Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 8 Useful and Harmful Microbes Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 9 Science Chapter 8 Useful and Harmful Microbes Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Useful and Harmful Microbes Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Complete the statements using the proper option from those given below. Explain the statements. (mycotoxins, budding, rhizobium)
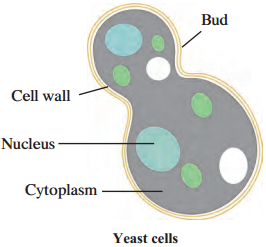
a. Yeast reproduces asexually by the …………………….. method.
Answer:
The yeast cells develop small round bodies on the parent cell. These are called buds. New daughter cells develop from these buds.

b. Toxins of fungal origin are called …………………….. .
Answer:
Mycotoxins are poisonous chemicals released into the food by fungi. This makes the food poisonous.
c. Leguminous plants can produce more proteins due to …………………….. .
Answer:
- (i) Nitrogenous compounds are required to produce proteins.
- (ii) Rhizobia produce nitrogenous compounds by fixing atmospheric nitrogen and make it available for their host plants like leguminous plants.
2. Write the names of microbes found in the following food materials.
yogurt, bread, root nodules of leguminous plants, idli, dosa, spoiled potato curry.
Answer:
| Food materials | Microbes |
| Yogurt | Lactobacilli |
| Bread | Yeast |
| Root nodules of leguminous plants | Rhizobium |
| Idli | Yeast, bacteria |
| Dosa | Yeast, bacteria |
| Spoiled potato curry | Clostridium |
3. Identify the odd word out and say why it is the odd one?
a. Pneumonia, diphtheria, chicken pox, cholera.
Answer:
Chickenpox. It is caused by a virus, whereas others are caused by bacteria.
b. Lactobacilli, rhizobia, yeast, clostridia.
Answer:
Yeast. It is a fungus, whereas the rest are bacteria.
c. Root rot, rust (tambura), rubella, mozaic.
Answer:
Rubella. It is a disease of humans, whereas the rest are diseases of plants.
4. Give scientific reasons.
a. Foam accumulates on a the surface of ‘dal’ kept for a long time in summer.
Answer:
- Dal is rich in proteins.
- During summer, bacteria attack the dal and cause fermentation resulting in the production of carbon dioxide gas.
- Therefore, foam accumulates on the surface of the ‘dal’ kept for long time in summer.

