Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Carbon: An Important Element Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 9 Science Chapter 13 Carbon: An Important Element Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Carbon: An Important Element Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Select the proper option and complete the statements
(single, all, double, ionic, carbon, give and take, hydrogen, multiple, share, most, covalent)
a. A carbon atom forms a ….……………. bond with other atoms. In this bond the two atoms ….electrons.
Answer:
covalent, share

b. All the carbon bonds in a saturated hydrocarbon ….……………. electrons.
Answer:
share
c. At least one carbon bond in an unsaturated hydrocarbon is ….…………… .
Answer:
multiple
d. ….……………. is the essential element in all the organic compounds.
Answer:
Carbon
e. The element hydrogen is present in ….. organic compound.
Answer:
all
2. Answer the following questions
a. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels?
Answer:
(i) The name ‘carbon’ is derived from Latin word ‘carbo’meaning coal. In the earth’s crust, carbon is present to an extent of approximately 0.27% in the form of carbonate, coal and petroleum. One of the non-crystalline and amorphous form of carbon is coal. Coal is a fossil fuel.
(ii) Peat, lignite, bituminous and anthracite are the four types of coal in the increasing order of their carbon content and heat produced respectively. Charcoal and coke are the other amorphous forms of carbon used as fuel.
(iii) Compounds of carbon such as hydrocarbons consist of carbon and hydrogen and they are easily combustible. For example, methane (CH 4 ) which occurs in natural gas is highly inflammable. It bums by reacting with oxygen to give a bluish flame. In this reaction, 213 Kcal/mol of heat is given out. Methane bums completely.
Chemical reaction:
CH
4
+ 2O
2
→ CO
2
+ 2H
2
O + Heat
(iv) Thus when hydrocarbons are burnt in air, large amount of heat is evolved with formation of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O). Due to evolution of heat on combustion, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels.

b. In which compound forms does carbon occur?
Answer:
Carbon in its combined state exists as various compounds such as:
- Carbon dioxide and in the form of carbonates such as calcium carbonate, marble, calamine (ZnCO 3 ).
- Fossil fuel – coal, petroleum, natural gas.
- Carbonaceous nutrients – carbohydrates, proteins, fats.
- Natural fibres – cotton, wool, silk.
- Hydrocarbons – compound of carbon and hydrogen.
c. Write the uses of the diamond.
Answer:
Uses of diamonds are:
- Diamonds are used in glass cutting and rock drilling machines.
- Diamonds are used in ornaments.
- Diamond knives are used in the eye surgery.
- Diamond dust is used for polishing other diamonds.
- Diamond is used to make windows giving protection from radiation in space and in artificial satellites.
3. Explain the difference:
a. Diamond and graphite.
Answer:
| Diamond | Graphite |
| (i) Diamond is a brilliant, hard and crystalline allotrope of carbon. | (i) Graphite is a black, soft, brittle and slippery crystalline allotrope of carbon. |
| (ii) In diamonds, every carbon atom is bonded to four neighbouring atoms by covalent bonds forming tetragonal three dimensional structure which makes it very hard. | (ii) In graphite, every carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds in such a way that a hexagonal layered structure is formed. A graphite crystal is made of many such layers of carbon atoms. These layers slip over each other on applying pressure. |
| (iii) Density of diamond is 3.5 g/cm 3 . | (iii) Density of graphite is 1.9 to 2.3 g/cm 3 . |
| (iv) Diamond is a bad conductor of electricity as it does not have free electrons. | (iv) Inside each layer of graphite, free electrons move continuously within the entire layer. Hence, graphite is a good conductor of electricity. |
b. Crystalline and non-crystalline forms of carbon.
Answer:
| Crystalline forms of carbon | Non-crystalline forms of carbon |
|
(i) A crystalline form has a regular and definite arrangement of atoms.
(ii) They have high melting points and boiling points. (iii) A crystalline form has a definite geometrical shape, sharp edges and plane surfaces. (iv) Diamond, graphite and fullerene are different crystalline forms of carbon. |
(i) A non-crystalline form does not have a regular and definite arrangement of atoms.
(ii) They have low melting points and boiling points. (iii) They are amorphous, hence, they do not have definite geometrical shape. (iv) Coal, charcoal and coke are different noncrystalline/amorphous forms of carbon. |

4. Write scientific reasons
a. Graphite is a conductor of electricity.
Answer:
- In graphite, each carbon is bonded to three other carbon atoms in such a way that a hexagonal layered structure is formed.
- Due to this structure, graphite has free electrons available.
- These free electrons move continuously within the entire layer.
- Hence, graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
b. Graphite is not used in ornaments.
Answer:
- Graphite is a black, soft, brittle and dull form of carbon.
- It is neither malleable nor ductile.
- These properties of graphite make it unsuitable for making of ornaments.
- Hence, graphite is not used for making ornaments.
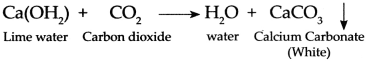
c. Limewater turns milky when CO
2
is passed through it.
Answer:
- Limewater traditionally means a weak solution of the alkali calcium hydroxide Ca(OH) 2 .
- When CO 2 is passed through limewater, it reacts with calcium hydroxide to form insoluble particulates (precipitate) of Calcium carbonate (CaCO 3 ).
- Calcium carbonate is weak basic salt and this gives a milky white precipitate.
- Hence, lime water turns milky when CO 2 gas is passed through it.
d. Biogas is an eco-friendly fuel.
Answer:
- Biogas is formed by the decomposition of animal dung, dry leaves, wet garbage in a biogas plant.
- This produces methane gas also called biogas.
- Biogas is a very cheap fuel option which meets the demand for cooking gas.
- Biogas is eco-friendly as it contains about 55% to 60% of methane and rest is carbon dioxide, hence, on combustion it does not produce harmful gases which cause pollution.
- Biogas is a fuel which is convenient to use and in addition to this it produces a very good manure as a side product of the process.
- Hence, biogas is an eco-friendly fuel.

