Differential Equation and Applications Class 12 Commerce Maths 1 Chapter 8 Exercise 8.3 Answers Maharashtra Board
Balbharati Maharashtra State Board Std 12 Commerce Statistics Part 1 Digest Pdf Chapter 8 Differential Equation and Applications Ex 8.3 Questions and Answers.
Std 12 Maths 1 Exercise 8.3 Solutions Commerce Maths
Question 1.
Solve the following differential equations:
(i) \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = x
2
y + y
Solution:
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = x
2
y + y
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y(x
2
+ 1)
∴ \(\frac{1}{y}\) dy = (x
2
+ 1) dx
Integrating, we get
∫\(\frac{1}{y}\) dy = ∫(x
2
+ 1) dx
∴ log |y|= \(\frac{x^{3}}{3}\) + x + c
This is the general solution.
(ii) \(\frac{d \theta}{d t}=-k\left(\theta-\theta_{0}\right)\)
Solution:
\(\frac{d \theta}{d t}=-k\left(\theta-\theta_{0}\right)\)
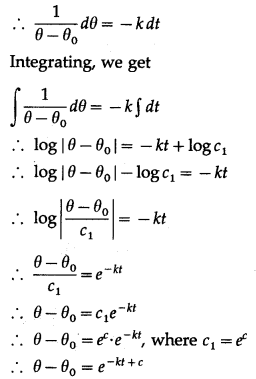
This is the general solution.

(iii) (x
2
– yx
2
) dy + (y
2
+ xy
2
) dx = 0
Solution:
(x
2
– yx
2
) dy + (y
2
+ xy
2
) dx = 0
∴ x
2
(1 – y) dy + y
2
(1 + x) dx = 0
∴ \(\frac{1-y}{y^{2}} d y+\frac{1+x}{x^{2}} d x=0\)
Integrating, we get
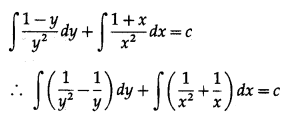
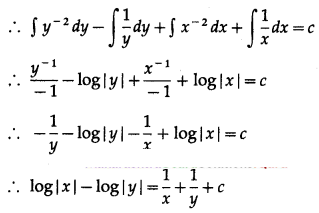
This is the general solution.
(iv) \(y^{3}-\frac{d y}{d x}=x \frac{d y}{d x}\)
Solution:
\(y^{3}-\frac{d y}{d x}=x \frac{d y}{d x}\)
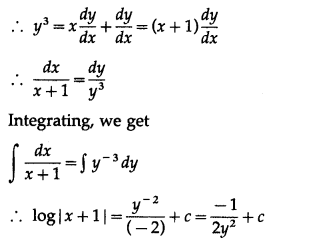
∴ 2y
2
log |x + 1| = 2cy
2
– 1 is the required solution.

Question 2.
For each of the following differential equations find the particular solution:
(i) (x – y
2
x) dx – (y + x
2
y) dy = 0, when x = 2, y = 0.
Solution:
(x – y
2
x) dx – (y + x
2
y) dy = 0
∴ x(1 – y
2
) dx – y(1 + x
2
) dy = 0

∴ the general solution is
log |1 + x
2
| + log |1 – y
2
| = log c, where c
1
= log c
∴ log |(1 + x
2
)(1 – y
2
) | = log c
∴ (1 + x
2
)(1 – y
2
) = c
When x = 2, y = 0, we have
(1 + 4)(1 – 0) = c
∴ c = 5
∴ the particular solution is (1 + x
2
)(1 – y
2
) = 5.
(ii) (x + 1) \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) -1 = 2e
-y
, when y = 0, x = 1.
Solution:
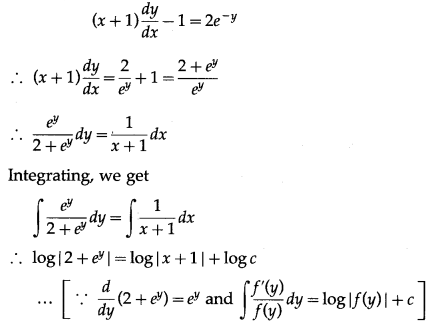
∴ log |2 + e
y
| = log |c(x + 1)|
∴ 2 + e
y
= c(x + 1)
This is the general solution.
Now, y = 0, when x = 1
∴ 2 + e
0
= c(1 + 1)
∴ 3 = 2c
∴ c = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
∴ the particular solution is
2 + e
y
= \(\frac{3}{2}\)(x + 1)
∴ 4 + 2e
y
= 3x + 3
∴ 3x – 2e
y
– 1 = 0

(iii) y(1 + log x) \(\frac{d x}{d y}\) – x log x = 0, when x = e, y = e
2
.
Solution:
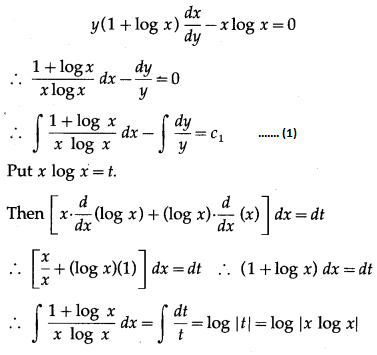
∴ from (1), the general solution is
log |x log x| – log |y| = log c, where c
1
= log c
∴ log |\(\frac{x \log x}{y}\)| = log c
∴ \(\frac{x \log x}{y}\) = c
∴ x log x = cy
This is the general solution.
Now, y = e
2
, when x = e
e log e = ce
2
1 = ce ……[∵ log e = 1]
c = \(\frac{1}{e}\)
∴ the particular solution is x log x = (\(\frac{1}{e}\)) y
∴ y = e
x
log x
(iv) \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 4x + y + 1, when y = 1, x = 0.
Solution:
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 4x + y + 1
Put 4x + y + 1 = v

∴ log |v + 4| = x + c
∴ log |4x + y + 1 + 4| = x + c
i.e. log |4x + y + 5| = x + c
This is the general solution.
Now, y = 1 when x = 0
∴ log|0 + 1 + 5| = 0 + c,
i.e. c = log 6
∴ the particular solution is
log |4x + y + 5| = x + log 6
∴ \(\log \left|\frac{4 x+y+5}{6}\right|\) = x