b. Why are naphthalene balls kept with clothes to be put away.
Answer:
- Naphthalene balls are balls of chemical pesticide and deodorant.
- They help to kill or repel insects such as moths, cockroaches, mice etc.
- Therefore, naphthalene balls are kept with clothes to be put away to prevent clothes from getting damaged.
5. Write down the modes of infection and the preventive measures against fungal diseases.
Answer:
- Mode of infection: Contact with infected person or his/her belongings like clothes.
- Preventive measure: Personal hygiene and avoid contact with infected person.
6. Match the pairs.
‘A’ group ‘B’ group
1. Rhizobium a. Food poisoning
2. Clostridium b. Nitrogen fixation
3. Penicillium c. Bakery products
4. Yeast d. Production of antibiotics
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – a),
(3 – d),
(4 – c)
7. Answer the following questions.
a. Which vaccines are given to infants? Why?
Answer:
- Hepatitis A and B, DTP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis.) Polio, MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella), Chicken pox, Influenza, Tetanus, BCG, Rotavirus, etc.
- Vaccines consist of dead or weakend microbes. When these are swallowed or injected, the body produces antibodies to fight them.
- These antibodies remain in the body and protect it from any future attack of the disease causing microbes.
- Therefore, vaccines are given to infants for preventing diseases.
b. How is a vaccine produced?
Answer:
- Vaccines are made using the disease causing bacteria or virus but in a form that will not harm the human beings.
- Vaccine is made from dead or weakened microbes or their toxins.
- Vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies which give life-long protection against the disease.
- There are specific vaccines for specific diseases.
c. How do antibiotics cure disease?
Answer:
Antibiotics cure diseases by destroying or preventing the growth of harmful micro-organisms.
d. Are the antibiotics given to humans and animals the same? Why?
Answer:
- Generally, antibiotics work against any harmful bacteria, whether it is attacking humans or animals.
-
But some of them are better suited to humans while some are better for animals. This is due to the adverse effects they show in different species.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- Also, the dosages of antibiotics for humans and animals differ.
e. Why is it necessary to safely store the pathogens of a disease against which vaccines are to be produced?
Answer:
- Pathogens are microbes which can cause diseases in us.
- For the preparation of a vaccine, a particular pathogen is cultured and grown in a laboratory.
- If these pathogens are not safely stored, they many get modified due to environmental factors, resulting in decrease in the efficiency of the vaccine.
- Also, the live pathogens may escape and cause diseases in us.
8. Answer the following questions in brief.
a. What are ‘broad-spectrum antibiotics’?
b. What is fermentation?
Answer:
- Yeast uses sugar for food.
- Yeast grows and multiplies rapidly due to the carbon compounds in the sugar solution.
- In the process of obtaining nutrition, yeast cells convert the carbohydrates in the food into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- Also, the bacteria Lactobacilli convert lactose, the sugar in milk into lactic acid.
- This process is called fermentation.
c. Define ‘Antibiotic’.
Answer:
- Carbon compounds obtained from some bacteria and fungi for destroying or preventing the growth of harmful micro -organisms are called antibiotics.
- Antibiotics, a discovery of the 20th century, have brought a revolution in the field of medicine.
- Antibiotics mainly act against bacteria. Some antibiotics can destroy protozoa.
- Some antibiotics are useful against a wide variety of bacteria they are called broad-spectrum antibiotics. Examples – Ampicillin, amoxicillin, tetracycline, etc.
-
When the pathogen cannot be identified even though the symptoms of the disease are visible, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- Whenever a pathogenic micro-organism is definitely known, then narrow-spectrum antibiotics are used. Examples: Penicillin, gentamycin, erythromycin, etc.
Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Useful and Harmful Microbes Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall?
Question 1.
What is meant by microbes? What are their characteristics?
Answer:
Microbes are tiny microscopic organisms which cannot be seen with the unaided eye.
Characteristics of Microbes.
- They are the smallest organisms on earth.
- They are composed of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells.
- They can be seen only with the help of a microscope.
- They are found in any kind of environment ranging from coolest polar regions to hottest of deserts. Also found in soil, water and air.
- Some of them are useful, whereas some of them are harmful micro-organisms.
Question 2.
How do you observe microbes?
Answer:
Microbes are observed using a microscope.
Answer the following.
Question 1.
Why are wineries located near Nashik in Maharashtra?
Answer:
-
Nashik in Maharashtra is the leading grape producer in the country as it has the soil suitable for the production of grapes.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- Glucose and fructose, the sugars present in grape juice are fermented with the help of yeast to produce wines. Therefore, wineries are located near Nashik in Maharashtra.
Question 2.
Find out the uses of fungi to plants and animals?
Answer:
- Fungi decompose the bodies of dead animals and convert them into simple carbon compounds. These substances easily mix with air, water and soil from where they are again absorbed by plants and enter the food chain.
- Some fungi living in symbiotic association with plants help to absorb water and inorganic compounds like nitrate and phosphate.
- Fungi are also used to derive antibiotics like penicillin which are useful to animals.
- Ants grow fungi in their anthill and obtain food from it.
- Some species of wasps and insects lay their eggs in the fungal bodies growing on trees, thus ensuring a food supply for their larvae.
Question 3.
What is the structure of lichen, a condiment? Where else is it used?
Answer:
- Lichen is a symbiotic association between a fungus and an algae (Cyanobacterium).
- Lichens are sensitive to environmental disturbances and are used in assessing air pollution in an area.
- Lichens are also used in making dyes, perfumes and in traditional medicines.
- A few lichen species are eaten by insects or animals such as reindeer.
Open-ended questions
Answer the following questions:
Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Useful And Harmful Microbes Exercise Question 1.
How is yoghurt made from milk? What exactly happens in this process?
Answer:
- Milk contains sugar called lactose which is broken down with help of Lactobacilli.
- Lactobacilli converts lactose into Lactic Acid. This process is called fermentation. As a result, the pH of milk decreases causing coagulation of milk proteins.
- Thus, milk proteins are separated from other constituents of milk and milk changes to yoghurt.
Useful And Harmful Microbes Class 9 Exercise Question 2.
Sometimes, you may notice a black powder or white discs floating on the pickle or murabba, when a jar is opened after a long time. What exactly is this? Why are such food items not good to eat?
Answer:
- A black powder or white disc floating on the pickle or murabba are fungi.
- Different fungal species depend on host (pickle and murabba) for their growth and reproduction.
-
During this process, fungi secretes mycotoxins which are poisonous chemicals; which ultimately spoil the food. Consuming such food can cause food poisoning.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- Therefore, such food items are not good to eat.
8 Useful And Harmful Microbes Class 9 Question 3.
How many different industries depend upon the Lactobacilli bacteria?
Answer:
Industries like milk products, cider, cocoa, pickles, pharmaceuticals depend on Lactobacilli bacteria.
Useful And Harmful Microbes Class 9 Question 4.
Which types of cottage industries and factories can be started in areas with abundant milk production?
Answer:
Cottage industries like the manufacture of milk products like ghee, cheese, paneer, curd, shrikhand, etc. and chocolate making can be started in areas with abundant milk production.
9th Class Science Chapter 8 Useful And Harmful Microbes Exercise Question 5.
Which changes do you notice in leather articles and gunny (jute) bags during the rainy season?
Answer:
In rainy season we can notice whitish-green cotton-like growth or black powder or white discs on leather articles and gunny (jute) bags during the rainy season as these articles are infected by fungus.
Class 9th Science Chapter 8 Useful And Harmful Microbes Exercise Question 6.
For how long afterwards can you use those articles?
Answer:
Those articles cannot be used for long as they wear out and do not last long.
Question 7.
Why do these articles not get spoilt during the summer or winter?
Answer:
- Spores of fungi can germinate when there is sufficient moisture.
- During summer or winter the weather is hot and dry and so fungus cannot grow in such weather.
- Also microbes cannot survive extreme hot or cold temperatures of summer or winter. Therefore, these articles do not get spoilt during summer or winter.
Question 8.
Why do doctors advise you to take yoghurt or buttermilk if you have indigestion or abdominal discomfort?
Answer:
- The Lactobacilli present in yoghurt or buttermilk help to restore the natural microbial flora in the intestine, thus helping in digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Also buttermilk helps to cool down the stomach and works as a laxative to ease the congestion during abdominal discomfort.
Question 9.
Sometimes, yoghurt becomes bitter and froths up. Why does this happen?
Answer:
- Sometimes yoghurt becomes bitter due to excess fermentation by bacteria.
- Excess amount of lactic acid is produced making the curd bitter.
Question 10.
Which different milk products are obtained at home by fermentation of the cream from the milk?
Answer:
Yoghurt, buttermilk, ghee, cheese, shrikhand, sour cream, etc.