5. Explain the following.
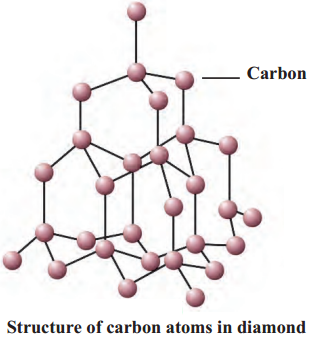
a. Diamond, graphite and fullerenes are crystalline forms of carbon.
Answer:
- Carbon exhibits a property of allotropy in which an element exists in more than one form in nature.
- The chemical properties of these different forms are the same but their physical properties are different.
- Carbon exists in crystalline as well as non-crystalline (amorphous form).
- Crystalline form has a regular and definite arrangement of atoms. They have high melting points and boiling points.
- A crystalline form has a definite geometrical shape, sharp edges and plane surfaces.
- Carbon has three crystalline allotropes such as diamond, graphite and fullerene.
- In the structure of diamond, every carbon atom is bonded to four neighbouring atoms by covalent bonds.
- Therefore, diamond has a tetragonal three dimensional structure which makes it very hard.
- Brilliant and pure diamond is the hardest natural substance.
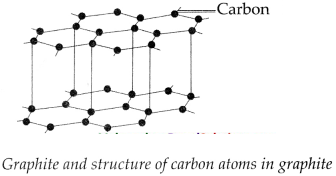
- In the structure of graphite, every carbon atom in graphite is bonded to three other carbon atoms in such a way that a hexagonal layered structure is formed.
- A graphite crystal is made of many sheets or layers of carbon atoms.
- These layers slip over each other on applying pressure. One layer of graphite is called graphene.
- Fullerene is rarely found in nature. It is found in soot and in interstellar space.
- The first example of fullerene is Buckminster fullerene (C 60 ).
- This allotrope of carbon is named fullerene after the architect.
- Richard Buckminster Fuller because the structure of C 60 resembles the structure of the geodesic dome he designed.
- (xi) Molecules of fullerenes are found in the form of buckyballs and buckytubes.
- (xii) There are 30 to 900 carbon atoms in one molecule of a fullerene. , C 60 , C 70 , C 76 , C 82 and C 86 are other examples of fullerene. Their molecules occur in small numbers in soot.
b. Methane is called marsh gas.
Answer:
- Methane is formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter in swamps or marshy areas.
- As methane gas bubbles out from marshy area, it is called as marsh gas.
c. Petrol, diesel, coal are fossil fuels.
Answer:
(i) A fossil fuel is a fuel formed by natural processes, such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. Fossil fuels contain high percentage of carbon. The word carbon is derived from the Latin word ‘Carbo’ meaning coal.
(ii) Coal is formed from the remains of trees and other vegetation. Approximately 350 million years ago, these remains were trapped on the bottom of swamps, accumulating layer after layer and creating a dense material called peat. As this peat was buried under more and more ground, the high temperature and pressure transformed it into coal.
(iii) Petrol and diesel are obtained from mineral oil. Mineral oil also called as crude oil or petroleum oil is formed from the remains of plants and animals that lived in the seas millions of years ago. This plant and animal matter has been drawn down and subjected to extremes of temperature and pressure over millions of years ago.

(iv) Mineral oil is commonly formed in rocks under the sea bed. The word petroleum is derived from Latin word ‘Rock oil’. Petrol and Diesel are obtained from mineral oil by the process called as fractional distillation.
Thus petrol, diesel and coal are fossil fuels.
d. Uses of various allotropes of carbon.
e. Use of CO
2
in fire extinguisher.
Answer:
- CO 2 based fire extinguishers do not cause corrosion and are non-conductors of electricity.
- It is beyond their capacity to extinguish a big fire.
- Therefore these fire extinguishers are used to extinguish small scale fire of electrical and electronic equipments.
f. Practical uses of CO
2
.
Answer:
Practical uses of CO
2
are:
- CO 2 is used to make aerated drinks.
- CO 2 obtained by chemical reaction or kept under pressure is used in fire extinguishers. Liquified CO 2 is used to remove caffeine from coffee.
- Liquid CO 2 is used as solvent in modem eco-friendly dry cleaning.
- Solid carbon dioxide is used in cold storage and to keep milk and milk products and frozen substances cool during transport. It is also used for getting special effects of a mist in dramas and movies.
6. Write two physical properties each.
a. Diamond
Answer:
Properties of diamond are:
- Brilliant and pure diamond is the hardest natural substance.
- The density of diamond is 3.5 g/cm 3 .
- The melting point of diamond is 3500 °C.
- When a diamond is heated at 800 °C in the presence of oxygen, CO 2 is given away. In this process no other product besides CO 2 is formed.
- Diamond does not dissolve in any solvent.
- Acids/bases have no effect on diamond.
- Diamond is a bad conductor of electricity as it does not have free electrons.

b. Charcoal
Answer:
- The charcoal that is made from animals is made from their bones, horns, etc.
- On the other hand, the charcoal made from plants is formed by combustion of wood in an insufficient supply of air.
c. Fullerene
Answer:
Properties of fullerenes are:
- Molecules of fullerenes are found in the form of buckyballs and buckytubes.
- There are 30 to 900 carbon atoms in one molecule of a fullerene.
- Fullerenes are soluble in organic solvents such as carbon disulphide, chlorobenzene.
7. Complete the following Chemical reactions.
1. ………………..+………………..→ CO + 2H
2
O + Heat
2. ………………..+………………..→ HCl + Cl + HCl
3. 2 NaOH + CO
2
→………………..+………………..
Answer:
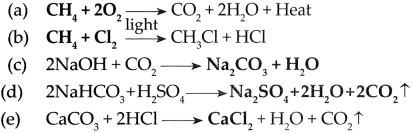
8. Write answers to the following in detail.
a. What are the different types of coal? What are their uses?
Answer:
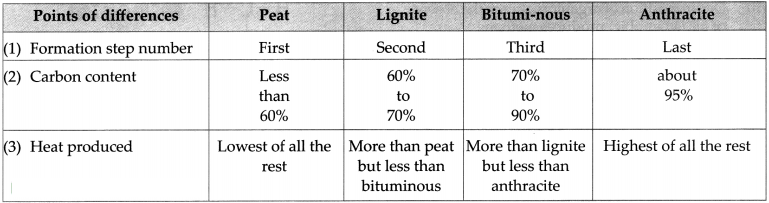
Coal is a fossil fuel. It contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. It also contains nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur. It occurs in the solid state. It is of four types.
-
Peat: Formation of peat is the first step in the formation of coal. It contains a high proportion
of water and less than 60% of carbon. Therefore, not much heat can be obtained from peat. - Lignite: Peat was transformed into Lignite due to increased pressure and temperature inside the earth. It contains 60 to 70% of carbon.- Lignite is the second step of the formation of coal.
- Bituminous coal: Bituminous coal was formed as the third step of formation of coal. It contains 70 to 90% of carbon.
- Anthracite: Anthracite is known as the pure form of coal. This coal is hard and contains about 95% of carbon.
Uses of coal:
- Coal is used as fuel in factories and homes.
- Coal is used to obtain coke, coal gas and coal tar.
- Coal is used in thermal power plants for generation of electricity.

