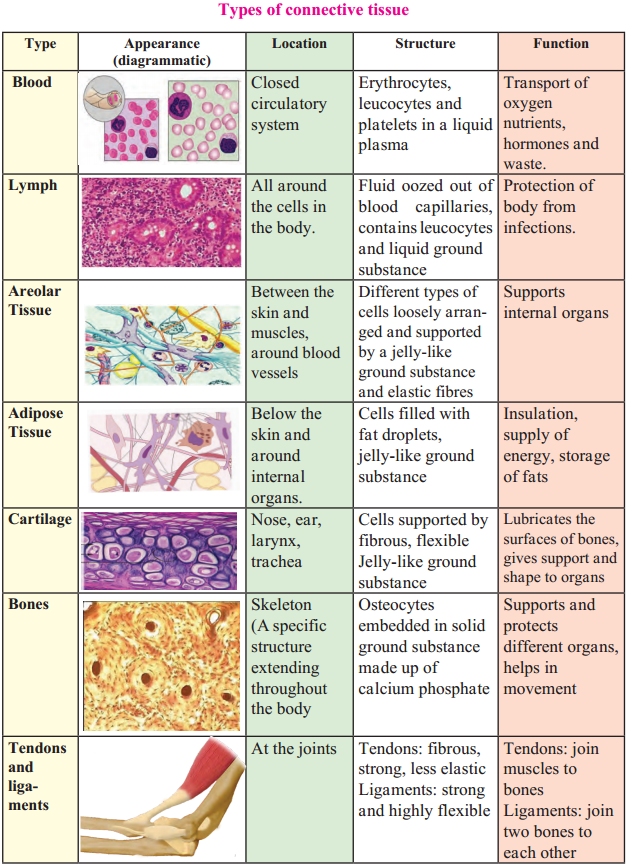
Write the structure and function of the following connective tissues:
(a) Blood
(b) Lymph
(c) Areolar tissue
(d) Adipose tissue
(e) Cartilage
(f) Bones
(g) Tendons and ligaments
Answer:

Question 2.
Describe the structure of nervous tissue with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
- Nervous tissue enables us to respond to stimuli like touch, sound, odour, colour, etc.
- Cells of the nervous tissue are specifically made to become excited and conduct the excitation from one part of the body to another.
- The main part of the nerve cell is the cell body which contains the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
- Numerous, small, branched fibres called dendrites arise from the cell body.
-
One of the fibres, is extremely long and is called
the axon. - The length of the nerve cell may be up to one metre.
- Many nerve cells are bound together with the help of connective tissue to form a nerve.
- Nervous tissue is present in the brain, spinal cord and the network of nerves spread all throughout the body.
-
In most animals, action in response to a stimulus occurs due to the integrated functioning of the nervous tissue and muscular tissue.
![Maharashtra-Board-Class-9-Science-Solutions-Chapter-17-Introduction-to-Biotechnology-1]()
Question 3.
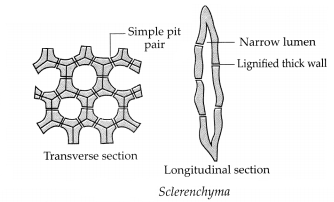
Explain the types of simple permanent tissues in plants.
Answer:
Types of simple permanent tissues.
Question 4.
Explain types, location and function of Meristematic tissue in tabular form:
Answer:
| Types | Apical | Intercalary | Lateral |
| Location | At tip of the root and stem | At the base of the petiole of leaves and branches | At sides of root and stem |
| Function | Increase the length of the root and stem | Growth of branches, the formation of leaves and flowers | Increases diameter of the root and stem |

Question 5.
Explain the types of simple permanent tissues in plants.
Answer:
Types of simple permanent tissues.
| Name of Tissue | Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| Structure of cells | Living cells with thin cell wall and intercellular spaces. | Elongated living cells with thickened cell wall at corners due to cellulose and pectin. | Dead and fibrous cells with tapering ends, cell wall contains lignin. |
| Location | All parts like roots, stem, leaves, flowers and seeds. | At the base of leaf petiole, branches and stem | Stem, veins of leaves, hard coats of seeds, outer covering of coconut. |
| Functions | Support, storage of food and filling vacant spaces. | Support and flexibility to various parts. | Give strength and rigidity to parts of the plants. |
| Sub types | Chlorenchyma: Leaves, perform photosynthesis. Aerenchyma: Helps aquatic plants, leaves and stem to float. |
Question 6.
Write down the applications of biotechnology (tissue culture) in floriculture, nurseries and forestry.
Answer:
Applications of biotechnology (tissue culture) in floriculture, nurseries and foresty:
- Tissue culture can be used to grow those plants on a large scale which bear flowers, fruits of excellent quality.
- Fully grown plants can be produced in shorter durations.
- Plants can be grown on a large scale even if means of pollination or germinating seeds are not available.
- For example, orchids or pitcher plants do not germinate but these plants can easily be produced by means of tissue culture.
- In a bioreactor, cells can be grown in a more nutritive medium and protected from pathogens.
- Bioreactors are useful for producing plantlets on a very large scale.
- A large number of seedlings/plantlets can be produced in a short time using minimum resources and materials.
- Usually, plants produced by tissue culture and genetic modification techniques are disease-free.
- Plantlets produced by tissue culture technique of the meristem are virus-free.
-
Embryos produced using conventional hybridization technique between two or more varieties may not grow fully for some reasons.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- However, embryos produced by tissue culture technique always complete their growth.
- Rare and endangered plants can be grown using tissue culture technique and can thus be protected from extinction.
- Similarly, various parts and seeds of such plants can be preserved by tissue culture and those varieties can be protected.