Question 11.
Recently, it has been made compulsory in India and some other countries to mix 10% ethanol with fuels like petrol and diesel. What is the reason for this?
Answer:
- Ethanol is a smokeless and high quality fuel. So it helps to reduce pollution when mixed with petrol or diesel.
- As petrol or diesel is a fossil fuel less consumption of it will lead to resourceful use of it and making the country self-efficient by moving towards sustainable fuel like ethanol.
Question 12.
Chapattis made from wheat only swell up but bread becomes spongy, soft and easy to digest. Why is it so?
Answer:
- The chapatti dough has water, which on heating converts into steam and tries to escape.
- While doing so, it lifts up the upper layer of the chapatti. Therefore, the chapatti swells up.
- Bread is made by adding yeast to the flour.
- In the process of obtaining nutrition, the yeast cells convert the carbohydrates into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
- When this dough is baked, the carbon dioxide escapes out making the bread spongy, soft and easy to digest.
Question 13.
Salt is applied on the inner surface of pickle jars and the pickle is covered with oil. Why is this done?
Answer:
- Salt acts as a preservative. It prevents the growth of bacteria by forcing the microbes to lose water by osmosis. Hence, salt is applied on the inner surface of pickle jars.
- Pickle is covered with oil as oil acts as preservative. It seals off the air from the item that is being pickled and provides an environment in which microbes cannot grow.
Question 14.
Which preservatives are mixed with ready to eat foods to prevent them from spoiling?
Answer:
Common salt, sugar, sodium benzoate, citric acid, sodium meta-bi-sulfite etc. are some 1 of the preservatives mixed with ready-to-eat foods to prevent them from spoiling.
Question 15.
Which plant and animal diseases are caused by micro-organisms and what are the 1 measures to be taken against them? Answer:
Plant diseases:
- Citrus canker is a bacterial disease that affects 1 trees of citrus fruits.
- Rust of wheat is a fungal disease that affects wheat crops.
- Yellow vein mosaic is a viral disease which affects vegetables like bhindi (okra).
Preventive Measures:
- Seeds which are healthy and disease-free should be selected for sowing.
- Infected plants should be removed.
- Plants should be sprayed with fungicides and germicides to prevent diseases.