b. How will you prove experimentally that graphite is good conductor of electricity?
Answer:
Apparatus required: Lead pendi, electrical wires, battery/cell, small bulb, etc.
Step-I: Remove the lead from a pencil and assemble the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
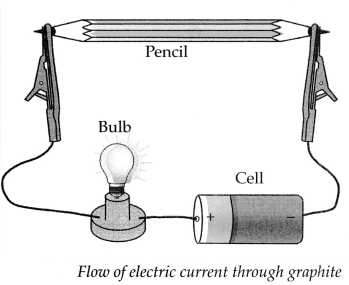
Step-II:
- Start the electric current in the circuit, the moment the electric current is passed through the circuit, the bulb glows.
- This experiment proves that graphite is a good conductor of electricity as graphite has free electrons moving continuously within the entire layer and these free electrons conduct electricity in the lead of the pencil.
c. Explain the properties of carbon.
Answer:
Allotropic nature of Carbon: Some elements occur in nature in more than one form. The chemical properties of these different forms are the same but their physical properties are different. This property of elements is called allotropy. Carbon shows the property of allotropy.
Carbon allotropes are of two types:
(A) Crystalline forms:
Carbon has three crystalline allotropes: Diamond, Graphite and Fullerene. Properties of crystalline forms of carbon are as follows:
- A crystalline form has a regular and definite arrangement of atoms.
- They are made up of only carbon atoms.
- They have high melting points and boiling points.
- A crystalline form has a definite geometrical shape, sharp edges and plane surfaces.
(B) Amorphous forms or non-crystalline forms: Coal, charcoal, coke are the non-crystalline forms of carbon.
Properties of non-crystalline forms of carbon are as follows:
- The arrangement of carbon atoms in this form is not regular.
- Apart from carbon atoms, they also contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur atoms.
- Compared to a crystalline form, they have low melting and boiling points.
- Most of them are used as fuels.

d. Classify carbon.
Answer:
Carbon is classified as follows:
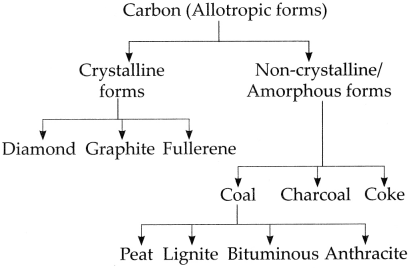
9. How will you verify the properties of carbon dioxide?
Answer:
Properties of carbon dioxide can be verified in the following ways:
- When a burning candle is placed in a gas jar of carbon dioxide, it extinguishes indicating that carbon dioxide is a non-combustible gas and does not support combustion.
- When carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, it turns lime water milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
- Moist blue litmus turns red in a gas jar of carbon dioxide indicating, it is acidic in nature.
- Carbon dioxide is fairly soluble in water, it dissolves in water forming carbonic acid.
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Carbon: An Important Element Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall?
Question 1.
Whatremains behind on complete combustion of any organic compound?
Answer:
A black colour substance ‘Carbon’ remains behind on complete combustion of any organic compound.
Question 2.
What type of element is carbon? Give some information about it.
Answer:
- Carbon is a non-metallic element. It is available ‘ abundantly in the nature and occurs in free as well as combined state.
- Carbon in free state is found as diamond and graphite and in combined state it is present to the extent of approximately 0.27% in the form of carbonate, coal, petroleum.
- In atmosphere, the proportion of carbon in the form of carbon dioxide is approximately 0.03%.

Question 3.
What is an element? What are the different types of elements.
Answer:
- A substance which cannot be decomposed into simple substances by any physical or simple chemical method is called as an Element.
- An element is composed of atoms of only one kind.
-
The different types of elements are:
(a) Metals – Examples: Gold, Silver, etc.
(b) Non-metals – Examples: Carbon, Sulphur, etc.
(c) Metalloids – Examples: Silicon, Antimony, etc.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Does an electric charge form on atoms when a covalent bond is formed between them? Why is a single bond between two carbon atoms strong and stable?
Answer:
- No, electric charge is not formed on atoms when a covalent bond is formed between them. This is because covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons.
- Therefore, there is no change in number of electrons and protons in these atoms and they remain electrically neutral.
- Covalent bonds occur when electrons are shared between two atoms. A single covalent bond is formed when only one pair of electrons is shared between atoms.
- In this sharing, the atomic orbitals directly overlap between the nuclei of two atoms forming the strongest type of covalent bond called as sigma bond.
- Hence, a single covalent bond between two carbon atoms is strong and stable.

Question 2.
In which of the solvents – water, kerosene and cooking oil does the coal powder dissolve?
Answer:
Solvents such as water, kerosene and cooking oil do not dissolve coal powder in them.
Question 3.
What inference will you draw about the solubility of carbon?
Answer:
Carbon is insoluble in water, kerosene and cooking oil.
Question 4.
Is the density of CO
2
more or less than that of air?
Answer:
- Density is defined as mass per unit volume of a substance, expressed as kilograms per cubic meter.
- At standard temperature and pressure, the density of air is 1.29 kg/m 3 . While that of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is 1.79 kg/m 3 . Hence, density of CO 2 is more than that of air.
Question 5.
What is a compound? How are compounds formed?
Answer:
- A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded with each other in definite proportion by weight.
-
When atoms or two or more different elements chemically react with each other in a definite proportion by weight, a compound is formed.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- The properties of a compound are altogether different from its constituent elements.
- Example: Pure water is a compound made up of two elements Hydrogen and Oxygen. Hydrogen (H) atoms and oxygen (O) atoms have chemically reacted with each other in definite proportion to form a compound-water (H 2 O). The proportion of hydrogen and oxygen in water by volume is 2 : 1 and by weight is 1 :8 respectively.
- The properties of water are altogether different from the properties of its constituent elements, hydrogen and oxygen.
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Carbon: An Important Element Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose and write the correct option:
Question 1.
The organic compound having double or triple bond in them is termed as
(a) unsaturated
(b) inorganic
(c) saturated
(d) complete
Answer:
(a) Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Question 2.
Covalent compounds are generally soluble in solvents.
(a) inorganic
(b) organic
(c) mixed
(d) mineral
Answer:
(b) organic
Question 3.
Methane is also called as
(a) maha gas
(b) mar’s gas
(c) Anthracite
(d) marsh gas
Answer:
(d) Marsh gas