Animal diseases:
- Anthrax is a disease that affects cattle. It is caused by a bacterium.
- Foot and mouth is a dangerous disease in cattle caused by a virus.
- Rabies is a viral disease that affects animals.
Preventive Measures:
- The place where animals are kept should be washed with germicides.
- Animals should be dewormed regularly.
- The animals should be treated with necessary antibiotics for infectious diseases.
- They should be regularly vaccinated.
- Take the animals to a veterinary hospital for proper treatment and vaccination.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Bring ‘active dry yeast’ from the market. Mix a spoonful of yeast, two spoonfuls sugar with a sufficient quantity of lukewarm water in a bottle. Fix a colourless, transparent balloon on the mouth of that bottle.
What changes do you observe after 10 minutes? Mix limewater with the gas accumulated in the balloon. Collect that limewater in a beaker and observe it. What do you notice?
Answer:
- After 10 minutes, the balloon is filled with a gas and gets inflated.
- Lime water turns milky thus proving that the gas accumulated is carbon dioxide.
Class 9 Science Chapter 8 Useful and Harmful Microbes Additional Important Questions and Answers
Select the correct option:
Question 1.
The rod-shaped bacteria found in milk or buttermilk are called ……………………. .
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Clostridium
(c) Lactobacilli
(d) Saccharomyces
Answer:
(c) Lactobacilli

Question 2.
Yoghurt has a specific sour taste due to ……………………. .
(a) lactic acid
(b) citric acid
(c) acetic acid
(d) alcohol
Answer:
(a) lactic acid
Question 3.
Bacteria found in the root nodules of leguminous plants are ……………………. .
(a) clostridium
(b) streptococcus
(c) Lactobacilli
(d) Rhizobium
Answer:
(d) Rhizobium
Question 4.
A mutually beneficial relationship is called ……………………. .
(a) symbiosis
(b) parasitism
(c) autotropism
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) symbiosis
Question 5.
Carbon compounds obtained from bacteria and fungi for destroying or preventing the growth of harmful micro-organisms are called ……………………. .
(a) probiotics
(b) antibiotics
(c) antibodies
(d) antigens
Answer:
(b) antibiotics

Question 6.
Fungi release ……………………. into the food, making the food poisonous.
(a) cyanotoxins
(b) dinotoxins
(c) mycotoxins
(d) cytotoxins
Answer:
(c) mycotoxins
Question 7.
……………………. produce bottle-shaped endospores in adverse conditions.
(a) Lactobacilli
(b) Clostridium
(c) Yeast
(d) Rhizobium
Answer:
(b) Clostridium
Question 8.
……………………. conducted important research on the toxin responsible for gas gangrene and the antitoxin responsible for treating it.
(a) Ida Bengston
(b) Van Ermengem
(c) Louis Pasteur
(d) Alexander Fleming
Answer:
(a) Ida Bengston
Question 9.
……………………. is a smokeless and high quality fuel.
(a) Methanol
(b) Ethanol
(c) Petrol
(d) Diesel
Answer:
(b) Ethanol

Question 10.
Antibiotics mainly act against ……………………. .
(a) bacteria
(b) viruses
(c) algae
(d) fungi
Answer:
(a) Bacteria
Question 11.
……………………. is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
(a) Gentamycin
(b) Penicillin
(c) Amoxicillin
(d) Erythromycin
Answer:
(c) Amoxicillin
Question 12.
……………………. is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
(a) Ampicillin
(b) Amoxicillin
(c) Tetracyclin
(d) Penicillin
Answer:
(d) Penicillin
Question 13.
Antibiotic penicillin was discovered by ……………………. .
(a) Louis Pasteur
(b) Alexander Fleming
(c) Ida Bengston
(d) Van Ermengem
Answer:
(b) Alexander Fleming

Question 14.
……………………. proved that the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium botulinum is responsible for food poisoning.
(a) Louis Pasteur
(b) Ida Bengston
(c) Alexander Fleming
(d) Van Ermengem
Answer:
(d) Van Ermengem
Question 15.
AIDS is caused by ……………………. .
(a) virus
(b) bacteria
(c) protozoa
(d) fungi
Answer:
(a) Virus
Question 16.
Dengue is caused by ……………………. .
(a) droplets spread in air
(b) contact with infected person
(c) mosquito bite
(d) contaminated water and food
Answer:
(c)mosquitobite
Question 17.
Pneumonia is caused by ……………………. .
(a) virus
(b) bacteria
(c) fungi
(d) protozoa
Answer:
(b) bacteria

Question 18.
……………………. can be prevented by vaccination.
(a) Malaria
(b) AIDS
(c) Leprosy
(d) Chicken pox
Answer:
(d) Chicken pox
Question 19.
Malaria is caused by ……………………. .
(a) protozoa
(b) bacteria
(c) fungi
(d) virus
Answer:
(a) protozoa
Question 20.
Bird flu (H
7
N
9
) and swine flu (H
1
N
1
) are caused by ……………………. .
(a) bacteria
(b) protozoa
(c) fungi
(d) virus
Answer:
(d) virus
Question 21.
The Lactobacilli convert lactose, the sugar in the milk, into ……………………. .
(a) lactic acid
(b) acetic acid
(c) alcohol
(d) citric acid
Answer:
(a) lactic acid

Question 22.
The ……………………. destroys harmful microbes present in the milk.
(a) high pH
(b) neutral pH
(c) low pH
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) low pH
Question 23.
Lactobacilli kill the harmful bacteria like ……………………. present in the alimentary canal.
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Saccharomyces
(c) Clostridium
(d) Alcanivorax
Answer:
(c) Clostridium
Question 24.
During fermentation, yeast cells convert carbohydrates into ……………………. .
(a) glucose and fructose
(b) alcohol and carbon dioxide
(c) proteins and fats
(d) fatty acids and amino acids
Answer:
(b) alcohol and carbon dioxide
Question 25.
Molasses is fermented with the help of yeast called ……………………. .
(a) Yarrowia lipolytica
(b) Alcanivorax
(c) Rhizobia
(d) Saccharomyces
Answer:
(d) Saccharomyces
Question 26.
A yeast ……………………. is used to absorb the toxins released during the production of palm oil.
(a) Yarrowia lipolytica
(b) Alcanivorax
(c) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(d) Penicillium
Answer:
(a) Yarrowia lipolytica

Question 27.
The bacteria which spoil cooked food are ……………………. .
(a) Saccharomyces
(b) Lactobacilli
(c) Clostridium
(d) Rhizobium
Answer:
(c) Clostridium
Question 28.
……………………. can grow and reproduce only in living cells.
(a) Bacteria
(b) Viruses
(c) Fungi
(d) Protozoa
Answer:
(b) Viruses
Find the odd man out:
Question 1.
AIDS, Hepatitis, Leprosy, Dengue.
Answer:
Leprosy. It is caused by bacteria, whereas the rest are caused by viruses.
Question 2.
Cholera, Leprosy, Pneumonia, Influenza.
Answer:
Influenza. It is caused by a virus, whereas the rest are caused by bacteria.
Question 3.
Ampicillin, Amoxycillin, Penicillin, Tetracycline.
Answer:
Penicillin. It is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, whereas others are broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Question 4.
Tetracycline, Penicillin, Gentamycin, Erythromycin.
Answer:
Tetracycline. It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, whereas others are narrow-spectrum antibiotics.

Complete the analogy:
Question 1.
(1) Dengue : Virus :: Malaria : …………………………. .
(2) Hepatitis : Virus :: Pneumonia : …………………………. .
(3) Cholera : Bacteria :: Swine flu : …………………………. .
(4) Swine flu : HJNJ : : Bird Flu : …………………………. .
(5) Measles : Virus :: Ringworm : …………………………. .
(6) Yoghurt: Lactobacilli : : Bread : …………………………. .
(7) Oil spills: Alcanivorax :: Absorption of arsenic : …………………………. .
(8) Rhizobium : Nitrogen fixation : : Clostridium : …………………………. .
Answer:
(1) Protozoa
(2) Bacteria
(3) Virus
(4) HyN9
(5) Fungi
(6) Yeast
(7) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(8) Food poisoning.
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Leprosy | (a) Virus |
| (2) Ringworm | (b) Fungi |
| (3) Influenza | (c) Protozoa |
| (4) Malaria | (d) Bacteria |
Answer:
(1 – d),
(2 – b),
(3 – a),
(4 – c)
State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statements:
(1) Lactobacilli are aerobic bacteria.
(2) Lactobacilli converts lactose sugar into alcohol.
(3) Yoghurt has a specific sour taste due to acetic acid.
(4) The bacteria Clostridium are present in the root . nodules of leguminous plants.
(5) Yeast cell is a prokaryotic cell.
(6) The use of Rhizobium has helped to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers.
(7) Ethanol is a smokeless and high quality fuel.
(8) A yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for absorbing toxins released during palm oil production.
(9) Gentamycin is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
(10) Antibiotics mainly act against bacteria.

(11) Oil spills in oceans are cleared with the help of Clostridium bacteria.
(12) Tetracycline is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic.
(13) Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
(14) Penicillin is a group of antibiotics obtained from a fungus Saccharomyces.
(15) Antibiotic Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming.
(16) The bacteria Lactobacilli cause food-poisoning.
(17) Clostridium bacteria grow in aerobic conditions.
(18) AIDS is caused by a virus.
(19) Influenza is caused by a bacteria.
(20) Antibiotics useful to one person can be suggested to others also.
(21) Dengue is caused by a bacteria.
(22) Dandruff and ringworm are caused by fungi.
(23) Pneumonia is spread through droplets spread in air by infected person.
(24) Chicken pox spread due to contaminated food and water.
(25) Ida Bengston was honoured with the Typhoid Medal’ in 1947.
Answer:
(1) False. Lactobacilli are anaerobic bacteria.
(2) False. The Lactobacilli converts lactose sugar into lactic acid.
(3) False. Yogurt has a specific sour taste due to lactic acid.
(4) False. The bacteria Rhizobium are present in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
(5) False. Yeast cell is a eukaryotic cell.
(6) True.