Question 4.
is an alio trope of carbon used to make ornaments.
Answer:
Diamond
Question 5.
The number of valence electrons in carbon is
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 3
Answer:
(a) 4
Question 6.
In saturated hydrocarbons, two carbon atoms are linked by
(a) double bond
(b) triple bond
(c) multiple bond
(d) single bond
Answer:
(d) single bond
Question 7.
Carbon has 4 valence electrons in its outermost shell, hence, it is
(a) divalent
(b) tetravalent
(c) trivalent
(d) pentavalent
Answer:
(b) tetravalent

Question 8.
Methanogenic bacteria act on the organic acids to produce
(a) oxygen gas
(b) nitrogen gas
(c) methane gas
(d) carbon dioxide gas
Answer:
(c) Methane gas
Question 9.
is used to remove caffeine from coffee.
(a) liquefied O
2
(b) liquefied N
2
(c) liquefied CO
2
(d) liquefied CH
4
Answer:
(c) Liquified CO
2
Question 10.
Exhaled air contains about CO
2
.
(a) 4%
(b) 3%
(c) 5%
(d) 6%
Answer:
(a) 4%
Question 11.
Electronic configuration of carbon is
(a) (2, 2)
(b) (2,4)
(c) (2, 5,4)
(d) (2, 6)
Answer:
(b) 2, 4

Question 12.
Molecular formula of ethane is
(a) C
3
H
4
(b) C
2
H
4
(c) C
2
H
6
(d) C
2
H
2
Answer:
(c) C
2
H
6
Question 13.
Molecular mass of carbon dioxide is
(a) 28
(b) 22
(c) 56
(d) 44
Answer:
(d) 44
Question 14.
On heating a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide gases at 300°C in the presence of nickel (catalyst) is formed.
(a) carbon dioxide gas
(b) oxygen gas
(c) methane gas
(d) ethylene gas
Answer:
(c) methane gas
Question 15.
Ethane with molecular formula C
2
H
6
has covalent bonds.
(a) six
(b) seven
(c) eight
(d) nine
Answer:
(b) seven

Question 15.
Weight of Kohinoor Diamond was
(a) 186 carats
(b) 27 carats
(c) 252 carats
(d) 23 carats
Answer:
(a) 186 carats
Question 16.
Covalent compounds have
(a) high melting point
(b) low melting point
(c) moderate melting point
(d) very high melting point
Answer:
(b) low melting point
Question 17.
Methane is
(a) C
2
H
6
(b) C
3
H
8
(C) CH
2
(d) CH
4
Answer:
(d) CH
4
Question 18.
Wohler, a German scientist synthesized the compound from an inorganic compound ammonium cyanate.
(a) methane
(b) ethylene
(c) urea
(d) acetic acid
Answer:
(c) urea

Question 19.
Molecular mass of methane is
(a) 19
(b) 16
(c) 17
(d) 18
Answer:
(b) 16
Question 20.
coal contains highest percentage of carbon.
(a) Bituminous
(b) Peat
(c) Anthracite
(d) Lignite
Answer:
(c) Anthracite
Question 21.
H
2
C = CH
2
is ……………………… .
(a) Propane
(b) Ethyne
(c) Ethane
(d) Ethene
Answer:
(d) Ethene
Question 22.
CH
3
– C = CH is ……………………… .
(a) Propene
(b) Propyne
(c) Ethyne
(d) Ethene
Answer:
(b) Propyne

Question 23.
Carbon dioxide gas is not used in
(a) photosynthesis
(b) aerated drinks
(c) glass cutting
(d) fire extinguishers
Answer:
(c) glass cutting
Question 24.
Melting point of diamond is
(a) 3700 °C
(b) 3500 °C
(c) 4000 °C
(d) 2500 °C
Answer:
(b) 3500 °C
Question 25.
Melting point of C02 is
(a) 26 °C
(b) 56 °C
(c)-56.6°C
(d)-98°C
Answer:
(c) -56.6 °C
Question 26.
Melting point o* methane is
(a) -182.5 °C
(b) -161.5 °C
(c) 182.5 °C
(d) 161.5 °C
Answer:
(a) -182.5 °C

Question 27.
Biogas contains about methane.
(a) 55% to 60%
(b) 20% to 25%
(c) 90% to 95%
(d) 40% to 45%
Answer:
(a) 55% to 60%
Question 28.
is not a property of carbon dioxide gas.
(a) Supporting combustion
(b) Odourless
(c) Colourless
(d) Turns blue litmus red
Answer:
(a) Supporting combustion
Name the following:
Question 1.
Industries that use methane in the form of natural gas.
Answer:
Fabric mills, paper mills, food processing industry, petrol purification.
Question 2.
Organic compounds prepared from methane.
Answer:
Ethanol, methyl chloride, methylene chloride, acetylene.
Question 3.
Chemicals used in regular fire extinguisher.
Answer:
Sodium bicarbonate and dilute sulphuric acid.

Question 4.
Components of biogas
Answer:
Methane, carbon dioxide
Question 5.
Organic solvents is which fullerenes are soluble.
Answer:
Carbon disulfide, chlorobenzene.
Question 6.
Use of carbon dioxide is dramas and movies
Answer:
The special effect of mist.
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
|
(1) Diamond
(2) Fullerenes (3) Graphite |
(a) Hexagonal layered structure
(b) Tetragonal three-dimensional structure (c) Geodesic dome |
Answer:
(1-b),
(2- c),
(3 – a)
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
|
(1) Peat
(2) Lignite (3) Bituminous (4) Anthracite |
(a) 60-70% of Carbon
(b) 95% of Carbon (c) less than 60% of Carbon (d) 70 – 90% of Carbon |
Answer:
(1 – c),
(2 – a),
(3 – d),
(4 – b)