(7) True.
(8) False. A yeast, Yarrowia lipolytic is used to absorb the toxins released during the production of palm oil.
(9) True.
(10) True.
(11) False. Oil spills in oceans are cleared with the help of Alcanivorax bacteria.
(12) False. Tetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
(13) True.
(14) False. Penicillin is a group of antibiotics obtained from a fungus Penicillium.
(15) True.
(16) False. The bacteria Clostridium cause food? poisoning.
(17) False. Clostridium bacteria grow in anaerobic conditions.
(18) True.
(19) False. Influenza is caused by a virus.
(20) False. Antibiotics useful to one person cannot be suggested to others as different diseases require different antibiotics.
(21) False. Dengue is caused by a virus.
(22) True.
(23) True.
(24) False. Chicken pox spread due to contact with infected person.
(25) False. Ida Bengston was honoured with the ‘Typhus Medal’ in 1947.
Complete the statements using the proper option from those given below. Explain the statements: (mycotoxins, budding, Rhizobium, molasses, endospores, broad-spectrum, Lactobacilli)
Question 1.
Lactobacilli bacteria are used for making yoghurt.
Answer:
The lactobacilli convert lactose, the sugar in the milk, into lactic acid. As a result, the pH of milk decreases causing a coagulation of milk proteins. Milk changes into yogurt.

Question 2.
The use of Rhizobium has helped to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers.
Answer:
Rhizobium bacteria are found in the root nodules of leguminous plants. They help to convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen compounds and provide it to the plants. This helps to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and their adverse effects.
Question 3.
Amoxicillin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Answer:
This antibiotic is useful against a wide variety of bacteria. It is used against pathogens which cannot be identified during symptoms of a disease.
Question 4.
Ethanol is produced by the fermentation of molasses.
Answer:
Molasses is produced from sugarcane juice. It is rich in carbohydrates. When it is fermented with the help of the yeast called Saccharomyces, ethanol (C2H5OH) is produced.
Question 5.
Clostridium bacteria produce bottle-shaped endospores.
Answer:
These endospores help them to survive in adverse conditions.
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Lactobacilli are used for making yoghurt from milk.
Answer:
- Lactobacilli convert lactose, the sugar in the milk, into lactic acid. This process is called fermentation.
- As a result, the pH of milk decreases causing coagulation of milk proteins.
- Thus, milk proteins are separated from other constituents of milk and milk changes into yoghurt.
- Yoghurt has a specific sour taste due to lactic acid. The low pH destroys harmful microbes present in the milk. Therefore, Lactobacilli are used for making yoghurt from milk.

Question 2.
Antibiotics should be taken only when prescribed by a doctor.
Answer:
- Antibiotics are a group of medicines used to kill disease-causing bacteria and certain protozoa.
- The doctor selects and prescribes the antibiotic best suited for our disease.
- If taken in extra dose, they can kill the useful bacteria present in our body.
- If the course of antibiotics is not completed, the bacteria develop resistance to that antibiotic making it ineffective.
- Therefore, antibiotics should be taken only when prescribed by a doctor.
Question 3.
Nowadays, seeds are coated with Rhizobial solution or powder before sowing.
Answer:
- When seeds coated with Rhizobial solution or powder are sown, Rhizobia enter the plantlets.
- This is called Rhizobial inoculation.
- Rhizobia can produce nitrogenous compounds from atmospheric nitrogen.
- This experiment has helped in the supply of nitrogen to cereal and other crops, besides leguminous crops.
- Therefore, nowadays seeds are coated with Rhizobial solution or powder before sowing.
Question 4.
Antibiotics are not effective against common cold or influenza.
Answer:
- Antibiotics are a group of medicines used to control inflections caused by bacteria.
- Common cold or influenza is caused by a virus.
- Antibiotics are not effective against viruses.
- Therefore, antibiotics are not effective against common cold or influenza.
Question 5.
Cotton fabrics, gunny bags, leather items and wooden items do not last long.
Answer:
- Microscopic spores of fungi are present in the air.
- If there is sufficient moisture, spores germinate on cotton fabric, gunny bags, leather, wooden items etc.
- The fungal hyphae (fibres of the fungus) penetrate deep into the material to obtain nutrition and to reproduce.
- This causes the materials to wear and become weak.
- As a result, cotton fabric, gunny bags, leather and wooden items do not last long.

Question 6.
Food on which fungi has grown cannot be eaten.
Answer:
- Various species of fungi grow on food items like pickles, murabba, jam, sauce, chutney etc.
- They use the nutrients in these food items for growth and reproduction.
- During this activity, fungi release mycotoxins, certain poisonous chemicals, into the food and thus food becomes poisonous.
- Hence, the food on which fungi have grown cannot be eaten.
Write short notes:
Question 1.
Rhizobial inoculation.
Answer:
- Nowadays, seeds are coated with rhizobial solution or powder before sowing.
- After sowing, Rhizobia enter the plantlets.
- This is called Rhizobial inoculation.
- This experiment has helped in the supply of nitrogen to cereal and other crops, besides leguminous crops.
Question 2.
Bio-remediation.
Answer:
- Bio-remediation is a technique that involves the use of organisms to break down environmental pollutants.
- Generally, fungi like yeast and bacteria are used for bio-remediation.
- A yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica is used to absorb the toxins released during the production of palm oil and the heavy metals and minerals released in some other industrial processes.
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for absorption of a pollutant, arsenic.
- Oil spills in oceans are cleaned with the help of Alcanivorax bacteria.
Question 4.
Clostridium.
Answer:
- Clostridium are the bacteria that spoil food.
- Out of about 100 different species of this bacterium, some are free living in the soil whereas some live in the alimentary canals of humans and other animals.
- These bacteria are rod-shaped and produce bottle-shaped endospores in adverse conditions.
- One special characteristic of these bacteria is that they cannot withstand the normal oxygen level of the air because they grow in anaerobic conditions.
Write down the mode of infection and preventive measures for the following:
Question 1.
Write down the causative pathogen, mode of infection and preventive measures of AIDS.
Answer:
- Causative Pathogen: Virus.
- Mode of infection: Through blood and semen of infected person and milk of mother suffering from AIDS.
- Preventive measure: Safe sexual contact, avoid resuse of needles and injections.

Question 2.
Write down the modes of infection and preventive measures against Bird Flu (H7N9) and Swine Flu (HjN.,).
Answer:
- Mode of infection: Contact with infected birds and animals.
- Preventive measure: Personal hygiene, properly cooked meat.
Question 3.
Write down the modes of infection and preventive measures against Malaria and dengue.
Answer:
- Mode of infection: Mosquito bite, unclean surroundings.
- Preventive measure: Cleanliness of surroundings, preventing stagnation of water, controlling mosquitoes.
Question 4.
Write down the modes of infection and preventive measures against Pneumonia.
Answer:
- Mode of infection: Droplets spread in air by infected person.
- Preventive measure: Vaccination, avoiding contact with infected person.
Question 5.
Write down the modes of infection and preventive measures for leprosy.
Answer:
- Mode of infection: Long term contact with infected person.
- Preventive measure: Avoiding contact with infected persons and their belongings.
Question 5.
What are the modes of infection and preventive measures for Hepatitis?
Answer:
- Mode of infection: Contaminated water and food.
- Preventive measure: Use clean and filtered water, proper storage of food.
Question 6.
What are the modes of infection and preventive measures for Influenza.
Answer:
- Mode of infection: Contact with infected person.
- Preventive measure: Personal hygiene and avoiding contact with infected person.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
How is bread made?
Answer:
- Bread is made using flour, yeast, salt and water. The yeast uses sugar as food.
-
In the process of obtaining nutrition, yeast cells convert the carbohydrates into alcohol and carbon dioxide. This process is called fermentation.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- The bubbles of carbon dioxide given off cause the dough to rise.
- This dough can be used to make bread.
- When this dough is baked, more bubbles of carbon dioxide reformed due to heat. As the gas escapes, the bread rises and becomes soft and fluffy.
Question 2.
What is the advantage of Rhizobium to farmers?
Answer:
- The use of Rhizobium has helped to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and thereby their adverse effects.
- It has also helped to reduce expenses on fertilizers and thus benefited the farmers.
Question 3.
How can we observe Lactobacilli in buttermilk?
Answer:
- Smear a drop of fresh buttermilk on a glass slide.
- Stain it with methylene blue and put a coverslip over it.
- Observe the smear under the 10X objective of a compound microscope and then with the more powerful 60X objective.
- The blue rod-shaped organisms moving about are Lactobacilli.
Question 4.
What is symbiosis? Give example.
Answer:
- Symbiosis is a mutually beneficial relationship.
- Example: Rhizobium living in root nodules of leguminous plants supply nitrates, nitrites and amino acids to that plant and in exchange get energy in the form of carbohydrates.
Complete the following table:
Question 1.
The spread and prevention of disease
Answer:
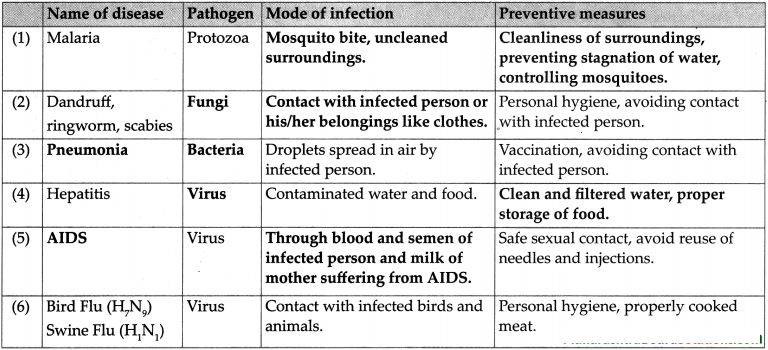