Question 3.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
|
(1) Propyne
(2) Propene (3) Propane |
(a) CH
3
– CH
2
– CH
3
(b) CH 3 – C = CH (c) CH 3 – CH = CH 2 |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – a)
Question 4.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
|
(1) Fullerene
(2) Diamond (3) Graphite |
(a) Lubricants
(b) Insulator (c) Ornaments |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – a)
Question 5.
| Column ‘A | Column ‘B’ |
|
(1) Water gas
(2) Methane gas (3) Producer gas (4) Carbon dioxide gas |
(a) CH
4
(b) CO + H 2 (c) CO 2 (d) CO + H 2 + CO 2 + N 2 |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – a),
(3 – d),
(4 – c)

State whether the following statements are true or false. Correct the false statement.
(1) Study of organic compounds is called as organic chemistry.
(2) Hydrocarbons with double bonds are called as saturated hydrocarbons.
(3) Ethene is saturated hydrocarbon.
(4) Covalent compounds are good conductor of electricity.
(5) Methane is a covalent compound.
(6) Covalent compounds are soluble in organic solvents.
(7) Graphite is used in making lubricants and lead pencils.
(8) The density of diamond is 9.8 g/cm
3
.
(9) Diamond knives are used in eye surgery.
(10) Fullerenes are used as insulators.
(11) Coke is used in production of water gas i.e. (CO
2
+ H
2
O).
(12) Structural formula of propyne is CH
3
– C = CH.
(13) COz is used to make aerated drinks.
(14) Methane gas is black in colour.
(15) Production of biogas is aerobic process.
Answer:
(1) True
(2) False. Hydrocarbons with double bonds are called as Unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(3) False. Ethene is Unsaturated hydrocarbon.
(4) False. Covalent compounds are bad conductor of electricity.
(5) True
(6) True
(7) True
(8) False: The density of diamond is 3.5 g/cm
3
.
(9) True
(10) True
(11) False. Coke is used in production of water gas i.e. (CO + H
2
).
(12) False. Structural formula of propyne is CH
3
– C = CH.
(13) True
(14) False. Methane gas is colourless.
(15) False. Production of biogas is anaerobic process.
Find the odd man out:
Question 1.
Propane, Methane, Ethene, Pentane.
Answer:
Ethene. It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with double bond between two carbon atoms while rest are saturated hydrocarbons with single bond between two carbon atoms.

Question 2.
CH
4
, C
2
H
6
, C
3
H
8
, CaCO
3
.
Answer:
CaCO
3
. It is a salt which is an inorganic’ compound, while rest are hydrocarbon compounds, i.e. organic compounds.
Question 3.
C
2
H
2
, C
3
H
8
, C
2
H
6
, CH
4
.
Answer:
C
2
H
2
. It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with triple bonds while rest are saturated hydrocarbons with single bonds between two carbon atoms.
Question 4.
Diamond, Fullerene, Graphite, Methane.
Answer:
Methane. It is a marsh gas while rest are allotropes of carbon.
Question 5.
Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas, Cotton
Answer:
Cotton. Cotton is a natural fibre while rest all are fossil fuels.
Question 6.
Cotton, Silk, Proteins, Wool
Answer:
Proteins. Proteins are carbonaceous nutrients while rest all are natural fibres.
Question 7.
Carbohydrates, Coal, Proteins, Fats
Answer:
Coal. Coal is a fossil fuel while rest all are carbonaceous nutrients.
Question 8.
Peat, Charcoal, Lignite, Bituminous
Answer:
Charcoal. Charcoal is a non-crystalline form of carbon while rest all are types of coal.

Question 9.
Lubricants, Electrodes, Ornaments, Arc Lamps
Answer:
Ornaments. Ornaments are made from diamonds while rest all are made from graphite.
Write the correlated terms:
(1) Propene : Double bond :: Propyne : ……………………. .
(2) Ethane : CH
3
– CH
3
:: Ethene : ……………………. .
(3) Hydrogen : Monovalent :: Carbon : ……………………. .
(4) Methane : Low melting point i.e. -182.5°C Diamond : ……………………. .
(5) Graphite : Hexagonal structure :: Diamond : ……………………. .
(6) Density of Diamond : 3.5 g/cm
3
:: Density of Graphite : ……………………. .
(7) Peat: 60% of carbon :: Anthracite : ……………………. .
(8) Melting point of CO
2
: -56.6°C :: Melting point of CH
4
: ……………………. .
Answer:
(1) Triple Bond
(2) CH
2
= CH
2
(3) Tetravalent
(4) High melting point i.e. 3500°C
(5) Tetragonal structure
(6) 1.9 to 2.3 g/cm
3
(7) 95% of carbon
(8) -182.5 °C
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Answer:
- When substances melt or boil, bonds between the molecules are broken due to heat supplied.
- On covalent compounds, the intermolecular forces of attraction are weak.
- Hence, intermolecular forces in covalent compounds are broken easily due to which they have low melting and boiling points.
Question 2.
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity whereas diamond is a non-conductor of electricity.
Answer:
- In diamond, each carbon atom uses all its four electronic to get bonded to another carbon atom, whereas in graphite each carbon uses there out of four electrons during bonding.
- Hence in diamond no free electrons are left whereas in graphite free electrons are available.
- Due to the presence of electron which are free to flow graphite is a good conductor of electricity, whereas due to the absence of free electrons diamond is a non-conductor of electricity.