Question 2.
Different species of Clostridium bacteria and the diseases caused by them.
Answer:
| Species of Clostridium | Diseases |
| Clostridium tetani | Tetanus |
| Clostridium perfringens | Food poisoning |
| Clostridium botulinum | Botulism (Paralysis of muscles) |
| Clostridium difficile | Colitis (Infection of the intestine) |
Answer in detail:
Question 1.
How is alcohol produced?
Answer:
- Alcohol is often produced along with sugar in sugar factories.
- Molasses is produced from sugarcane juice. It is rich in carbohydrates.
- Molasses is fermented with the help of the yeast Saccharomyces.
- In this process, ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH) alcohol is produced as a primary product and ester and other alcohols are produced as secondary products.
- Besides molasses, maize, barley and other grains are also used for industrial production of alcohol.
- Glucose and fructose, the sugars present in grape juice are also fermented with the help of yeast to produce alcohol which is used to make wines.
Question 2.
Give the uses of Lactobacilli.
Answer:
Uses of Lactobacilli:
- Various milk products like yoghurt, buttermilk, ghee, cheese, shrikhand, etc. can be obtained by fermentation of milk.
- Lactobacilli fermentation is useful for large scale production of cider, cocoa, pickles of vegetables etc.
- Lactobacilli and some other useful microbes taken together are used to treat abdominal discomfort.
- Leavened fodder offered to domestic cattle like cows and buffaloes is fodder fermented with the help of lactobacilli.
- The Lactobacilli fermentation process is used to make wine and some types of bread.
Question 3.
What is Penicillin? What is it used for?
Answer:
- Penicillin is a group of antibiotics obtained from a fungus, penicillium.
- It is used for controlling the infections caused by bacteria like Staphylococci, Clostridia, Streptococci, etc.
- Medicines containing Penicillin are useful to treat certain bacterial infections of the ear, nose, throat and skin as well as diseases like Pneumonia and scarlet fever.

Question 4.
How was the antibiotic penicillin discovered?
Answer:
- Alexander Fleming, a professor of microbiology at St. Mary’s Hospital had cultured varieties of bacteria and fungi in petri dishes in his laboratory.
- On 3rd September 1928, while observing Staphylococci cultures, he made an interesting observation in one petri dish.
- In that petri dish, fungal colonies had grown but the area around those colonies was clean and clear, i.e. the bacteria had actually been destroyed.
- After further studies, he confirmed that the fungus growing there was Penicillium and its secretion had destroyed the bacterial colonies.
- Thus, the first antibiotic – penicillin had been discovered accidentlly and this formed the basis to find cures for incurable diseases.
Question 5.
What are the precautions to be followed while taking antibiotics?
Answer:
- Antibiotics should be taken only when prescribed by a doctor.
- Don’t purchase any antibiotic from medical stores without a prescription from a doctor.
- Don’t consume antibiotics on your own to treat common diseases like a throat infection, common cold or influenza.
- Even if you feel well before completing of the prescribed course of the antibiotics, you must continue and complete it.
- Don’t suggest to others the antibiotics which were useful to you.
Question 6.
How can we observe Rhizobium bacteria in the roots of leguminous plant?
Answer:
-
Take a plantlet of fenugreek, groundnut or any other bean and sterilize it with a 3 to 5% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- Afterwards, keep it in a 70% solution of ethyl alcohol for 4 to 5 minutes.
- Clean the roots with sterile water and take thin sections of the root nodules.
- Select a good section and place it an a solution of saffranin for 2 to 3 minutes.
- Place the stained section on a glass slide, cover it with a coverslip and observe it under the compound microscope. The pinkish rod-shaped organisms are the Rhizobium bacteria.