Question 3.
Graphite is used as a lubricant.
Answer:
- Lubricants are used to reduce friction and wear and tear of mechanical parts.
- Graphite is smooth and slippery and hence is useful in reducing friction. Hence, graphite is used as a lubricant.
Question 4.
Methane is used as a domestic fuel.
Answer:
- Methane is highly inflammable.
- It burns by reacting with oxygen to give a bluish flame.
- It burns completely and producers 213 Kcal/ mol of heat.
- Being the smallest hydrocarbon, the proportion of CO2 released in the combustion of methane is small.
- Therefore methane is used as a domestic fuel.
Answer in short:
Question 1.
What was the contribution of chemist Wohier in organic chemistry?
Answer:
- The German chemist Wohier synthesized an organic compound urca from an inorganic compound ammonium cyanate,
- Ever since then, many organic compounds have been made from inorganic compounds.
- Carbon was found to he the main element in all these compounds.
- Hence, organic chemistry is also referred to as chem is try of carbon corn pounds.
Question 2.
With neat diagram explain the structure of diamond.
Ans.
- In diamond, every carbon atom is bonded to four neighbouring atoms by covalent bonds.
-
Therefore, diamond has a tetragonal three dimensional structure which makes it very hard.
![Maharashtra-Board-Class-9-Science-Solutions-Chapter-13-Carbon-An-Important-Element-29]()
Question 3.
With neat diagram explain the structure of graphite?
Answer:
- Every carbon atom in graphite is bonded to three other carbon atoms in such a way that a hexagonal layered structure is formed.
- A graphite crystal is made of many sheets or layers of carbon atoms.
- These layers slip over each other on applying pressure.
-
One layer of graphite is called graphene.
![Maharashtra-Board-Class-9-Science-Solutions-Chapter-13-Carbon-An-Important-Element-30]()
Question 4.
Give the properties of graphite.
Answer:
Properties of graphite are:
- Graphite found in nature is black, soft, brittle and slippery.
-
Inside each layer of graphite, free electrons move continuously within the entire layer. That is why graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- Due to the layered structure graphite can be used for writing on paper.
- The density of graphite is 1.9 to 2.3 g/cm3.
- Graphite does not dissolve in most solvents.
Question 5.
Give the uses of graphite.
Answer:
Uses of graphite are:
- Graphite is used for making lubricants.
- Graphite is used for making carbon electrodes.
- Graphite is used in pencils for writing.
- Graphite is used in paints and polish.
- Graphite is used in arc lamps which gives a very bright light.
Question 6.
Give the uses of fullerenes.
Answer:
Uses of Fullerenes are:
- Fullerenes are used as insulators.
- Fullerenes are used as a catalyst in water purification.
- At a certain temperature, fullerene exhibits superconductivity.
Question 7.
What is Coal?
Answer:
- Coal is a fossil fuel. It contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
- It also contains nitrogen, phosphorus and sulphur.
- It occurs in the solid state. It is of four types – peat, lignite, bituminous and anthracite.

Question 8.
What is Coke?
Answer:
The pure coal that remains when coal gas has been taken away from coal, is called coke.
Question 9.
Give the uses of Coal.
Answer:
Uses of Coal are:
- Coal is used as fuel in factories and homes.
- Coal is used to obtain coke, coal gas and coal tar.
- Coal is used in thermal power plants for generation of electricity.
Question 10.
Give the uses of Coke.
Answer:
Uses of Coke are:
- Used as domestic fuel.
- Coke is used as a reducing agent.
- Coke is used in production of water gas (CO + H 2 ) and producer gas (CO + H 2 + CO 2 + N 2 )
Question 11.
Name the types of coal and give the differences in them.
Answer:
The four types of coal are Peat, Lignite, Bituminous and Anthracite.

Question 12.
Give the properties of covalent compounds.
Answer:
Properties of covalent compounds:
- Covalent compounds have low melting points and boiling points.
- Generally they are insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Question 13.
What are saturated hydrocarbons? Give examples.
Answer:
- The hydrocarbons having only single bonds between carbon atoms are called saturated hydrocarbons.
- For example, ethane (C 2 H 6 ) which is (CH 3 – CH 3 ), propane (C 3 H 8 ) which is (CH 3 – CH 2 – CH 3 ).
Question 14.
What are unsaturated hydrocarbons? Give examples.
Answer:
- Some hydrocarbons have a multiple bond between two carbon atoms.
- A multiple bond can be a double bond or a triple bond.
- Hydrocarbons having at least one multiple bond are called unsaturated hydrocarbons.
- For example, ethene (H 2 C = CH 2 ), ethyne (HC = CH), propene (CH 3 – CH = CH 2 ), propyne (CH 3 – C = CH).
Question 15.
Give the following information of carbon dioxide: Molecular formula, Molecular mass, Melting point, Percentage occurrence in air.
Answer:
Molecular formula – CO
2
, Molecular mass – 44, Melting point -56.6 °C Percentage occurrence in air – 0.03%.
Question 16.
Give the physical and chemical properties of carbon dioxide.
Answer:
Physical properties of carbon dioxide are:
- It is an odourless gas.
- It is a colourless gas.
Chemical properties of carbon dioxide are:
- It is non-combustible and does not support combustion.
- It turns lime water milky.
- It is fairly soluble in water and dissolves in water forming carbonic acid.
- It turns blue litmus red indicating it is acidic in nature.
- The colour of universal indicator turns orange/ yellow in C02 indicating its pH value between 4 and 6, i.e. acidic in nature.

Question 17.
Give the uses of Carbon dioxide.
Answer:
Uses of Carbon dioxide are:
- CO 2 is used to make aerated drinks
- Solid carbon dioxide is used in cold storage and also to keep milk and milk products and frozen substances cool during transport. It is also used for getting special effects of a mist in dramas and movies.
- CO 2 obtained by chemical reaction or kept under pressure is used in fire extinguishers.
- Liquified CO 2 is used to remove caffeine from coffee.
- Liquid CO 2 is used as solvent in modern eco-friendly dry cleaning.
- Plants use CO 2 in air for photosynthesis.
Question 18.
Give the occurrence of methane.
Answer:
The occurrence of methane is as follows:
- Methane occurs in natural gas to the extent of 87%.
- Decomposition of organic matter in the absence of air (anaerobic) produces methane.
- Methane is present in biogas.
- Methane is found in coal mines.
- Methane is found at the surface of marshy places which is why it is also called marsh gas.
- On heating a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide gases at 300 °C in the presence of nickel (catalyst), methane gas is formed.
- Fractional distillation of natural gas gives methane in pure form.

Question 19.
Give the physical properties of methane.
Answer:
Physical properties of methane are:
- Melting point of methane is (-182.5 °C).
- Boiling point of methane is (-161.5 °C).
- It is a colourless gas.
- The density of liquid methane is less than that of water.
- Methane is sparingly soluble in water. It is highly soluble in organic solvents like gasoline, ether and alcohol.
- Methane is in gaseous state at room temperature.
Question 20.
Give the uses of methane.
Answer:
Uses of methane are:
- Methane in the form of natural gas is used in industries such as fabric mills, paper mills, food processing industry, petrol purification.
- Being the smallest hydrocarbon, the proportion of CO 2 released in the combustion of methane is small and, therefore, it is used as a domestic fuel.
- Methane is used for production of organic compounds such as ethanol, methyl chloride, methylene chloride and acetylene.
Question 21.
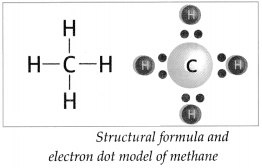
How is methane formed? Give structural formula and electron dot model of methane.
Answer:
- Atomic number of carbon is 6. The electronic configuration of carbon is (2, 4). The valency of carbon is 4.
- Carbon atom can form four covalent bonds with other carbon atoms or atoms of different elements.
-
When a carbon atom shares one electron each with four hydrogen atoms and forms four C-H bonds, a methane (CH
4
) molecule is formed.
![Maharashtra-Board-Class-9-Science-Solutions-Chapter-13-Carbon-An-Important-Element-4]()

Question 22.
What are organic and inorganic compounds?
Answer:
Compounds obtained directly or indirectly from plants and animals are called organic compounds and compounds obtained from minerals are called inorganic compounds.
Question 23.
What is allotropy?
Answer:
- Allotropy – Some elements occur in nature in more than one form.
- The chemical properties of these different forms are the same but their physical properties are different.
- This property of elements is called allotropy.
Question 24.
What are basic organic compounds? What are they also called as?
Answer:
- The compounds formed from only carbon and hydrogen are called basic organic compounds.
- These are also called hydrocarbons.
Write a balanced chemical equation and explain the following chemical reactions.
Question 1.
Preparation of urea from Ammonium cyanate:
Answer:
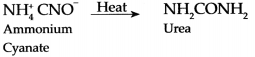
Organic compound Urea can be synthesized from an inorganic compound Ammonium cyanate.
Question 2.
Coal when burnt in air
Answer:
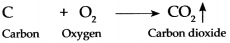
When coal is burnt in air, the carbon present in coal combines with oxygen present in air to form carbon dioxide gas.
Question 3.
Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid:
Answer:
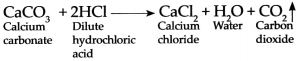
When Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric add it forms Caldum chloride, water and Carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
Question 4.
Carbon dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Sodium hydroxide:
Answer:
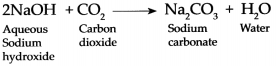
When Carbon dioxide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of Sodium hydroxide it forms Sodium carbonate and Water.
Question 5.
Carbon dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Sodium carbonate:
Answer:
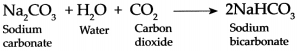
When carbon dioxide is passed through an aqueous solution of Sodium carbonate, it forms Sodium bicarbonate.

Question 6.
Carbon dioxide is passed through freshly prepared lime water for a short duration and then for longer duration:
Answer:
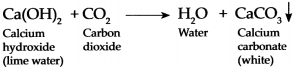
When Carbon dioxide is passed through freshly prepared lime water, it forms water and white precipitate of Calcium carbonate because of which lime water turns milky.
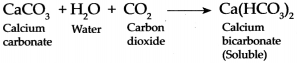
When Carbon dioxide is continuously passed through milky lime water, it forms Calcium bicarbonate which is soluble in water and therefore, water once again turns colourless.
Question 7.
Carbon dioxide gas is dissolved in water.
Answer:
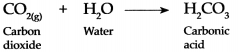
Carboh dioxide gas is fairly soluble in water, it dissolves in water under pressure to form Carbonic acid.
Question 8.
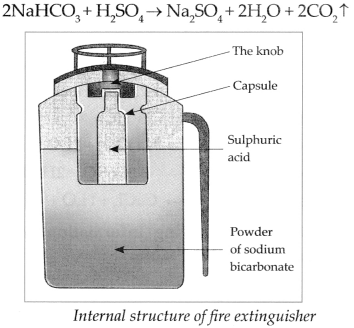
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute Sulphuric acid, (reaction in fire extinguisher):
Answer:
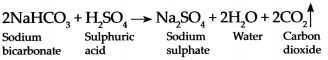
When Sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute Sulphuric acid it forms Sodium sulphate, water and Carbon dioxide gas.
Question 9.
Methane gas is burnt in air:
Answer:
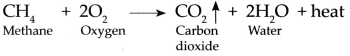
Methane is highly inflammable, it burns in air with a bluish flame and combines with oxygen present in air to form Carbon dioxide and water. In these reaction 213 kcal/mol of heat is given out.

Question 10.
Methane and Chlorine gases react with each other.
Answer:
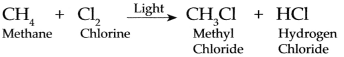
Methane and chlorine gases react with each other at the temperature of 250 °C to 400 °C in presence of ultra voilet light and form mainly Methyl chloride (Chloromethane and ‘ Hydrogen chloride)
This reaction is called Chlorination of methane.
Question 11.
Production of methane gas in biogas plant.
Answer:
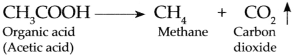
In biogas plant, microbes act on the bio-degradable complex organic compounds and produce organic acids.
The methanogenic bacteria act on the organic acids to produce Methane gas and Carbon dioxide gas.
Question 12.
Production of water gas:
Answer:
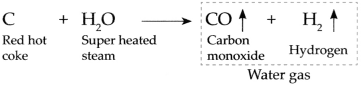
When super heated steam is passed over red hot coke at high temperature, it forms carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas.
This gaseous product of carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas together is called as water gas.
With the help of ne abelled diagram explain the following:
Question 1.
Regular fire extinguisher.
Answer:
- A fire extinguisher contains Sodium bicarbonate powder. There is also dilute sulphuric acid placed in a glass capsule.
- On pressing the knob, the capsule breaks and sulphuric acid comes in contact with the sodium bicarbonate. These two react chemically to release CO 2 which comes out.
-
CO
2
based fire extinguishers do not cause corrosion and are non-conductors of electricity. Therefore, they are used when electrical or electronic equipment catches fire.
![Maharashtra-State-Board-Solutions]()
- CO 2 based fire extinguishers are used to extinguish small scale fire. It is beyond their capacity to extinguish a big fire.
- In modern fire extinguishers liquid and solid CO 2 is filled under pressure. On reducing the pressure, it becomes gaseous and comes out forcefully through the horn-like hose pipe.
-
Chemical reaction:
![Maharashtra-Board-Class-9-Science-Solutions-Chapter-13-Carbon-An-Important-Element-18]()
Question 2.
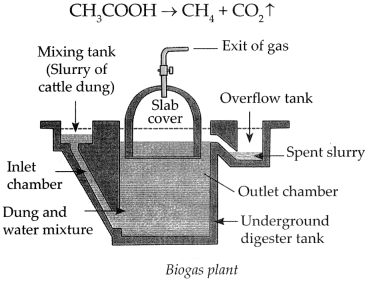
Biogas plant.
Answer:
- Animal dung, dry leaves, wet garbage get decomposed by anaerobic microbes in a biogas plant.
- This produces methane gas, also called biogas.
- Biogas is a very cheap fuel option which meets the demand for cooking gas. It is also used for the production of electricity.
- Biogas contains about 55% to 60% methane and the rest is carbon dioxide.
- Biogas is a fuel which is convenient to use and, in addition to this, a very good manure is also produced as a side product of the process.
-
Biogas production process – Production of biogas is an anaerobic process. It takes place in two stages.
(a) Production of acids – The microbes act on the biodegradable complex organic compound and produce organic acids.
(b) Methane gas production – The methanogenic bacteria act on the organic acids to produce methane gas.
Chemical reaction:
Answer the following
Question 1.
What happens when substances like milk, sugar, wool, dry leaves, hair and seeds are heated strongly in hard glass test tube?
Answer:
When milk, sugar, wool, dry leaves, hair and seeds are heated strongly in hard glass test tube, they get charred and a black substance is left behind. This black substance is carbon.

Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Take some milk in an evaporating dish. Heat the evaporating dish on a bunsen burner. What remains behind at the bottom of an evaporating dish on complete evaporation of the milk?
Answer:
- On complete evaporation of milk, a black residue is left behind.
- This residue is of carbon.
Question 2.
Take small samples of sugar, wool, dry leaves, hair, seeds, split pulses and plastic in separate test tubes. Heat each test tube and observe the changes taking place in the substances. What does the black substance in each test tube indicate?
Answer:
- On heating the above samples, they get charred and a black substance is left behind.
- The black substance is carbon.
Question 3.
Apparatus : Coal, match box, moist litmus paper, etc.
Procedure : Ignite the coal. Hold the moist blue litmus paper over the gas released on igniting the coal. Note the observation.
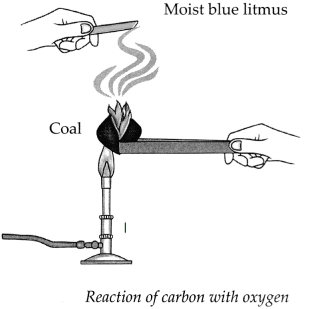
(a) With which gas in the air does the coal react on igniting?
Answer:
Coal reacts with oxygen gas present in the air, on igniting.
(b) What is the substance formed?
Answer:
The substance formed is carbon dioxide.

(c) What change takes place in the litmus paper?
Answer:
The moist blue litmus paper turns red.
(d) Write down the chemical reaction taking place in the above procedure.
Answer:
(i) Carbon combines with oxygen to form Carbon dioxide gas.
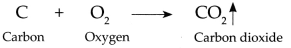
(ii) This C02 combines with water present on moist blue litmus paper to form Carbonic acid which turns blue litmus to red.
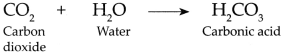
Question 4.
Apparatus : Pencil, electrical wires, battery/ cell, small bulb, water, kerosene, test tube, lead pencils, etc.
Procedure : Remove the lead from a pencil and arrange the apparatus as shown in the above diagram. Note your observations for the following.
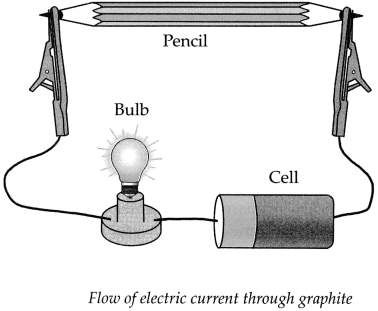
(a) What is the colour of lead in the pencil? .
Answer:
The colour of the lead in the pencil is black as it is made from graphite which is an allotrophic form of carbon.
(b) Try to break lead with your hand.
Answer:
The lead breaks easily as it is made up of graphite which is brittle in nature.
(c) Start the electric current in the circuit and observe. What did you find?
Answer:
When we start the electric current in the circuit, the bulb in the circuit glows, indicating that the lead in the pencil is a good conductor of electricity.

(d) Take some water in a test tube. Take some kerosene in another test tube. Put lead dust in both the test tube. What did you observe?
Answer:
(i) Lead dust does not dissolve in water nor in kerosene.
(ii) It remains insoluble in both the test tubes.
Question 5.
Apparatus : Test tube, straw, lime water, etc.
Procedure: Take freshly prepared lime water in a test tube. Blow air in it for some time through the straw and observe the lime water. Note the observation.
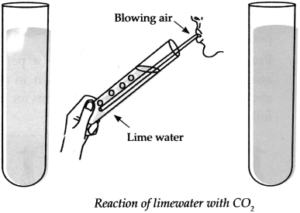
(a) What did you see?
Answer:
When we blow air through the straw in freshly prepared lime water, it turns milky.
(b) What might be the reason behind the change?
Answer:
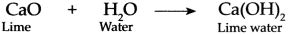
Freshly prepared lime water is obtained by dissolving lime (CaO) in water (H
2
O).
When we blow air through the straw in lime water, carbon dioxide (CO
2
) present in the air reacts with lime water to form white precipitate (insoluble substance) of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO
3
) due to which lime water turns milky.
Question 6.
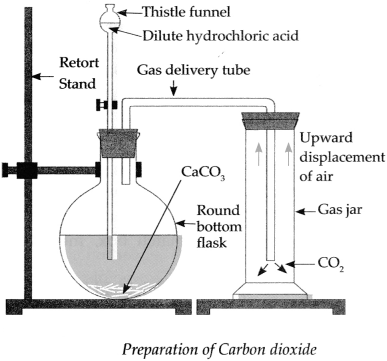
With the help of a neat labelled diagram explain the laboratory preparation of Carbon dioxide gas.
Answer:
The laboratory preparation of Carbon dioxide gas is as follows:

Apparatus : Retort stand, round bottom flask, thistle funnel, gas delivery tube, gas jars.
Chemicals : Calcium carbonate (Pieces of Shahabad tiles/marble pieces/limestone), dilute hydrochloric acid.
Procedure:
- Assemble the apparatus as shown in the figure. While assembling, place CaCO 3 in the round bottom flask.
- Add dilute HCl in the flask through thistle funnel. See to it that the end of the funnel dips in the acid.
-
CO
2
is formed as a result of the reaction between CaCO
3
and HCl. Collect this gas in four to five gas jars. The chemical equation of the above reaction is as follows. CaCO
3
+ 2HCl → CaCl
2
+ H
2
O + CO
2
↑
![Maharashtra-Board-Class-9-Science-Solutions-Chapter-13-Carbon-An-Important-Element-27]()